|
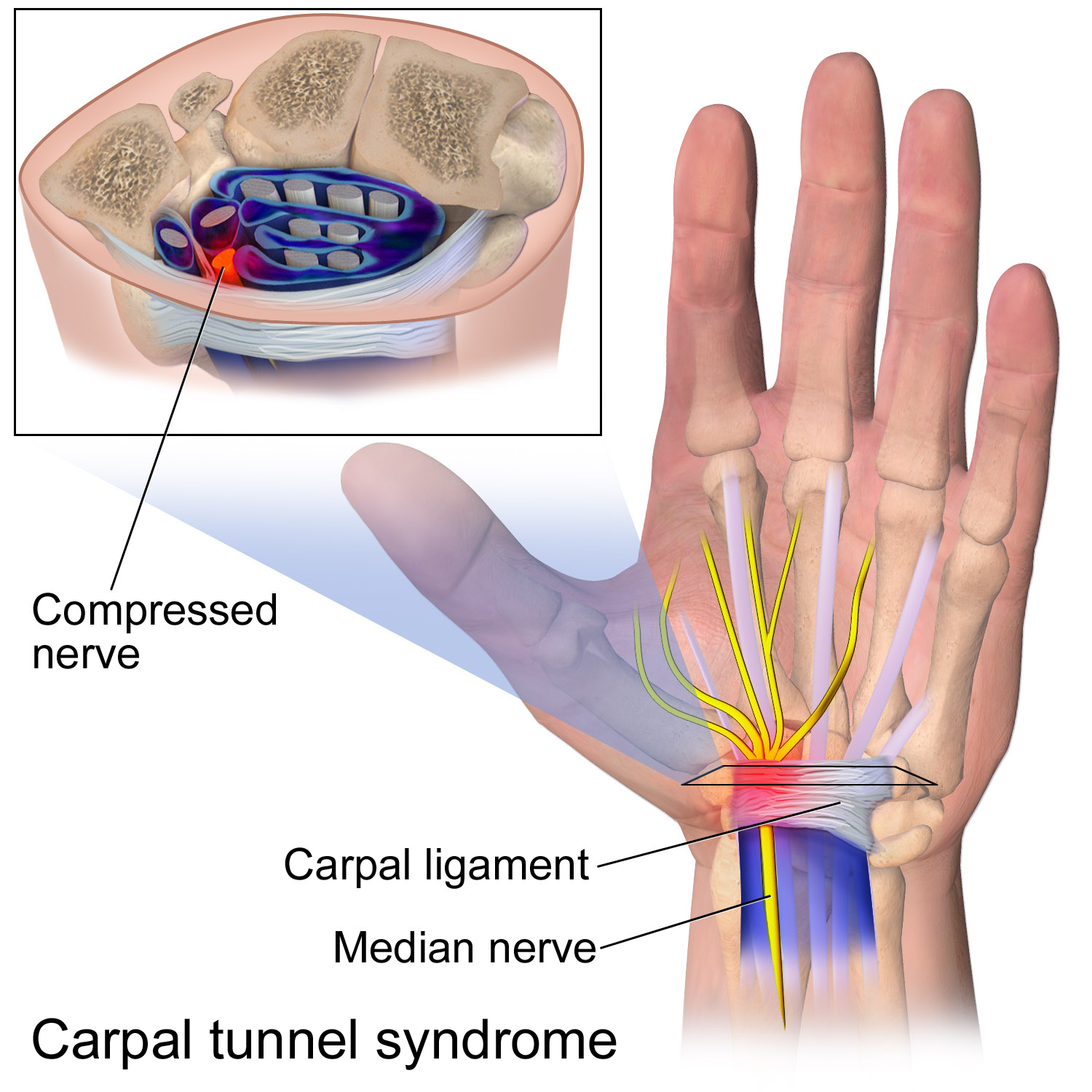
Guyons Canal
The ulnar canal or ulnar tunnel (also known as Guyon's canal or tunnel) is a semi-rigid longitudinal canal in the wrist that allows passage of the ulnar artery and ulnar nerve into the hand. (These are named after the ulna, the long bone on the little finger side of the arm.) The roof of the canal is made up of the superficial palmar carpal ligament, while the deeper flexor retinaculum and hypothenar muscles comprise the floor. The space is medially bounded by the pisiform and pisohamate ligament more proximally, and laterally bounded by the hook of the hamate more distally. It is approximately 4 cm long, beginning proximally at the transverse carpal ligament and ending at the aponeurotic arch of the hypothenar muscles. Eponym The ulnar tunnel is named after the French surgeon Jean Casimir Félix Guyon, who originally described the canal in 1861. Clinical significance Entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the ulnar canal can result in symptoms of ulnar neuropathy, including num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Artery
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the Human Anatomical Terms#Anatomical directions, medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist. Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins. The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the Elbow-joint, elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between the elbow and the wrist. It then runs along the ulnar border to the wrist, crosses the transverse carpal ligament on the radial side of the pisiform bone, and immediately beyond this bone divides into two branches, which enter into the formation of the Superficial palmar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve
The ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna, one of the two long bones in the forearm. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds. This nerve can cause an electric shock-like sensation by striking the medial epicondyle of the humerus posteriorly, or inferiorly with the elbow flexed. The ulnar nerve is trapped between the bone and the overlying skin at this point. This is commonly referred to as bumping one's "funny bone". This name is thought to be a pun, based on the sound resemblance between the name of the bone of the upper arm, the humerus, and the word " humorous". Alternatively, according to the Oxfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the Radius (bone), radius, the forearm's other long bone. Longer and thinner than the radius, the ulna is considered to be the smaller long bone of the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the Human leg#Structure, lower leg is the fibula. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in standard anatomical position, is found on the Medial (anatomy), medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony Process (anatomy), process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is also a radial notch for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmar Carpal Ligament
The palmar carpal ligament (also volar carpal ligament or ''Guyon's Tunnel'') is a thickened portion of antebrachial fascia on anterior/palmar side of the wrist which - together with the flexor retinaculum of the hand - retains the tendons of most of the flexor muscles of the hand. The palmar carpal ligament corresponds in location and structure to the extensor retinaculum of the hand also known as the dorsal carpal ligament, on the opposite side of the wrist with which the PCL is continuous as both are formations of the antebrachial fascia. The flexor retinaculum is also known as the transverse carpal ligament. Anatomy Relations The palmar carpal ligament is superficial and proximal to the flexor retinaculum. The ulnar nerve and the ulnar artery run through the ulnar canal, which is deep to the palmar carpal ligament and superficial to the flexor retinaculum of the hand, flexor retinaculum. References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Retinaculum Of The Hand
The flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament or anterior annular ligament) is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel. Structure The flexor retinaculum is a strong, fibrous band that covers the carpal bones on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It attaches to the bones near the radius and ulna. On the ulnar side, the flexor retinaculum attaches to the pisiform bone and the hook of the hamate bone. On the radial side, it attaches to the tubercle of the scaphoid bone, and to the medial part of the palmar surface and the ridge of the trapezium bone. The flexor retinaculum is continuous with the palmar carpal ligament, and deeper with the palmar aponeurosis. The ulnar artery and ulnar nerve, and the cutaneous branches of the median and ulnar nerves, pass on top of the flexor retinaculum. On the radial side of the retinaculum is the tendon of the flexor car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothenar Muscles
The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger. The three muscles are: * Abductor digiti minimi * Flexor digiti minimi brevis * Opponens digiti minimi Structure The muscles of hypothenar eminence are from medial to lateral: * Opponens digiti minimi * Flexor digiti minimi brevis * Abductor digiti minimi The intrinsic muscles of hand can be remembered using the mnemonic, "A OF A OF A" for, Abductor pollicis brevis, Opponens pollicis, Flexor pollicis brevis (the three thenar muscles), Adductor pollicis, and the three hypothenar muscles, Opponens digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi brevis, Abductor digiti minimi. Clinical significance "Hypothenar atrophy" is associated with the lesion of the ulnar nerve, which supplies the three hypothenar muscles. Hypothenar hammer syndrome is a vascular occlusion of this region. See also * Thenar eminence * Palmaris brevis Palmaris brevis muscle is a thin, quadrilateral muscle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisiform
The pisiform bone ( or ), also spelled pisiforme (from the Latin ''pisiformis'', pea-shaped), is a small knobbly, sesamoid bone that is found in the wrist. It forms the ulnar border of the carpal tunnel. Structure The pisiform is a sesamoid bone, with no covering membrane of periosteum. It is the last carpal bone to ossify. The pisiform bone is a small bone found in the proximal row of the wrist ( carpus). It is situated where the ulna joins the wrist, within the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle. It only has one side that acts as a joint, articulating with the triquetral bone. It is on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. The pisiform bone has four surfaces: # The ''dorsal surface'' is smooth and oval, and articulates with the triquetral: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. # The ''palmar surface'' is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, the flexor carpi uln ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisohamate Ligament
The pisohamate ligament is a ligament in the hand. It connects the pisiform, a sesamoid bone in the wrist, to the hook of the hamate. It is a prolongation of the tendon of the flexor carpi ulnaris. It serves as part of the origin for the abductor digiti minimi. It also forms the floor of the ulnar canal, a canal that allows the ulnar nerve and ulnar artery The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the Human Anatomical Terms#Anatomical directions, medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins ... into the hand. References Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook Of The Hamate
The hamate bone (from Latin hamatus, "hooked"), or unciform bone (from Latin ''uncus'', "hook"), Latin os hamatum and occasionally abbreviated as just hamatum, is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-like process ("hamulus") projecting from its palmar surface. Structure The hamate is an irregularly shaped carpal bone found within the hand. The hamate is found within the distal row of carpal bones, and abuts the metacarpals of the little finger and ring finger. Adjacent to the hamate on the ulnar side, and slightly proximal and ulnar to it, is the pisiform bone. Adjacent on the radial side is the capitate, and proximal is the lunate bone. Surfaces The hamate bone has six surfaces: * The ''superior'', the apex of the wedge, is narrow, convex, smooth, and articulates with the lunate. * The ''inferior'' articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, by concave facets which are separated by a ridge. * The ''dorsal'' is triangular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Casimir Félix Guyon
Jean Casimir Félix Guyon (21 July 1831 – 2 August 1920) was a French surgeon and urologist born in Saint-Denis, Ile-Bourbon (Réunion). He studied medicine in Paris, receiving his doctorate in 1858. He was appointed ''médecin des hôpitaux'' in 1864, and was later a professor of surgical pathology (from 1877) and genitourinary surgery (from 1890) at the University of Paris. In 1878 he became a member of the ''Académie de Médecine''. At Hôpital Necker he held clinics that were attended by students worldwide In 1907, he along with urologists from Europe, the United States and South America established the ''Association Internationale d'Urologie''. In 1979 he was commemorated on a postage stamp, issued by France on the occasion of the 18th Congress of the ''Association Internationale d'Urologie'', held in Paris. The Hôpital Félix Guyon, located in Saint-Denis, Réunion, is named in his honour. Although he was primarily known for work with genitourinary anatomy, Guyon is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment
Idiopathic ulnar neuropathy at the elbow is a condition where pressure on the ulnar nerve as it passes through the cubital tunnel causes ulnar neuropathy. The symptoms of neuropathy are paresthesia (tingling) and numbness (loss of sensation) primarily affecting the little finger and ring finger of the hand. Ulnar neuropathy can progress to weakness and atrophy of the muscles in the hand (interossei and small and ring finger lumbricals). Symptoms can be alleviated by the use of a splint to prevent the elbow from flexing while sleeping. Signs and symptoms In general, ulnar neuropathy will result in symptoms in a specific anatomic distribution, affecting the little finger, the ulnar half of the ring finger, and the intrinsic muscles of the hand. The specific symptoms experienced in the characteristic distribution depend on the specific location of ulnar nerve compression. The hallmark symptoms of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow (cubital tunnel syndrome) is paresthesia (tingling). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Neuropathy
Ulnar neuropathy is a disorder involving the ulnar nerve. Ulnar neuropathy may be caused by entrapment of the ulnar nerve with resultant numbness and tingling. It may also cause weakness or paralysis of the muscles supplied by the nerve. Ulnar neuropathy may affect the elbow as cubital tunnel syndrome. At the wrist a similar neuropathy is ulnar tunnel syndrome. Signs and symptoms In terms of the signs/symptoms of ulnar neuropathy trauma and pressure to the arm and wrist, especially the elbow, the medial side of the wrist, and other sites close to the course of the ulnar nerve are of interest in this condition. Many people complain of sensory changes in the fourth and fifth digits. Rarely, an individual actually notices that the unusual sensations are mainly in the medial side of the ring finger (fourth digit). Sometimes the third digit is also involved, especially on the ulnar (medial) side. The sensory changes can be a feeling of numbness or a tingling, pain rarely occurs in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |