|
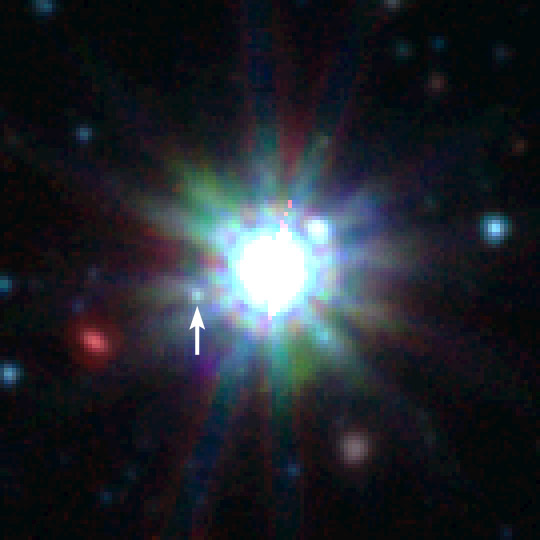
HD 203030
HD 203030, also known as V457 Vulpeculae, is a single, yellow-orange hued star with a sub-stellar companion in the northern constellation of Vulpecula. The designation HD 203030 is from the ''Henry Draper Catalogue'', which is based on spectral classifications made between 1911 and 1915 by Annie Jump Cannon and her co-workers, and was published between 1918 and 1924. This star is invisible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 8.45. It is located at a distance of 128 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −17 km/s. The stellar classification of HD 203030 is K0V, indicating this is a K-type main-sequence star. It is likely very young, belonging to the 45 million years old IC 2391 open cluster. Based on photometric measurements by Hipparcos, it was found to exhibit low amplitude periodic variability with a range of 0.0139 in magnitude and a period of 4.14 days. However the General Cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzer IRAC HD 203030B
Spitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Andre Spitzer (1945–1972), Israeli fencing coach and victim of the Munich massacre * Bernard Spitzer (1924–2014), American real estate developer and philanthropist, father of Eliot Spitzer * Doreen Canaday Spitzer (1914–2010), American archaeologist * Eliot Spitzer (born 1959), 54th Governor of New York (2007–2008) * Frank Spitzer (1926–1992), Austrian-born American mathematician, author of Spitzer's formula * Frédéric Spitzer, 19th century art dealer, after whom the Spitzer Cross is named * Leo Spitzer (1887–1960), Austrian linguist * Lyman Spitzer (1914–1997), American theoretical physicist and mountaineer * Moritz Spitzer, scholar who gave his name to the Spitzer Manuscript * Robert Spitzer (priest) (born 1952), American Jesuit priest and president of Gonzaga University (1998–2009) * Robert R. Spitzer (1922–2019), American agricultural researcher and president of the Milwaukee School of Engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IC 2391
IC 2391 (also known as the Omicron Velorum Cluster or Caldwell 85) is an open cluster in the constellation Vela consisting of hot, young, blueish stars, some of which are binaries and one of which is a quadruple. Persian astronomer A. a.-R. al-Sufi first described it as "a nebulous star" in . It was re-found by Abbe Lacaille and cataloged as Lac II 5. Description IC 2391 is centred about 490 light-years away from Earth and can be seen with the naked eye. It contains about 30 stars with a total visual magnitude of 2.5, spread out across 50 arcminutes. Member stars These are some of the prominent members of IC 2391: The stars' era of formation is similar to open cluster IC 2602 in neighbouring Carina, and has a lithium depletion boundary age of about 50 million years. The latter group averages about the same distance, placed at about 485 light years away. Argus Association The components formed at about the same time as a nearer group, known as the "Argus Association" which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-type Main-sequence Stars
K-type may refer to: *AEC K-type, a bus chassis *K-type star, a stellar spectral classification *K-type filter Constant k filters, also k-type filters, are a type of electronic filter designed using the image method. They are the original and simplest filters produced by this methodology and consist of a ladder network of identical sections of passive co ..., a type of electronic filter * K-type asteroid, an unusual kind of asteroid {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Mass
In astronomy, planetary mass is a measure of the mass of a planet-like astronomical object. Within the Solar System, planets are usually measured in the astronomical system of units, where the unit of mass is the solar mass (), the mass of the Sun. In the study of extrasolar planets, the unit of measure is typically the mass of Jupiter () for large gas giant planets, and the mass of Earth () for smaller rocky terrestrial planets. The mass of a planet within the Solar System is an adjusted parameter in the preparation of ephemerides. There are three variations of how planetary mass can be calculated: * If the planet has natural satellites, its mass can be calculated using Newton's law of universal gravitation to derive a generalization of Kepler's third law that includes the mass of the planet and its moon. This permitted an early measurement of Jupiter's mass, as measured in units of the solar mass. * The mass of a planet can be inferred from its effect on the orbits of other pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brown Dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big enough to sustain nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores, but massive enough to emit some light and heat from the deuterium fusion, fusion of deuterium (deuterium, 2H). The most massive ones (> ) can lithium burning, fuse lithium (lithium-7, 7Li). Astronomers classify self-luminous objects by Stellar classification#Spectral types, spectral type, a distinction intimately tied to the surface temperature, and brown dwarfs occupy types M (2100–3500 Kelvin, K), L (1300–2100 Kelvin, K), T (600–1300 Kelvin, K), and Y ( 80 ''M''J), which have spectral classes L2 to L6. Spectral class T As GD 165B is the prototype of the L dwarfs, Gliese 229B is the prototype of a second ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projected Separation
This glossary of astronomy is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to astronomy and cosmology, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. Astronomy is concerned with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth. The field of astronomy features an extensive vocabulary and a significant amount of jargon. A B C D E F G H I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, such as the greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total ( bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated. It extends into a star's surface until the plasma becomes opaque, equivalent to an optical depth of approximately , or equivalently, a depth from which 50% of light will escape without being scattered. A photosphere is the region of a luminous object, usually a star, that is transparent to photons of certain wavelengths. Stars, except neutron stars, have no solid or liquid surface. Therefore, the photosphere is typically used to describe the Sun's or another star's visual surface. Etymology The term ''photosphere'' is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos'', ''photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it being a spherical surface that is perceived to emit light. Temperature The surface of a star is defined to have a temperature given by the effective temperature in the Stefan–Boltzmann law. Various stars have photospheres of vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BY Draconis Variable
BY Draconis variables are variable stars of late spectral types, usually K or M, and typically belong to the main sequence. The name comes from the archetype for this category of variable star system, BY Draconis. They exhibit variations in their luminosity due to rotation of the star coupled with starspots, and other chromospheric activity. Resultant brightness fluctuations are generally less than 0.5 magnitudes. Light curves of BY Draconis variables are quasiperiodic. The period is close to the star's mean rotational rate. The light curve is irregular over the duration of the period and it changes slightly in shape from one period to the next. For the star BY Draconis the shape of the light curve over a period remained similar for a month. Nearby K and M stars that are BY Draconis variables include Barnard's Star, Kapteyn's Star, 61 Cygni, Ross 248, Lacaille 8760, Lalande 21185, Epsilon Eridani and Luyten 726-8. Ross 248 is the first discovered BY Draconis variable, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Activity
A stellar magnetic field is a magnetic field generated by the motion of conductive Plasma (physics), plasma inside a star. This motion is created through convection, which is a form of energy transport involving the physical movement of material. A localized magnetic field exerts a force on the plasma, effectively increasing the pressure without a comparable gain in density. As a result, the magnetized region rises relative to the remainder of the plasma, until it reaches the star's photosphere. This creates starspots on the surface, and the related phenomenon of coronal loops. Measurement A star's magnetic field can be measured using the Zeeman effect. Normally the atoms in a star's atmosphere will absorb certain frequencies of energy in the electromagnetic spectrum, producing characteristic dark absorption lines in the spectrum. However, when the atoms are within a magnetic field, these lines become split into multiple, closely spaced lines. The energy also becomes Polarizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Catalog Of Variable Stars
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently granted posthumously to George Washington and Ulysses S. Grant * (" general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * ''Intrinsic variables'', whose luminosity actually changes periodically; for example, because the star swells and shrinks. * ''Extrinsic variables'', whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars exhibit at least some oscillation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |