|
Guelb Er Richat
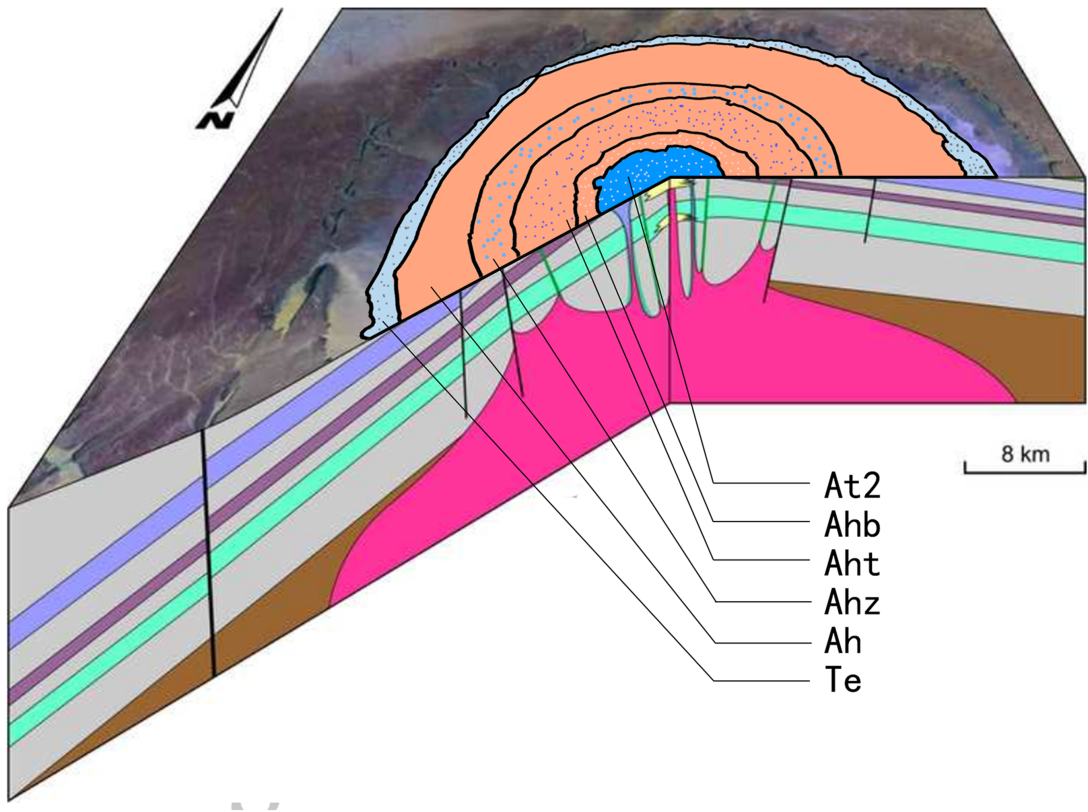
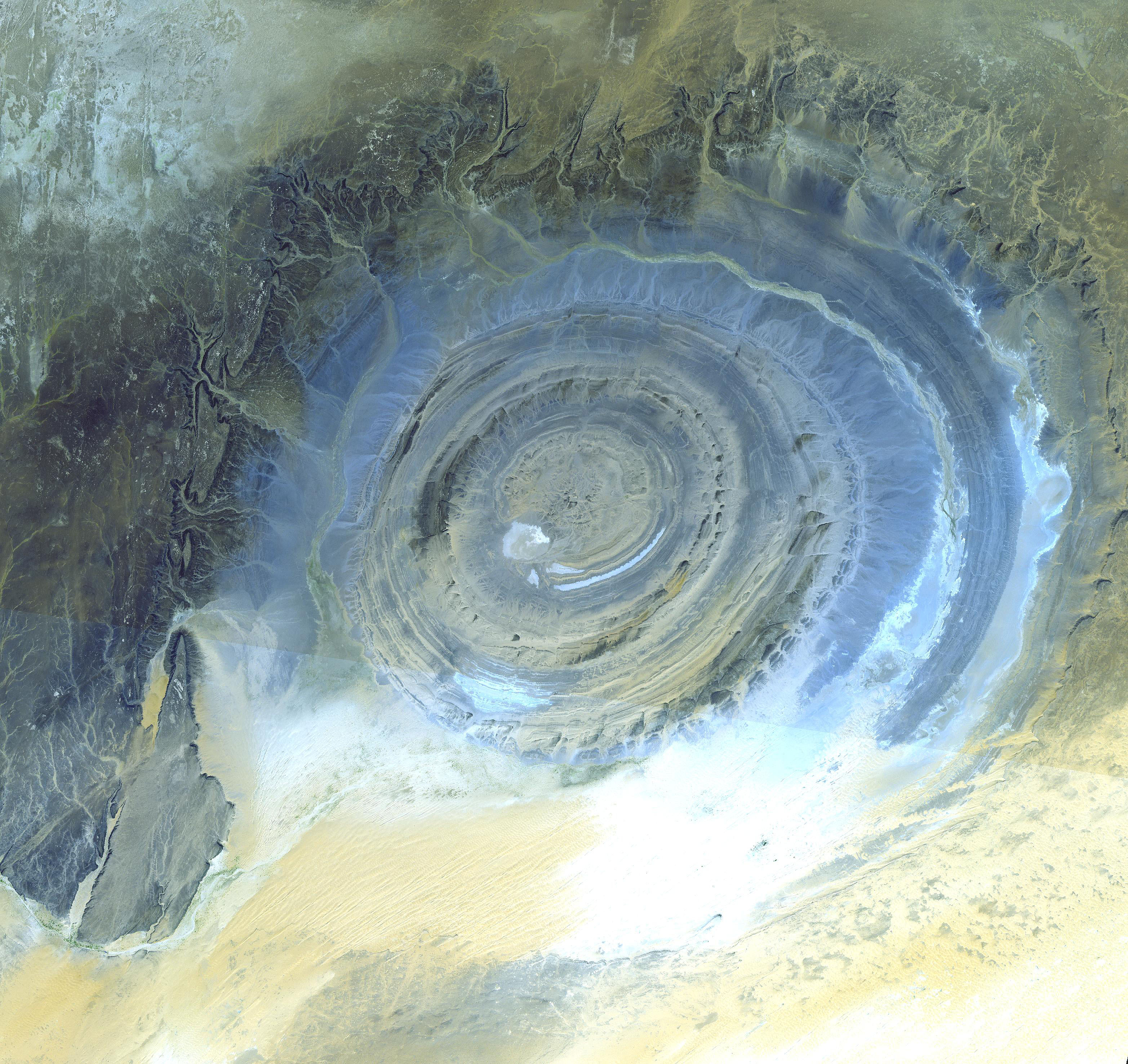
The Richat Structure, or ''Guelb er Richât'' (, ), is a prominent circular geological feature in the Adrar Plateau of the Sahara. It is located near Ouadane in the Adrar Region of Mauritania. In Hassaniya Arabic, ''rīšāt'' means ''feathers'' and it is also known locally in Arabic as ''tagense'', referring to the circular opening of the leather pouch that is used to draw water from local wells. It is an eroded geological dome, in diameter, caused by a subsurface igneous intrusion deforming the overlying sedimentary rock layers, causing the rock to be exposed as concentric rings with the oldest layers exposed at the centre of the structure. Igneous rock is exposed inside and there are rhyolites and gabbros that have undergone hydrothermal alteration, and a central megabreccia. The structure is also the location of exceptional accumulations of Acheulean Paleolithic stone tools. It was selected as one of the 100 geological heritage sites identified by the International Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology where a circular part of the Earth's surface has been pushed upward, tilting the pre-existing layers of earth away from the center. In technical terms, it consists of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective wikt:apex, apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, sphere, spherical-to-ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. A slice parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of stratum, strata. If the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in Multiview_orthographic_projection#Plan, plan view appears as a Bullseye_(target), bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of Deposition_(geology), deposition, then later deformed by the Tectonic uplift, uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by Hominini, hominins, 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, 11,650 Before Present#Radiocarbon calibration, cal Before Present, BP. The Paleolithic Age in Europe preceded the Mesolithic Age, although the date of the transition varies geographically by several thousand years. During the Paleolithic Age, hominins grouped together in small societies such as band society, bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals. The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of Knapping, knapped stone tools, although at the time humans also used wood and bone tools. Other organic commodities were adapted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Université Du Québec à Chicoutimi
The (, ''University of Quebec in Chicoutimi'', UQAC), is a branch of the network founded in 1969 and based in the Chicoutimi borough of Saguenay, Quebec, Saguenay, Quebec, Canada. UQAC has secondary study centres in La Malbaie, Saint-Félicien, Quebec, Saint-Félicien, Alma, Quebec, Alma, and Sept-Îles, Quebec, Sept-Îles. In 2017, 7500 students were registered and 209 professors worked for the university, making it the fourth largest of the ten branches, after (UQAM), (UQTR), and (ETS). Academics It offers over forty undergraduate and graduate programs. The university is especially well known for its researchers in aluminium (with two research centres), forestry, icing (in French, givrage), geology and historical population studies. In 2005, UQAC opened programs for students from foreign countries in partnership with universities from Morocco, Lebanon, China, Senegal, Colombia, and Brazil. In 2006, Université de Sherbrooke opened a building of its medical school on U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breccia
Breccia ( , ; ) is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or Rock (geology), rocks cementation (geology), cemented together by a fine-grained matrix (geology), matrix. The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of different origins, as indicated by the named types including sedimentary breccia, fault (geology), fault or tectonics, tectonic breccia, igneous breccia, Impact event, impact breccia, and Hydrothermal circulation, hydrothermal breccia. A megabreccia is a breccia composed of very large rock fragments, sometimes kilometers across, which can be formed by landslides, impact events, or caldera collapse. Types Breccia is composed of coarse rock fragments held together by cement or a fine-grained matrix. Like Conglomerate (geology), conglomerate, breccia contains at least 30 percent of gravel-sized particles (particles over 2mm in size), but it is distinguished from Conglomerate (geol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuesta
A cuesta () is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology, the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer layer, the whole being tilted somewhat from the horizontal. This results in a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of resistant strata, called caprock. Where erosion has exposed the frontslope of this, a steep slope or escarpment occurs. The resulting terrain may be called scarpland. Definition In general usage, a cuesta is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope (backslope) on one side, and a steep slope (frontslope) on the other. The word is from Spanish: "flank or slope of a hill; hill, mount, sloping ground". In geology and geomorphology, cuesta refers specifically to an asymmetric ridge with a long and gentle backslope called a dip slope that conforms with the dip of a resistant stratum or strata, called caprock. The outcrop of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock that was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts, and hence quartzite is a metasandstone. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike And Dip
In geology, strike and dip is a measurement convention used to describe the plane orientation or Attitude (geometry), attitude of a Plane (geometry), planar Geology, geologic feature. A feature's strike is the azimuth of an imagined horizontal line across the plane, and its dip is the angle of inclination (or depression angle) measured downward from horizontal. They are used together to measure and document a structure's characteristics for study or for use on a geological map. A feature's orientation can also be represented by dip and dip direction, using the azimuth of the dip rather than the strike value. Linear features are similarly measured with trend and plunge, where "trend" is analogous to dip direction and "plunge" is the dip angle. Strike and dip are measured using a compass and a clinometer. A compass is used to measure the feature's strike by holding the compass horizontally against the feature. A clinometer measures the feature's dip by recording the inclination pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks. Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar, because they are the most resistant minerals to the weathering processes at the Earth's surface. Like uncemented sand, sandstone may be imparted any color by impurities within the minerals, but the most common colors are tan, brown, yellow, red, grey, pink, white, and black. Because sandstone beds can form highly visible cliffs and other topography, topographic features, certain colors of sandstone have become strongly identified with certain regions, such as the red rock deserts of Arches National Park and other areas of the Southwestern United States, American Southwest. Rock formations composed of sandstone usually allow the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period Megaannum, Ma (million years ago) to the start of the Silurian Period Ma. The Ordovician, named after the Celtic Britons, Welsh tribe of the Ordovices, was defined by Charles Lapworth in 1879 to resolve a dispute between followers of Adam Sedgwick and Roderick Murchison, who were placing the same Rock (geology), rock beds in North Wales in the Cambrian and Silurian systems, respectively. Lapworth recognized that the fossil fauna in the disputed Stratum, strata were different from those of either the Cambrian or the Silurian systems, and placed them in a system of their own. The Ordovician received international approval in 1960 (forty years after Lapworth's death), when it was adopted as an official per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozoic, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". The Proterozoic is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. It covers the time from the appearance of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life on the Earth during the Cambrian Explosion. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two words of Greek origin: meaning "former, earlier", and , meaning "of life". Well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes via symbiogenesis; several global glaciations, which produced the 300 million years-long Huronian glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptical Dome
An elliptical dome, or an ''oval dome'', is a dome whose bottom Cross section (geometry), cross-section takes the form of an ellipse. Technically, an ''ellipsoidal dome'' has a circular cross-section, so is not quite the same. While the cupola can take different Geometric shape, geometries, when the ceiling's cross-section takes the form of an ellipse, and due to the reflecting properties of an ellipse, any two persons standing at a Focus (geometry), focus of the floor's ellipse can have one whisper, and the other hears; this is a whispering gallery. The largest elliptical dome in the world is at the Sanctuary of Vicoforte in Vicoforte, Italy. In architecture Elliptical domes have many applications in architecture; and are useful in covering rectangular spaces. The Spheroid#Oblate_spheroids, oblate, or horizontal elliptical dome is useful when there is a need to limit height of the space that would result from a spherical dome. As the mathematical description of an elliptical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |