|
Greyfriars Kirkyard
Greyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, Edinburgh, Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by the City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building. History Greyfriars takes its name from the Franciscan friary on the site (the friars of which wear grey habits), which was dissolved in 1560. The churchyard was founded in August 1562 after royal sanctions were granted to replace the churchyard at St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The latter burial ground was not used after around 1600. The Kirkyard was involved in the history of the Covenanters. The Covenanting movement began with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
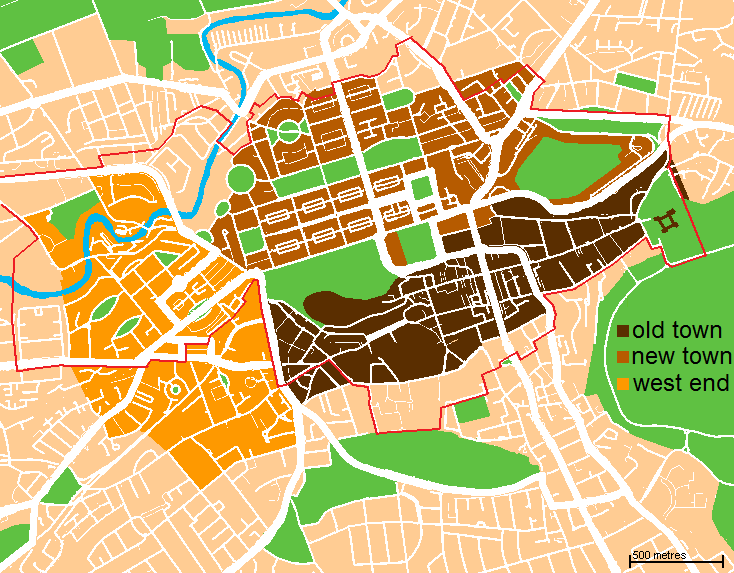
Old Town, Edinburgh
The Old Town () is the oldest part of Scotland's capital city of Edinburgh. The area has preserved much of its medieval street plan and many Scottish Reformation, Reformation-era buildings. Together with the 18th/19th-century New Town, Edinburgh, New Town, and West End, Edinburgh, West End, it forms part of a protected UNESCO World Heritage Site. Royal Mile The "Royal Mile" is a name coined in the early 20th century for the main street of the Old Town which runs on a downwards slope from Edinburgh Castle to Holyrood Palace and the ruined Holyrood Abbey. Narrow ''List of closes on the Royal Mile, closes'' (alleyways), often no more than a few feet wide, lead steeply downhill to both north and south of the main spine which runs west to east. Significant buildings in the Old Town include St. Giles' Cathedral, the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, the National Museum of Scotland, the Old College, University of Edinburgh, Old College of the University of Edinburgh, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Adamson (photographer)
Robert Adamson (26 April 1821 – 14 January 1848) was a Scotland, Scottish chemist and pioneer photographer at Hill & Adamson. He is best known for his pioneering photographic work with David Octavius Hill and producing some 2500 calotypes, mostly portraits, within 5 years after being hired by Hill in 1843. Early years Adamson was born in St Andrews, one of ten children of Rachel Melville and Alexander Adamson, a Fife tenant farmer. He grew up in Burnside of Duntrune, Burnside and was educated at Madras College in St Andrews where he showed exceptional talents in mathematics and mechanics, twice winning the prize for mathematics. He became employed at an engineering shop from a young age, and apprenticed as a millwright for several months. Career Adamson was keen on becoming an engineer, but ill health led to him pursuing photography. He was taught calotype by his brother, John Adamson (physician), John, and by the physicist David Brewster of the University of St Andrews in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donato Bramante
Donato Bramante (1444 – 11 April 1514), born as Donato di Pascuccio d'Antonio and also known as Bramante Lazzari, was an Italian architect and painter. He introduced Renaissance architecture to Milan and the High Renaissance style to Rome, where his plan for St. Peter's Basilica formed the basis of the design executed by Michelangelo. His Tempietto (San Pietro in Montorio) marked the beginning of the High Renaissance in Rome (1502) when Pope Julius II appointed him to build a sanctuary over the spot where Peter was martyred. Life Urbino Bramante was born under the name Donato d'Augnolo, Donato di Pascuccio d'Antonio, or Donato Pascuccio d'Antonio in Fermignano near Urbino. Here, in 1467, Luciano Laurana was adding to the Palazzo Ducale an arcaded courtyard and other Renaissance features to Federico da Montefeltro's ducal palace. Bramante's architecture has eclipsed his painting skills: he knew the painters Melozzo da Forlì and Piero della Francesca well, who were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
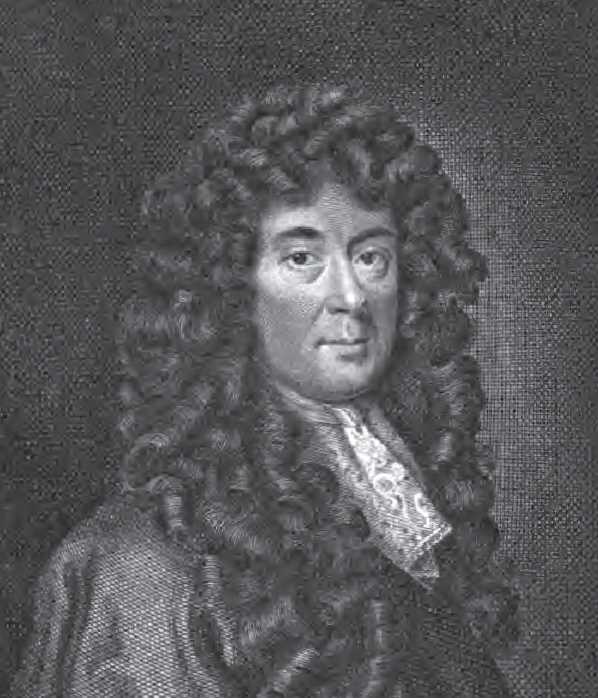
James Smith (architect, Died 1731)
James Smith (c. 1645–1731) was a Scottish architect, who pioneered the Palladian style in Scotland. He was described by Colen Campbell, in his ''Vitruvius Britannicus'' (1715–1725), as "the most experienced architect of that kingdom". Biography Born in Tarbat, Ross, Smith was the son of James Smith (died c.1684), a mason, who became a burgess of Forres, Moray, in 1659.Colvin, pp.755–758 The architect is generally identified as the "James Smith of Morayshire" who attended the Scots College, Rome from 1671–75, initially with the aim of entering the Catholic priesthood, although some scholars are cautious about the certainty of this identification. He had certainly travelled abroad, however, and was well-educated, with a knowledge of Latin.Gifford, pp.62–67 By December 1677, Smith was in touch with Sir William Bruce, the most prominent architect of the time in Scotland, and the designer of the rebuilt Holyrood Palace, Edinburgh. Here, Smith served as a mason, under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Mackenzie (lawyer)
Sir George Mackenzie of Rosehaugh (1636 – May 8, 1691) was a Scotland, Scottish lawyer, Lord Advocate, essayist and legal writer. He was nicknamed Bloody Mackenzie. Early life Mackenzie, who was born in Dundee, was the son of Sir Simon Mackenzie of Lochslin (died c. 1666) and Elizabeth Bruce, daughter of the Reverend Peter Bruce, minister of St Leonard's, and Principal of St Leonard's Hall in the University of St Andrews. He was a grandson of Kenneth Mackenzie, 1st Lord Mackenzie of Kintail, Kenneth, Lord Mackenzie of Kintail and a nephew of George Mackenzie, 2nd Earl of Seaforth. He was educated at the King's College, Aberdeen, King's College, University of Aberdeen (which he entered in 1650), the University of St Andrews, and the University of Bourges in France. Career Mackenzie was elected to the Faculty of Advocates in 1659, and spoke in defence at the trial of Archibald Campbell, 1st Marquess of Argyll, Archibald Campbell, Marquis of Argyll in 1661. He acted as justic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Medical College
The University of Edinburgh Medical School (also known as Edinburgh Medical School) is the medical school of the University of Edinburgh in Scotland and the United Kingdom and part of the College of Medicine and Veterinary Medicine. It was established in 1726, during the Scottish Enlightenment, making it the oldest medical school in the United Kingdom and the oldest medical school in the English-speaking world. The medical school in 2025 was ranked 5th by the Complete University Guide, 6th in the UK by The Guardian University Guide, and 7th by The Times University Guide. It also ranked 21st in the world by both the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and the QS World University Rankings in the same year. According to a Healthcare Survey run by Saga in 2006, the medical school's main teaching hospital, the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, was considered the best hospital in Scotland. The medical school is associated with 13 Nobel Prize laureates: 7 in the Nobel Prize i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Snatcher
Body snatching is the illicit removal of corpses from graves, morgues, and other burial sites. Body snatching is distinct from the act of grave robbery as grave robbing does not explicitly involve the removal of the corpse, but rather theft from the burial site itself. The term 'body snatching' most commonly refers to the removal and sale of corpses primarily for the purpose of dissection or anatomy lectures in medical schools. The term was coined primarily in regard to cases in the United Kingdom and United States throughout the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. However, there have been cases of body snatching in many countries, with the first recorded case dating back to 1319 in Bologna, Italy. Those who practiced the act of body snatching and sale of corpses during this period were commonly referred to as resurrectionists or resurrection men. Resurrectionists in the United Kingdom, who often worked in teams and who primarily targeted more recently dug graves, would be hired in ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortsafe
A mortsafe or mortcage was a construction designed to protect graves from disturbance, used in the United Kingdom. Resurrectionists in the United Kingdom, Resurrectionists had supplied schools of anatomy since the early 18th century. This was due to the necessity for medical students to learn anatomy by attending dissections of human subjects, which was frustrated by the very limited allowance of dead bodies – for example the corpses of executed criminals – granted by the government, which controlled the supply. Official inaction The British authorities turned a blind eye to grave-rifling because surgeons and students were working to advance medical knowledge. They kept publicity to a minimum to prevent people from realising what was happening. The cases of grave-robbing that came to light caused riots, damage to property and even fatal attacks. In the early 19th century, with the great increase in numbers of schools and students, there was continual rifling of secluded gravey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortsafe In Greyfriars Kirkyard
A mortsafe or mortcage was a construction designed to protect graves from disturbance, used in the United Kingdom. Resurrectionists had supplied schools of anatomy since the early 18th century. This was due to the necessity for medical students to learn anatomy by attending dissections of human subjects, which was frustrated by the very limited allowance of dead bodies – for example the corpses of executed criminals – granted by the government, which controlled the supply. Official inaction The British authorities turned a blind eye to grave-rifling because surgeons and students were working to advance medical knowledge. They kept publicity to a minimum to prevent people from realising what was happening. The cases of grave-robbing that came to light caused riots, damage to property and even fatal attacks. In the early 19th century, with the great increase in numbers of schools and students, there was continual rifling of secluded graveyards, fights in city burial grounds and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George IV Bridge
George IV Bridge is an Viaduct, elevated street in Edinburgh, Scotland, and is home to a number of the city's important public buildings. History A bridge connecting the High Street to the south was first suggested in 1817, but was originally planned further west and was non-linear and complicated. Plans developed through the early 1820s, concluding in 1825 that a linear form aligned with Bank Street (which connects to The Mound, Edinburgh, The Mound and Princes Street) was more logical, even though this required greater destruction of existing buildings. This would be a bridge over the Cowgate and Merchant Street. The foundation stone was laid on 15 August 1827. Measuring in length, the bridge was constructed between 1827 and 1836 as a result of the Edinburgh Improvement Act 1827 (7 & 8 Geo. 4. c. lxxvi). Named after King George IV, it was designed by architect Thomas Hamilton (architect), Thomas Hamilton (1784–1858) to connect the South Side district of Edinburgh to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyfriars Bobby
Greyfriars Bobby (4 May 1855 – 14 January 1872) was a Skye Terrier or Dandie Dinmont Terrier who became known in 19th-century Edinburgh for spending 14 years guarding the grave of his owner until his death on 14 January 1872. The story continues to be well known in Scotland, through several books and films. A prominent commemorative statue and nearby graves are a tourist attraction. Traditional view The best-known version of the story is that Bobby belonged to #John Gray, John Gray, who worked for the Edinburgh City Police as a watchman (law enforcement), nightwatchman. When John Gray died he was buried in Greyfriars Kirkyard, the kirkyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in the Old Town of Edinburgh. Bobby then became known locally, spending the rest of his life sitting on his master's grave.greyfriarsbobby.co.uk (11 February 2013).Education Scotland website (11 February 2013). In 1867 the lord provost of Edinburgh, Sir William Chambers (publisher), William Chambers, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Edinburgh Council
The City of Edinburgh Council (Scottish Gaelic: ''Comhairle Baile Dhùn Èideann'') is the local government authority covering the City of Edinburgh council area. Almost half of the council area is the built-up area of Edinburgh, capital of Scotland. With a population of in , it is the second most populous local authority area in Scotland. The council took on its current form in 1996 under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994, replacing the City of Edinburgh District Council of the Lothian region, which had been created in 1975. The history of local government in Edinburgh, however, stretches back much further. Around 1130, David I made the town a royal burgh and a burgh council, based at the Old Tolbooth is recorded continuously from the 14th century. The council is currently based in Edinburgh City Chambers with a main office nearby at Waverley Court. History Origins The date of Edinburgh's formation as a burgh is unknown, but it is referred to as a royal burgh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |