|
Griko Dialect
Griko (endonym: /), sometimes spelled Grico, is one of the two dialects of Italiot Greek (the other being Calabrian Greek or ), spoken by Griko people in Salento, province of Lecce, Italy. Some Greek linguists consider it to be a Modern Greek dialect and often call it () or (). Griko and Standard Modern Greek are partially mutually intelligible. Classification The most popular hypothesis on the origin of Griko is the one by Gerhard Rohlfs and Georgios Hatzidakis, that Griko's roots go as far back in history as the time of the ancient Greek colonies in Southern Italy and Sicily in the eighth century BC. The Southern Italian dialect is thus considered to be the last living trace of the Greek elements that once formed Magna Graecia. There are, however, competing hypotheses according to which Griko may have preserved some Doric elements, but its structure is otherwise mostly based on Koine Greek, like almost all other Modern Greek dialects. Thus, Griko should rather be des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salento
Salento (; Salentino dialect, Salentino: ''Salentu''; Griko language, Salento Griko: ) is a Cultural area, cultural, List of historical states of Italy, historical, and geographic region at the southern end of the administrative region of Apulia, in southern Italy. It is a sub-peninsula of the Italian Peninsula, sometimes described as the "heel" of the Italian "boot". It encompasses the entire Local government, administrative area of the Province of Lecce, most of the Province of Brindisi (all of it except Fasano, Ostuni and Cisternino), and the south-eastern part of the Province of Taranto (like Grottaglie and Avetrana, but not Taranto itself). Etymology In ancient times the peninsula was named ''Sallentina'', or ''Messapia''. To this peninsula the term ''Calabria'' was originally applied during the ancient Roman and early Byzantine era, but since 580 the administrative scope of ''Calabrian'' province was gradually expanded towards western regions, encompassing ancient Brutti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Greek
Modern Greek (, or , ), generally referred to by speakers simply as Greek (, ), refers collectively to the dialects of the Greek language spoken in the modern era, including the official standardized form of the language sometimes referred to as Varieties of Modern Greek#Standard Modern Greek, Standard Modern Greek. The end of the Medieval Greek period and the beginning of Modern Greek is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic features of the modern language arose centuries earlier, having begun around the fourth century AD. During most of the Modern Greek period, the language existed in a situation of diglossia, with regional spoken dialects existing side by side with learned, more archaic written forms, as with the vernacular and learned varieties (''Dimotiki'' and ''Katharevousa'') that co-existed in Greece throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. Variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th centuryAD, it endured until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. The term 'Byzantine Empire' was coined only after its demise; its citizens used the term 'Roman Empire' and called themselves 'Romans'. During the early centuries of the Roman Empire, the western provinces were Romanization (cultural), Latinised, but the eastern parts kept their Hellenistic culture. Constantine the Great, Constantine I () legalised Christianity and moved the capital to Constantinople. Theodosius I, Theodosius I () made Christianity the state religion and Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use. The empire adopted a defensive strategy and, throughout its remaining history, expe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic; Greek: ) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The conquests of Alexander the Great, and the ensuing Hellenistic period, had caused Greek to spread throughout Anatolia and the Eastern Mediterranean. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
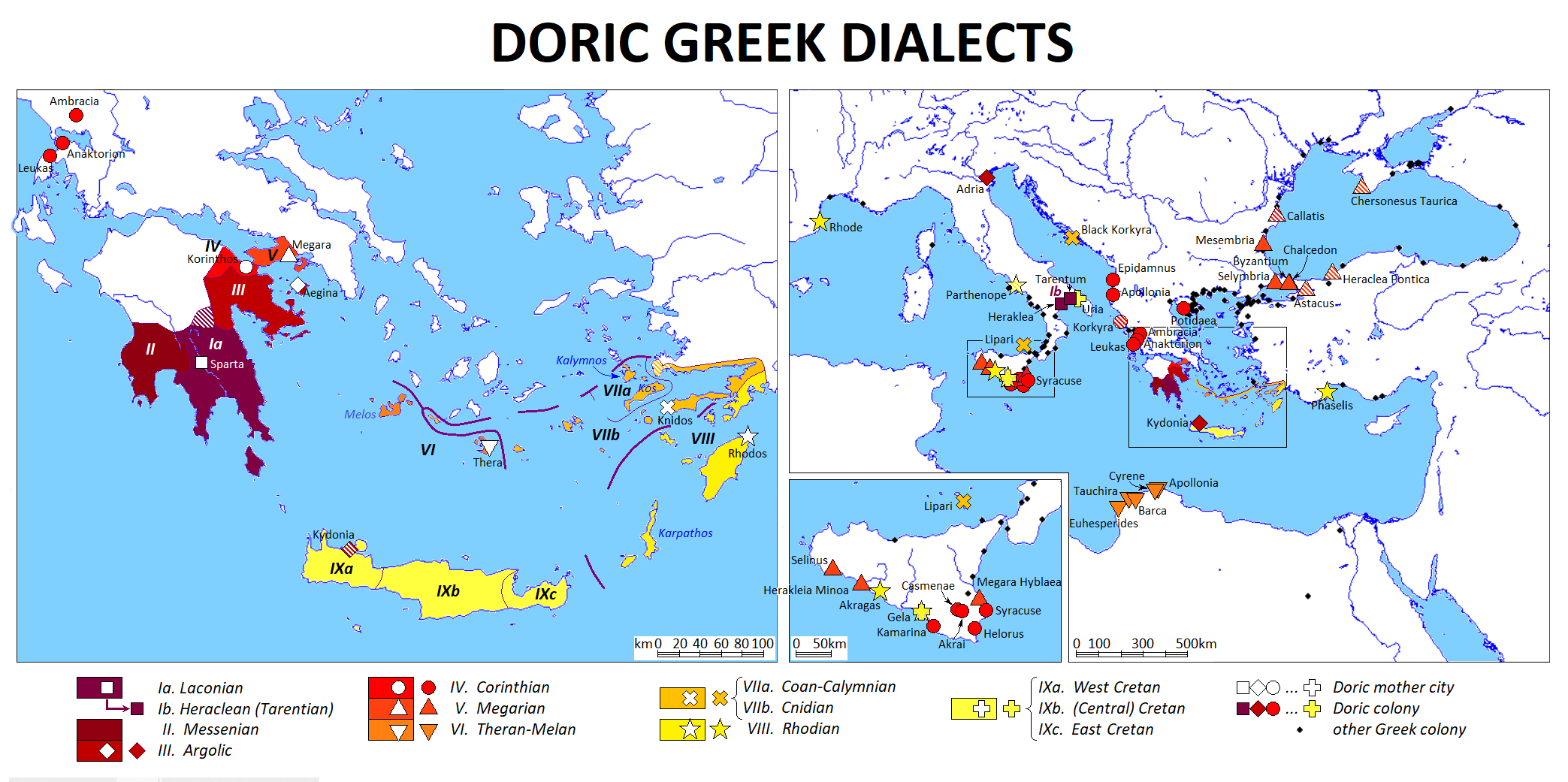
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by Greeks beginning in the 8th century BC. Initially founded by their ''metropoleis'' (mother cities), the settlements evolved into independent and powerful Greek city-states (''poleis''). The settlers brought with them Ancient Greece, Hellenic civilization, which over time developed distinct local forms due to both their distance from Greece and the influence of the indigenous peoples of southern Italy. This interaction left a lasting imprint on Italy, including on Ancient Rome, Roman culture. The Greek settlers also influenced native groups such as the Sicels and the Oenotrians, many of whom adopted Greek culture and became Hellenization, Hellenized. In areas like architecture and urban planning, the colonies sometimes surpassed the achievem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4.7 million inhabitants, including 1.2 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is both the largest and most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in #Art and architecture, arts, Music of Sicily, music, #Literature, literature, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine, and Sicilian Baroque, architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Italy
Southern Italy (, , or , ; ; ), also known as () or (; ; ; ), is a macroregion of Italy consisting of its southern Regions of Italy, regions. The term "" today mostly refers to the regions that are associated with the people, lands or culture of the Historical region, historical and cultural region that was once politically under the administration of the former Kingdoms of Kingdom of Naples, Naples and Kingdom of Sicily, Sicily (officially denominated as one entity and , i.e. "Kingdom of Sicily on the other side of Strait of Messina, the Strait" and "across the Strait") and which later shared a common organization into Italy's largest List of historical states of Italy, pre-unitarian state, the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. The island of Sardinia, which was not part of the aforementioned polity and had been under the rule of the Alps, Alpine House of Savoy, which would eventually annex the Bourbons' southern Italian kingdom altogether, is nonetheless often subsumed into the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonies In Antiquity
Colonies in antiquity were post-Iron Age city-states founded from a mother-city or metropolis rather than from a territory-at-large. Bonds between a colony and its metropolis often remained close, and took specific forms during the period of classical antiquity. Generally, colonies founded by the ancient Phoenicians, Ancient Carthage, Carthage, Ancient Rome, Rome, Alexander the Great and his Diadochi, successors remained tied to their metropolis, though Ancient Greece, Greek colonies of the Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, Classical eras were sovereign and self-governing from their inception. While earlier Greek colonies were often founded to solve Stasis (political history), social unrest in the mother-city by expelling a part of the population, Hellenistic, Roman Empire, Roman, History of Carthage, Carthaginian, and Han dynasty, Han Chinese colonies served as centres for trade (entrepôts), expansionism , expansion and Imperialism, empire-building. Sabean Colonizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgios Hatzidakis
Georgios Nicolaou Hatzidakis, aka Georgios Nikolaou Chatzidakis (; , in Myrthios, Ottoman Crete – 28 June 1941, in Athens) was a Greek philologist, who is regarded as the father of linguistics in Greece. He was the first chair of Linguistics and Indian Philology at the University of Athens in 1890–1923. Life and work His family was traditionally part of the Cretan revolts against the Ottoman Empire. His grandfather Kyriakos had taken part as a captain in the uprising of 1821. After his schooling at Rethymno, Georgios at the age of 18 fought himself by the side of his father in the uprising of 1866. After a three-year school visit in Athens, Chatzidakis was enrolled at the faculty of philosophy of the University of Athens for classical philology. In 1877, he won in a university competition a scholarship for linguistics study in Germany, which he pursued afterwards at the University of Leipzig Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard Rohlfs
Gerhard Rohlfs (July 14, 1892 – September 12, 1986) was a German linguist. He taught Romance languages and literature at the universities in Tübingen and Munich. He was described as an "archeologist of words". Biography Rohlfs was born in Berlin-Lichterfelde. His main interest was the languages and dialects spoken in Southern Italy and he travelled extensively in this region. He studied Italiot Greek (a language still spoken in a few places in Salento, southern Apulia, and in Bovesia, southern Calabria) and found several indications suggesting that Italiot-Greek is a direct descendant of the language originally spoken by the Greek colonists of Magna Grecia. He first advanced this theory in his book (''Greeks and Romans in Southern Italy'', 1924). He also published two complete vocabularies of the dialects of Bovesia (1938–1939) and Salento (1956–1961). His main work is considered to be his ''Historical Grammar of the Italian Language and its Dialects'' (, 1949– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |