|
Gustav Von Senden-Bibran
Gustav Ernst Otto Egon Freiherr (Baron) von Bibran-Modlau, Senden-Bibran (23 July 1847, Rokitki, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Reisicht, Lower Silesia, Germany – 23 November 1909 in Berlin) was an admiral of the Kaiserliche Marine, German Imperial Navy. Biography His father was a Silesian landowner who had served in the Austro-Hungarian Cavalry. He entered the Prussian Navy at age 15, never married, and dedicated his life to building a strong German Navy.The Entourage of Kaiser Wilhelm II, 1888-1918 by Isabel V. Hull; Cambridge University Press, 2004 , p. 178-80. After service in the Franco-Prussian War, from 1871 to 1874 Senden-Bibran attended the post-graduate Naval War College, the German Imperial Naval Academy 1872-1918, ''Marineakademie'', along with the future admiral and colleague Otto von Diederichs.Gottschall, Terrel D.: "By Order of the Kaiser. Otto von Diederichs and the Rise of the Imperial German Navy, 1865-1902", Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, 2003. Send ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rokitki, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Rokitki () is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Chojnów, within Legnica County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north of Chojnów, north-west of Legnica, and west of the regional capital Wrocław. Transport There is railway station in Rokitki, and the Voivodeship road 328 passes through the village. References Villages in Legnica County {{Legnica-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaiser Wilhelm II
Wilhelm II (Friedrich Wilhelm Viktor Albert; 27 January 18594 June 1941) was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia from 1888 until his abdication in 1918, which marked the end of the German Empire as well as the Hohenzollern dynasty's 300-year rule of Prussia. Born during the reign of his granduncle Frederick William IV of Prussia, Wilhelm was the son of Prince Frederick William and Victoria, Princess Royal. Through his mother, he was the eldest of the 42 grandchildren of Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom. In March 1888, Wilhelm's father, Frederick William, ascended the German and Prussian thrones as Frederick III. Frederick died just 99 days later, and his son succeeded him as Wilhelm II. In March 1890, the young Kaiser dismissed longtime Chancellor Otto von Bismarck and assumed direct control over his nation's policies, embarking on a bellicose "New Course" to cement Germany's status as a leading world power. Over the course of his reign, the German colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of The Crown (Prussia)
The Royal Order of the Crown () was a Prussian order of chivalry. Instituted in 1861 as an honour equal in rank to the Order of the Red Eagle, membership could only be conferred upon commissioned officers (or civilians of approximately equivalent status), but there was a medal associated with the order which could be earned by non-commissioned officers and enlisted men. Officially the Order of the Red Eagle and the Order of the Crown were equal. Most officials did however prefer to be appointed in the older Order of the Red Eagle. The Order of the Crown was often used as an award for someone who had to be rewarded while the Prussian government did not want to use the Order of the Red Eagle. Classes The Order had six classes: *Grand Cross – wore the Grand Cross badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *1st Class – wore the badge on a sash on the right shoulder, plus the star on the left chest; *2nd Class – wore the badge on a necklet, plus t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a significant role in the unification of Germany in 1871 and was a major constituent of the German Empire until its German Revolution of 1918–1919, dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the Prussia (region), region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin. The list of monarchs of Prussia, kings of Prussia were from the House of Hohenzollern. The polity of Brandenburg-Prussia, predecessor of the kingdom, became a military power under Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg, known as "The Great Elector". As a kingdom, Prussia continued its rise to power, especially during the reign of Frederick the Great, Frederick II "the Great".Horn, D. B. "The Youth of Frederick the Great 1712–30." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Alexander Von Müller
Georg Alexander von Müller (24 March 1854 – 18 April 1940) was an Admiral of the Imperial German Navy and a close friend of the Wilhelm II, Kaiser in the run up to the World War I, First World War. Career Müller grew up in Sweden, where his father worked as a professor of agriculture. He joined the Imperial Navy in 1871 and served in many different positions, including commander of the gunboat in East Asia from 1891 to 1892, and then officer on the staff of Prince Heinrich of Prussia. He was Adjutant from 1904 to Kaiser Wilhelm II. He was named to the Prussian nobility (''Adelstitel'') in 1900. In 1906, he succeeded Gustav von Senden-Bibran as Chief of the German Imperial Naval Cabinet and served until the end of the German Empire in 1918. As chief of the Naval Cabinet, he dealt with not only with technical issues but also the Court and many politicians. By the start of the First World War, he had become an ally of Chancellor Theobald von Bethmann Hollweg in his attempts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
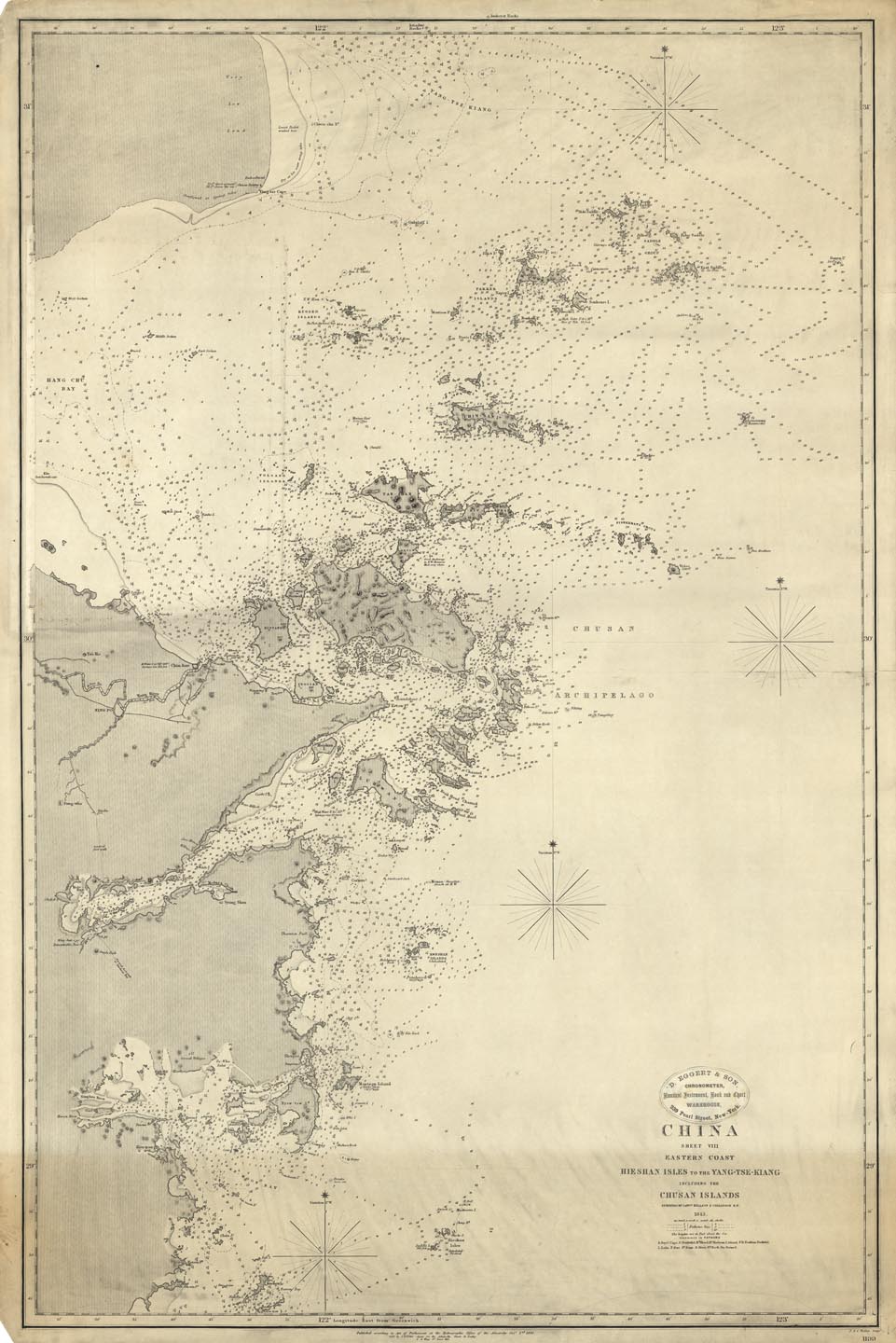
Hangzhou Bay
Hangzhou Bay is a funnel-shaped inlet of the East China Sea on the middle eastern coast of Mainland China, bordered by the province of Zhejiang to the west and south, and the municipality of Shanghai to north. The bay extends westwards to its head at the city of Hangzhou, the provincial capital of Zhejiang, from which its name is derived. The east and southeast margin of Hangzhou Bay are marked by numerous islands off the shores of Ningbo, collectively called the Zhoushan Islands, which are an urbanized archipelago that forms the prefecture-level city of Zhoushan. At Hangzhou, the Qiantang River flows into the bay, providing fresh water from the west, while seawater comes in from the east. Thus, Hangzhou Bay, especially its western end, is sometimes called the Qiantang River Estuary in the scientific literature. At less than in depth, the Hangzhou Bay is relatively shallow. Consequently, the main port in the bay area is the Port of Ningbo-Zhoushan, the busiest ports in the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhoushan
Zhoushan is an urbanized archipelago with the administrative status of a prefecture-level city in the eastern Chinese province of Zhejiang. It consists of an archipelago of islands at the southern mouth of Hangzhou Bay off the mainland city of Ningbo. The prefecture's city proper is Dinghai on Zhoushan Island, now administered as the prefecture's Dinghai District. During the 2020 census, Zhoushan Prefecture's population was 1,157,817, out of whom 882,932 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of two urban districts of Dinghai and Putuo. On 8 July 2011, the central government approved Zhoushan as Zhoushan Archipelago New Area, a state-level new area. History The archipelago was inhabited 6,000 years ago, during the Neolithic by people of the Hemudu culture. During the Spring and Autumn period, Zhoushan was called Yongdong, referring to its location east of the Yong River. At the time, it belonged to the state of Yue. The fishermen and sailors who inhabit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In modern times, the term ''Far East'' has widely fallen out of use and been substituted by Asia–Pacific, while the terms Middle East and Near East, although now pertaining to different territories, are still commonly used today. The term first came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 15th century, particularly the British people, British, denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "Easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East. Likewise, during the Qing dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term "Far West (Taixi), Tàixī ()" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries. Since the mid-20th century, the term has mostly gone out of use for the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Imperial Naval Office
The Imperial Naval Office () was a government agency of the German Empire. It was established in April 1889, when the German Imperial Admiralty was abolished and its duties divided among three new entities: the Imperial Naval High Command (''Kaiserliches Oberkommando der Marine''), the Imperial Naval Cabinet (''Kaiserliches Marinekabinett'') and the Imperial Naval Office performing the functions of a ministry for the Imperial German Navy. Structure and tasks According to the 1871 Constitution of the German Empire, the federal states were responsible for the German land forces and the imperial government for the navy. So while there were Prussian, Bavarian, Saxon and Württemberg armies, there was a single Imperial Navy, the only formation under the direct authority of the German Reich beside the colonial ''Schutztruppe'' forces. The head of the Naval Office was a Secretary of State who reported directly to the Imperial Chancellor (''Reichskanzler''). While the operational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral Tirpitz
Alfred Peter Friedrich von Tirpitz (; born Alfred Peter Friedrich Tirpitz; 19 March 1849 – 6 March 1930) was a German grand admiral and State Secretary of the German Imperial Naval Office, the powerful administrative branch of the German Imperial Navy from 1897 until 1916. Prussia never had a major navy, nor did the other German states before the German Empire was formed in 1871. Tirpitz took the modest Imperial Navy and, starting in the 1890s, turned it into a world-class force that could threaten Britain's Royal Navy. However, during World War I, his High Seas Fleet proved unable to end Britain's command of the sea and its chokehold on Germany's economy. The one great engagement at sea, the Battle of Jutland, ended in a narrow German tactical victory but a strategic failure. As the High Seas Fleet's limitations became increasingly apparent during the war, Tirpitz became an outspoken advocate for unrestricted submarine warfare, a policy which would ultimately bring Germany into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of Berlin, and lies embedded in a hilly morainic landscape dotted with many lakes, around 20 of which are located within Potsdam's city limits. It lies some southwest of Berlin's city centre. The name of the city and of many of its boroughs are of Slavic languages, Slavic origin. Potsdam was a residence of the Prussian kings and the German Emperor until 1918. Its planning embodied ideas of the Age of Enlightenment: through a careful balance of architecture and landscape, Potsdam was intended as "a picturesque, pastoral dream" which would remind its residents of their relationship with nature and reason. The city, which is over 1,000 years old, is widely known for its palaces, its lakes, and its overall historical and cultural significance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |