|
Hairy-fronted Muntjac
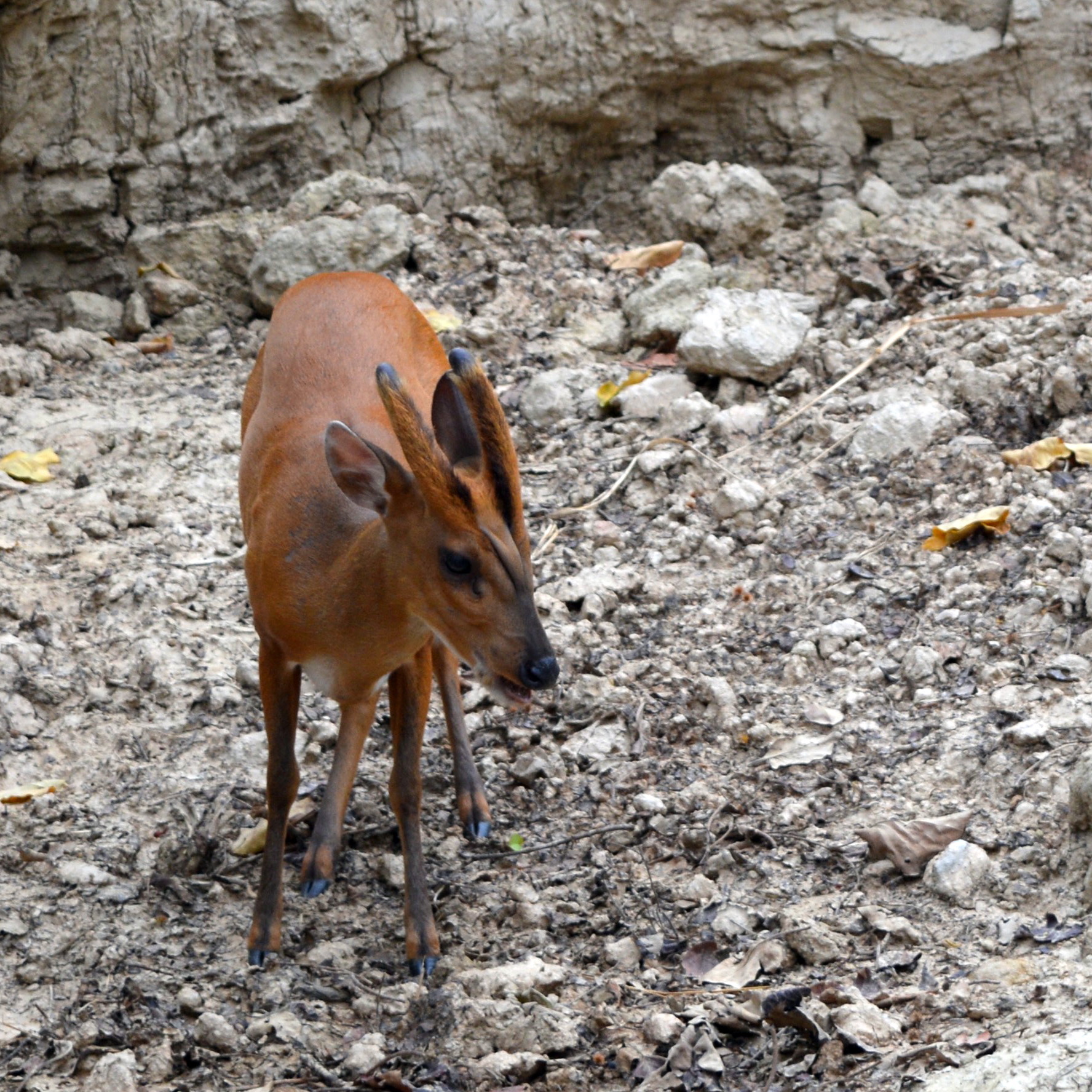
The hairy-fronted muntjac or black muntjac (''Muntiacus crinifrons'') is a type of deer currently found in Zhejiang, Anhui, Jiangxi and Fujian in southeastern China. It is considered to be endangered, possibly down to as few as 5–10,000 individuals spread over a wide area. Reports of hairy-fronted muntjacs from Burma result from considering the hairy-fronted muntjac and Gongshan muntjac as the same species. This suggestion is controversial. It is similar in size to the common muntjac. Hairy-fronted muntjacs are extremely difficult to study because of their shyness. Camera-trap photographs have revealed the presence of hairy-fronted muntjacs where they were believed not to have existed for decades, for example in the Wuyanling National Nature Reserve. This species was for a very long time one of the most poorly known deer in the world. It was also considered highly endangered; up to 1975, it was only known from a few museum specimens, at least to western scientists. The speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Sclater
Philip Lutley Sclater (4 November 1829 – 27 June 1913) was an England, English lawyer and zoologist. In zoology, he was an expert ornithologist, and identified the main zoogeographic regions of the world. He was Secretary of the Zoological Society of London for 42 years, from 1860 to 1902. Early life Sclater was born at Tangier Park, in Wootton St Lawrence, Hampshire, where his father William Lutley Sclater had a country house. George Sclater-Booth, 1st Baron Basing was Philip's elder brother. Philip grew up at Hoddington House where he took an early interest in birds. He was educated in school at Twyford and at thirteen went to Winchester College and later Corpus Christi College, Oxford where he studied scientific ornithology under Hugh Edwin Strickland. In 1851, Sclater began to study law and was admitted a Fellow of Corpus Christi College. In 1856 he travelled to America and visited Lake Superior and the upper St. Croix River (Wisconsin–Minnesota), St. Croix River, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Y Chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the Y chromosome causes offspring produced in sexual reproduction to be of male sex. In mammals, the Y chromosome contains the SRY gene, which triggers development of male gonads. The Y chromosome is passed only from male parents to male offspring. Overview Discovery The Y chromosome was identified as a sex-determining chromosome by Nettie Stevens at Bryn Mawr College in 1905 during a study of the mealworm ''Tenebrio molitor''. Edmund Beecher Wilson independently discovered the same mechanisms the same year, working with Hemiptera. Stevens proposed that chromosomes always existed in pairs and that the smaller chromosome (now labelled "Y") was the pair of the X chromosome discovered in 1890 by Hermann Henking. She realized that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Fauna Of China
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or becomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Of China
This is a list of the mammal species recorded in China. There are 495 mammal species in China, of which thirteen are critically endangered, twenty-four are endangered, forty-seven are vulnerable, and seven are near threatened. One of the species listed for China can no longer be found in the wild. The following tags are used to highlight each species' conservation status as assessed by the International Union for Conservation of Nature: Some species were assessed using an earlier set of criteria. Species assessed using this system have the following instead of near threatened and least concern categories: Order: Sirenia (manatees and dugongs) Sirenia is an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit rivers, estuaries, coastal marine waters, swamps, and marine wetlands. All four species are endangered. *Family: Dugongidae **Genus: ''Dugong'' ***Dugong, ''D. dugon'' Order: Proboscidea (elephants) The elephants comprise three living species and are the larges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntjacs
Muntjacs ( ), also known as the barking deer or rib-faced deer, (URL is Google Books) are small deer of the genus ''Muntiacus'' native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Muntjacs are thought to have begun appearing 15–35 million years ago, with remains found in Miocene deposits in France, Germany and Poland. Most are listed as least-concern species or Data Deficient by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), although others such as the black muntjac, Bornean yellow muntjac, and giant muntjac are vulnerable, near threatened, and critically endangered, respectively. Name The present name is a borrowing of the Latinized form of the Dutch , which was borrowed from the Sundanese ''mencek'' (). The Latin form first appeared as in Zimmerman in 1780. An erroneous alternative name of ''Mastreani deer'' has its origins in a mischievous Wikipedia entry from 2011 and is incorrect. Distribution The present-day species are native to Asia and can be found in Pak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Endangered And Protected Species Of China
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole". Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muller's Ratchet
In evolutionary genetics, Muller's ratchet (named after Hermann Joseph Muller, by analogy with a ratchet effect) is a process which, in the absence of recombination (especially in an asexual population), results in an accumulation of irreversible deleterious mutations. (original paper as cited by, e.g.: ; ) This happens because in the absence of recombination, and assuming reverse mutations are rare, offspring bear at least as much mutational load as their parents. Muller proposed this mechanism as one reason why sexual reproduction may be favored over asexual reproduction, as sexual organisms benefit from recombination and consequent elimination of deleterious mutations. The negative effect of accumulating irreversible deleterious mutations may not be prevalent in organisms which, while they reproduce asexually, also undergo other forms of recombination. This effect has also been observed in those regions of the genomes of sexual organisms that do not undergo recombination. Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
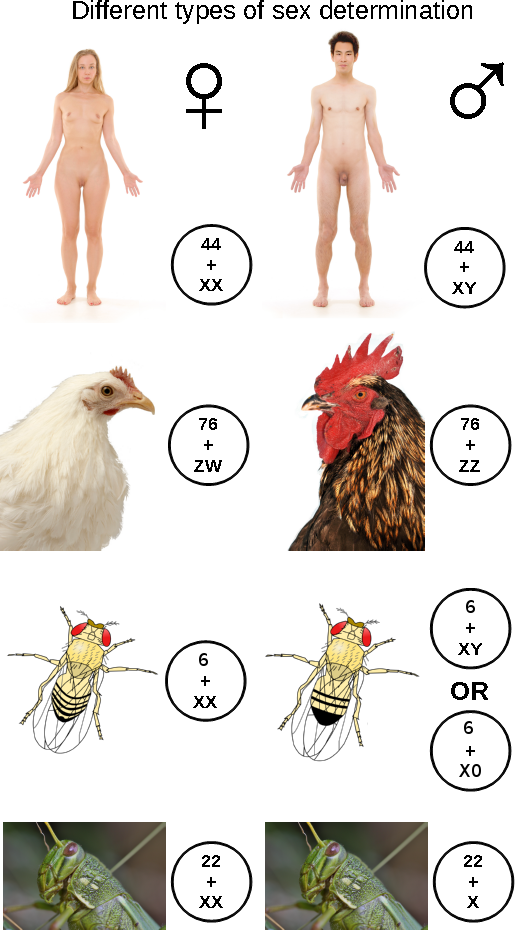
Sex-determination System
A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism. Most organisms that create their offspring using sexual reproduction have two common sexes, males and females, and in other species, there are hermaphrodites, organisms that can function reproductively as either female or male, or both. There are also some species in which only one sex is present, temporarily or permanently. This can be due to parthenogenesis, the act of a female reproducing without fertilization. In some plants or algae the gametophyte stage may reproduce itself, thus producing more individuals of the same sex as the parent. In some species, sex determination is genetic: males and females have different alleles or even different genes that specify their sexual morphology. In animals this is often accompanied by chromosomal differences, generally through combinations of XY, ZW, XO, ZO chromosomes, or haplodiploidy. The sexual di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X Chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its unique properties by early researchers, which resulted in the naming of its counterpart Y chromosome, for the next letter in the alphabet, following its subsequent discovery. Discovery It was first noted that the X chromosome was special in 1890 by Hermann Henking in Leipzig. Henking was studying the testicles of '' Pyrrhocoris'' and noticed that one chromosome did not take part in meiosis. Chromosomes are so named because of their ability to take up staining (''chroma'' in Greek means ''color''). Although the X chromosome could be stained just as well as the others, Henking was unsure whether it was a different class of the object and consequently named it ''X element'', which later became X chromosome after it was established that it w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhejiang
) , translit_lang1_type2 = , translit_lang1_info2 = ( Hangzhounese) ( Ningbonese) (Wenzhounese) , image_skyline = 玉甑峰全貌 - panoramio.jpg , image_caption = View of the Yandang Mountains , image_map = Zhejiang in China (+all claims hatched).svg , mapsize = 275px , map_caption = Location of Zhejiang in China , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = China , named_for = Old name of Qiantang River , seat_type = Capital and largest city , seat = Hangzhou , established_title = Annexation by the Qin dynasty , established_date = 222 BC , established_title2 = Jiangnandong Circuit , established_date2 = 626 , established_title3 = Liangzhe Circuit , established_date3 = 997 , established_title4 = Zhejiang Province formed , established_date4 = 1368 , established_title5 = Republican Period , established_date5 = 1 January 1912 , established_title6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuyanling National Nature Reserve
Wuyanling National Nature Reserve () is a nature reserve in Taishun County, in the southern part of Zhejiang Province. The reserve occupies a mountainous, forested area. The highest peak is Baiyun Peak, which is high.Wuyanling National Nature Reserve Official page (in Chinese) Wildlife considers Wuyanling Reserve as an (IBA). Birds of particular conservation value in the reserve include |
Common Muntjac
The southern red muntjac (''Muntiacus muntjak'') is a deer species native to Southeast Asia. It was formerly known as the Indian muntjac or the common muntjac before the species was taxonomically revised to represent only populations of Thailand, Sunda and perhaps Malaysia. The other populations being attributed to this species are now attributed to ''Muntiacus vaginalis'' ( Northern red muntjac). Muntjacs are also referred to as barking deer. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List. This muntjac has soft, short, brownish or grayish hair, sometimes with creamy markings. It is among the smallest deer species. It is an omnivore and eats grass, fruit, shoots, seeds, bird eggs, and small animals, and occasionally scavenges on carrion. Its calls sound like barking, often when frightened by a predator, hence the common name "barking deer". Males have canines, short antlers that usually branch just once near the base, and a large postorbital scent gland used to mark ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |