|
Groß-Gerau Station
Groß-Gerau () is the district seat of the Groß-Gerau district, lying in the southern Frankfurt Rhein-Main Region in Hesse, Germany, and serving as a hub for the surrounding area. In 1994, the town hosted the 34th Hessentag state festival. Geography Location Groß-Gerau lies in the north of the ''Hessisches Ried'', the northeastern section of the Rhine rift. Neighbouring communities Groß-Gerau borders in the north on the community of Nauheim, in the northeast on the town of Mörfelden-Walldorf, in the east on the community of Büttelborn, in the southeast on the town of Griesheim (Darmstadt-Dieburg), in the south on the community of Riedstadt and in the west on the community of Trebur. Constituent communities Groß-Gerau consists of the centres of Berkach, Dornberg, Dornheim, Auf Esch, Groß-Gerau and Wallerstädten. History Already by Roman times, the area forming today's town of Groß-Gerau had great importance. A fort in the area of the constituent community of Auf Esch ens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt
The statistical offices of the German states (German language, German: ) carry out the task of collecting official statistics in Germany together and in cooperation with the Federal Statistical Office of Germany, Federal Statistical Office. The implementation of statistics according to Article 83 of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution is executed at state level. The Bundestag, federal government has, under Article 73 (1) 11. of the constitution, the exclusive legislation for the "statistics for federal purposes." There are 14 statistical offices for the States of Germany, 16 states: See also * Federal Statistical Office of Germany References {{Reflist National statistical services, Germany Lists of organisations based in Germany, Statistical offices Official statistics, Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
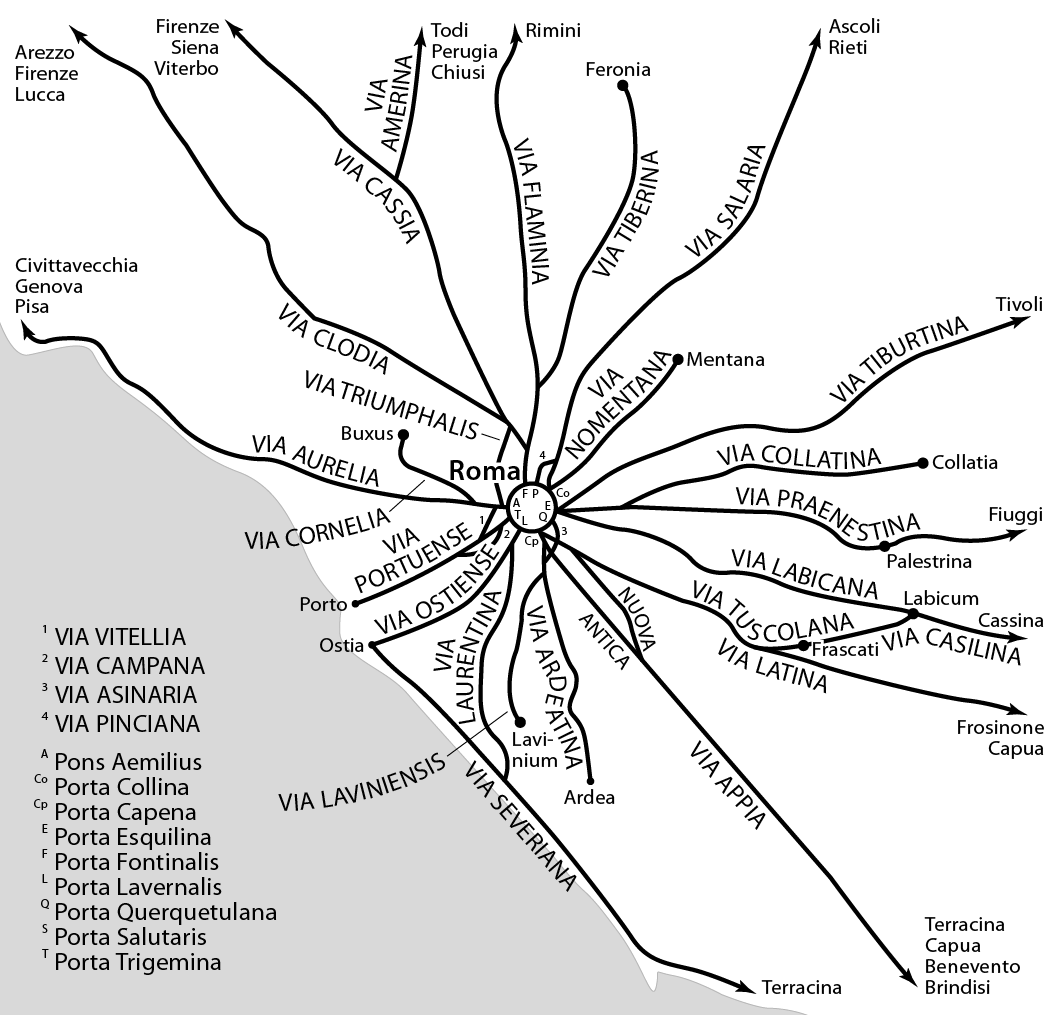
Roman Road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, 1986. At the peak of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrialization
Industrialisation (British English, UK) American and British English spelling differences, or industrialization (American English, US) is the period of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial society. This involves an extensive reorganisation of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Industrialisation is associated with increase of Pollution, polluting industries heavily dependent on fossil fuels. With the increasing focus on sustainable development and green industrial policy practices, industrialisation increasingly includes Leapfrogging, technological leapfrogging, with direct investment in more advanced, cleaner technologies. The reorganisation of the economy has many unintended consequences both economically and socially. As industrial workers' incomes rise, markets for consumer goods and services of all kinds tend to expand and provide a further stimulus to industrial investment and economic growth. Moreo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landtag
A ''Landtag'' (State Diet) is generally the legislative assembly or parliament of a federated state or other subnational self-governing entity in German-speaking nations. It is usually a unicameral assembly exercising legislative competence in non-federal matters. The States of Germany and Austria are governed by ''Landtage''. In addition, the legislature of the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol is known in German as a ''Landtag''. Historically, states of the German Confederation also established ''Landtage''. The Landtag of Liechtenstein is the nation's unicameral assembly. Name The German word Landtag is composed of the words ''Land'' (state, country or territory) and ''Tag'' (day). The German word ''Tagung'' (meeting) is derived from the German word ''Tag'', as such meetings were held at daylight and sometimes spanned several days. Historic Landtag assemblies States of the Holy Roman Empire In feudal society, the formal class system was reflected in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhenish Guilder
The Rhenish ''gulden'' or Rhenish ''guilder'' (; ) was a gold, standard currency coin of the Rhineland in the 14th and 15th centuries. They weighed between 3.4 and 3.8 grams (). History The Rhenish gold ''gulden'' was created when the Prince-elector, electors of Electorate of Cologne, Cologne, Electorate of Trier, Trier and Archbishopric of Mainz, Mainz were rewarded for their support in the election of Charles IV (HRR), Charles IV with a right to mint gold coins (), a right derived from the Golden Bull of Charles IV, Golden Bull. Trier was given the privilege on 25 November 1346, Cologne on 26 November 1346 and Mainz on 22 January 1354. The Rhenish ''gulden'' or ''florin'' began in 1354 as a copy of the Florentine ''florin'' (weight th a Cologne Mark of gold, 23 karats fine, or 3.43 g fine gold). However, by the early 15th century it has lost nearly one quarter of its gold content. In 1419 it was th a Cologne Mark of gold, 19 karats fine; hence 2.76 g fine gold. As a result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landgrave
Landgrave (, , , ; , ', ', ', ', ') was a rank of nobility used in the Holy Roman Empire, and its former territories. The German titles of ', ' ("margrave"), and ' ("count palatine") are of roughly equal rank, subordinate to ' ("duke"), and superior to the rank of a ' ("count"). Etymology The English word landgrave is the equivalent of the German ''Landgraf'', a compound of the words ''Land'' and ''Graf'' (English: Count). Description The title referred originally to a count who possessed imperial immediacy, or a feudal duty owed directly to the Holy Roman Emperor. His jurisdiction stretched over a sometimes quite considerable territory, which was not subservient to an intermediate power, such as a duke, a bishop or count palatine. The title originated within the Holy Roman Empire (first recorded in Lower Lotharingia from 1086: Henry III, Count of Louvain, as landgrave of Brabant). By definition, a landgrave exercised sovereign rights. His decision-making power was compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland, the , which is commonly translated to English as ''sheriff''. Description In British English, the political or legal office of a sheriff, term of office of a sheriff, or jurisdiction of a sheriff, is called a shrievalty in England and Wales, and a sheriffdom in Scotland. In modern times, the specific combination of legal, political and ceremonial duties of a sheriff varies greatly from country to country. * In England, Northern Ireland, or Wales, a sheriff (or high sheriff) is a ceremonial county or city official. * In Scotland, sheriffs are judges. * In the Republic of Ireland, in some counties and in the cities of Dublin and Cork, sheriffs are legal officials similar to bailiffs. * In the United States The United States of America (USA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schultheiß
In medieval Germany, the ''Schultheiß'' () was the head of a municipality (akin to today's office of mayor), a '' Vogt'' or an executive official of the ruler. As official (''villicus'') it was his duty to order his assigned village or county (''villicatio'') to pay the taxes and perform the services due to the ruler. The name originates from this function: ''Schuld'' 'debt' + ''heißen'' 'to order'. Later, the title was also used for the head of a town (''Stadtschultheiß'') or village (''Dorfschultheiß''). The office held by a ''Schultheiß'' was called ''Scholtisei'', ''Scholtisse'' (around 1400), ''Schultessy'', ''Schultissīe'', ''Schultissei'' (15th century); Latinized forms: ''sculdasia'' (10th century), ''scultetia'' (13th century). The title first appears in the '' Edictum Rothari'' of 643 AD, where it is spelled in post-Roman Latin as ''sculdahis''. This title reappears again in the Lombard laws of Liutprand in 723 AD. The title was originally spelled in Old High G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katzenelnbogen
Katzenelnbogen () is the name of a castle and small town in the district of Rhein-Lahn-Kreis in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. Katzenelnbogen is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Aar-Einrich. History Katzenelnbogen originated as a castle built on a promontory over the river Lahn around 1095. The lords of the castle became important local magnates, acquiring during the centuries some key and highly lucrative customs rights on the Rhine. The Counts of Katzenelnbogen also built Burg Neukatzenelnbogen and Burg Rheinfels on the Rhine. The male line of the German family died out in 1479, while the Austrian lineage continued, and the county became disputed between Hesse and Nassau. In 1557, the former finally won, but when Hesse was split due to the testament of Philipp the Magnanimous, Katzenelnbogen was split as well, between Hesse-Darmstadt and the small new secondary principality of Hesse-Rheinfels. When the latter line expired in 1583, its pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynasty's most prominent rulers – Frederick I (1155), Henry VI (1191) and Frederick II (1220) – ascended the imperial throne and also reigned over Italy and Burgundy. The non-contemporary name of 'Hohenstaufen' is derived from the family's Hohenstaufen Castle on Hohenstaufen mountain at the northern fringes of the Swabian Jura, near the town of Göppingen. Under Hohenstaufen rule, the Holy Roman Empire reached its greatest territorial extent from 1155 to 1268. Name The name Hohenstaufen was first used in the 14th century to distinguish the 'high' (''hohen'') conical hill named Staufen in the Swabian Jura (in the district of Göppingen) from the village of the same name in the valley below. The new name was applied to the hill c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |