|
H4K20me
H4K20me is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H4. It is a mark that indicates the methylation at the 20th lysine residue of the histone H4 protein. This mark can be mono-, di-, or tri-methylated. It is critical for genome integrity including DNA damage repair, DNA replication and chromatin compaction. H4K20me2 is the most common methylation state on histone H4 and was one of the earliest modified histone residues to be identified back in pea and calf extracts in 1969. It is one of only two identified methylated lysine residues on the H4 histone, the other being monomethylated H4K12. Each degree of methylation at H4K20 has a very different cellular process. The loss of H4K20me3 along with a reduction of H4K16ac is a strong indicator of cancer. Nomenclature H4K20me indicates monomethylation of lysine 20 on histone H4 protein subunit: Lysine methylation : This diagram shows the progressive methylation of a lysine residue. The mono-methylation (se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Methylation
Histone methylation is a process by which methyl groups are transferred to amino acids of histone proteins that make up nucleosomes, which the DNA double helix wraps around to form chromosomes. Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids in the histones are methylated, and how many methyl groups are attached. Methylation events that weaken chemical attractions between histone tails and DNA increase transcription because they enable the DNA to uncoil from nucleosomes so that transcription factor proteins and RNA polymerase can access the DNA. This process is critical for the regulation of gene expression that allows different cells to express different genes. Function Histone methylation, as a mechanism for modifying chromatin structure is associated with stimulation of neural pathways known to be important for formation of long-term memories and learning. Histone methylation is crucial for almost all phases of anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H4K16ac
H4K16ac is an epigenetic modification to the DNA packaging protein Histone H4. It is a mark that indicates the acetylation at the 16th lysine residue of the histone H4 protein. H4K16ac is unusual in that it has both transcriptional activation AND repression activities. The loss of H4K20me3 along with a reduction of H4K16ac is a strong indicator of cancer. Lysine acetylation and deacetylation Proteins are typically acetylated on lysine residues and this reaction relies on acetyl-coenzyme A as the acetyl group donor. In histone acetylation and deacetylation, histone proteins are acetylated and deacetylated on lysine residues in the N-terminal tail as part of gene regulation. Typically, these reactions are catalyzed by enzymes with ''histone acetyltransferase'' (HAT) or ''histone deacetylase'' (HDAC) activity, although HATs and HDACs can modify the acetylation status of non-histone proteins as well. The regulation of transcription factors, effector proteins, molecular ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
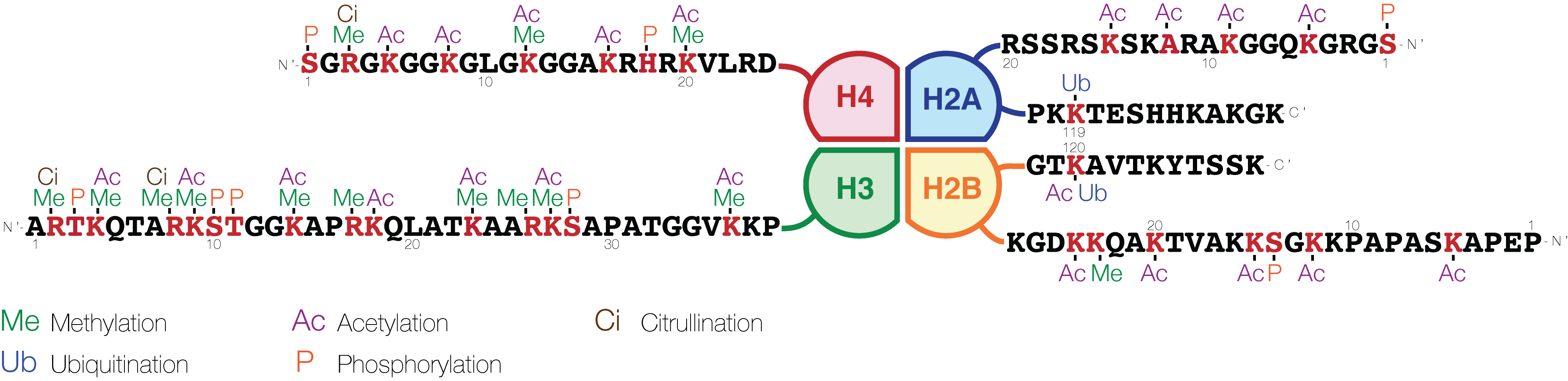
Histones
In biology, histones are highly Base (chemistry), basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei and in most Archaea, Archaeal Phylum, phyla. They act as spools around which DNA winds to create structural units called nucleosomes. Nucleosomes in turn are wrapped into 30-nanometer fibers that form tightly packed chromatin. Histones prevent DNA from becoming tangled and protect it from DNA damage. In addition, histones play important roles in gene regulation and DNA replication. Without histones, unwound DNA in chromosomes would be very long. For example, each human cell has about 1.8 meters of DNA if completely stretched out; however, when wound about histones, this length is reduced to about 9 micrometers (0.09 mm) of 30 nm diameter chromatin fibers. There are five families of histones, which are designated H1/H5 (linker histones), H2, H3, and H4 (core histones). The nucleosome core is formed of two H2A-H2B protein dimer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Code
The histone code is a hypothesis that the transcription of genetic information encoded in DNA is in part regulated by chemical modifications (known as ''histone marks'') to histone proteins, primarily on their unstructured ends. Together with similar modifications such as DNA methylation it is part of the epigenetic code. Histones associate with DNA to form nucleosomes, which themselves bundle to form chromatin fibers, which in turn make up the more familiar chromosome. Histones are globular proteins with a flexible N-terminus (taken to be the tail) that protrudes from the nucleosome. Many of the histone tail modifications correlate very well to chromatin structure and both histone modification state and chromatin structure correlate well to gene expression levels. The critical concept of the histone code hypothesis is that the histone modifications serve to recruit other proteins by specific recognition of the modified histone via protein domains specialized for such purposes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
Progeria is a specific type of progeroid syndrome, also known as Hutchinson–Gilford syndrome or Hutchinson–Gilford progeroid syndrome (HGPS). A single gene mutation is responsible for causing progeria. The affected gene, known as lamin A (''LMNA''), makes a protein necessary for holding the cell nucleus together. When this gene mutates, an abnormal form of lamin A protein called progerin is produced. Progeroid syndromes are a group of diseases that cause individuals to age faster than usual, leading to them appearing older than they actually are. People born with progeria typically live until their mid- to late-teens or early twenties. Severe cardiovascular complications usually develop by puberty, later on resulting in death. Signs and symptoms Most children with progeria appear normal at birth and during early infancy. Children with progeria usually develop the first symptoms during their first few months of life. The earliest symptoms may include a failure to thrive and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone H4
Histone H4 is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminus, N-terminal tail, H4 is involved with the structure of the nucleosome of the 'beads on a string' organization. Histone proteins are highly post-translationally modified. Covalently bonded modifications include acetylation and methylation of the N-terminal tails. These modifications may alter Gene expression, expression of genes located on DNA associated with its parent histone octamer. Histone H4 is an important protein in the structure and function of chromatin, where its sequence variants and variable modification states are thought to play a role in the dynamic and long term regulation of genes. Genetics Histone H4 is encoded in multiple genes at different loci including: HIST1H4A, HIST1H4B, HIST1H4C, HIST1H4D, HIST1H4E, HIST1H4F, HIST1H4G, HIST1H4H, HIST1H4I, HIST1H4J, HIST1H4K, HIST1H4L, HIST2H4A, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
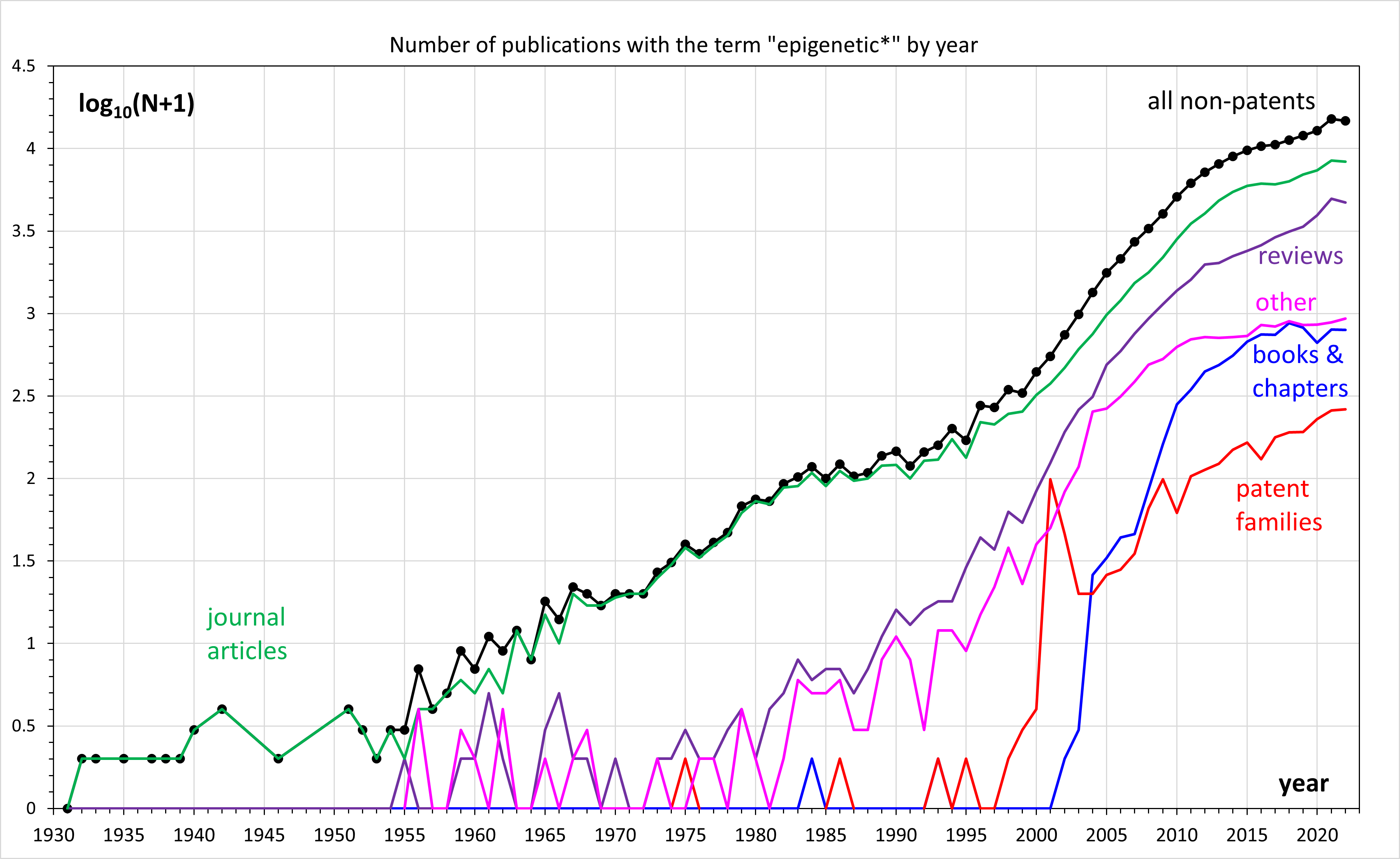
Epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of changes in gene expression that happen without changes to the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix ''epi-'' (ἐπι- "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are "on top of" or "in addition to" the traditional (DNA sequence based) genetic mechanism of inheritance. Epigenetics usually involves a change that is not erased by cell division, and affects the regulation of gene expression. Such effects on cellular and physiological traits may result from environmental factors, or be part of normal development. The term also refers to the mechanism of changes: functionally relevant alterations to the genome that do not involve mutation of the nucleotide sequence. Examples of mechanisms that produce such changes are DNA methylation and histone modification, each of which alters how genes are expressed without altering the underlying DNA sequence. Further, non-coding RNA sequences have been shown to play a key role in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyllysine
Methyllysine is derivative of the amino acid residue lysine where the sidechain ammonium group has been methylated one or more times. Such methylated lysines play an important role in epigenetics; the methylation of specific lysines of certain histones in a nucleosome alters the binding of the surrounding DNA to those histones, which in turn affects the expression of genes on that DNA. The binding is affected because the effective radius of the positive charge is increased (methyl groups are larger than the hydrogen atoms they replace), reducing the strongest potential electrostatic attraction with the negatively charged DNA. It is thought that the methylation of lysine (and arginine) on histone tails does not directly affect their binding to DNA. Rather, such methyl marks recruit other proteins that modulate chromatin structure. In Protein Data Bank The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules such as pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Methyltransferase
Histone methyltransferases (HMT) are histone-modifying enzymes (e.g., histone-lysine N-methyltransferases and histone-arginine N-methyltransferases), that catalyze the transfer of one, two, or three methyl groups to lysine and arginine residues of histone proteins. The attachment of methyl groups occurs predominantly at specific lysine or arginine residues on histones H3 and H4. Two major types of histone methyltranferases exist, lysine-specific (which can be SET (Su(var)3-9, Enhancer of Zeste, Trithorax) domain containing or non-SET domain containing) and arginine-specific. In both types of histone methyltransferases, S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) serves as a cofactor and methyl donor group. The genomic DNA of eukaryotes associates with histones to form chromatin. The level of chromatin compaction depends heavily on histone methylation and other post-translational modifications of histones. Histone methylation is a principal epigenetic modification of chromatin that determines g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tn5 Transposon
A transposase is any of a class of enzymes capable of binding to the end of a transposon and catalysing its movement to another part of a genome, typically by a cut-and-paste mechanism or a replicative mechanism, in a process known as transposition. The word "transposase" was first coined by the individuals who cloned the enzyme required for transposition of the Tn3 transposon. The existence of transposons was postulated in the late 1940s by Barbara McClintock, who was studying the inheritance of maize, but the actual molecular basis for transposition was described by later groups. McClintock discovered that some segments of chromosomes changed their position, jumping between different loci or from one chromosome to another. The repositioning of these transposons (which coded for color) allowed other genes for pigment to be expressed. Transposition in maize causes changes in color; however, in other organisms, such as bacteria, it can cause antibiotic resistance. Transposition is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ChIP-sequencing
ChIP-sequencing, also known as ChIP-seq, is a method used to analyze protein interactions with DNA. ChIP-seq combines chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) with massively parallel DNA sequencing to identify the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins. It can be used to map global binding sites precisely for any protein of interest. Previously, ChIP-on-chip was the most common technique utilized to study these protein–DNA relations. Uses ChIP-seq is primarily used to determine how transcription factors and other chromatin-associated proteins influence phenotype-affecting mechanisms. Determining how proteins interact with DNA to regulate gene expression is essential for fully understanding many biological processes and disease states. This epigenetic information is complementary to genotype and expression analysis. ChIP-seq technology is currently seen primarily as an alternative to ChIP-chip which requires a hybridization array. This introduces some bias, as an array is restr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ENCODE
The Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) is a public research project which aims "to build a comprehensive parts list of functional elements in the human genome." ENCODE also supports further biomedical research by "generating community resources of genomics data, software, tools and methods for genomics data analysis, and products resulting from data analyses and interpretations." The current phase of ENCODE (2016-2019) is adding depth to its resources by growing the number of cell types, data types, assays and now includes support for examination of the mouse genome. History ENCODE was launched by the US National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) in September 2003. Intended as a follow-up to the Human Genome Project, the ENCODE project aims to identify all functional elements in the human genome. The project involves a worldwide consortium of research groups, and data generated from this project can be accessed through public databases. The initial release of ENCODE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |