|
Grendel (novel)
''Grendel'' is a 1971 novel by the American author John Gardner. It is a retelling of part of the Old English poem ''Beowulf'' from the perspective of the antagonist, Grendel. In the novel, Grendel is portrayed as an antihero. The novel deals with finding meaning in the world, the power of literature and myth, and the nature of good and evil. In a 1973 interview, Gardner said, "In ''Grendel'' I wanted to go through the main ideas of Western civilization – which seemed to me to be about ... twelve? – and go through them in the voice of the monster, with the story already taken care of, with the various philosophical attitudes (though with Sartre in particular), and see what I could do, see if I could break out." On another occasion, he noted that he used Grendel to "represent Sartre's philosophical position" and that "a lot of ''Grendel'' is borrowed from sections of Sartre's '' Being and Nothingness''". ''Grendel'' has become one of Gardner's best-known and best-reviewe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gardner (American Writer)
John Champlin Gardner Jr. (July 21, 1933 – September 14, 1982) was an American novelist, essayist, literary critic, and university professor. He is best known for his 1971 novel ''Grendel (novel), Grendel'', a retelling of the Beowulf myth from the monster's point of view. Early life and education Gardner was born in Batavia, New York. His father was a lay preacher and dairy farmer, and his mother taught third grade at a small school in a nearby village. Both parents were fond of poetry, and would often recite their favorite poetry and poetry they wrote about life on the farm at friends' homes. Gardner was active in The Boy Scouts of America and achieved the rank of Eagle Scout. The young Gardner attended public school and worked on his father's farm. In April 1945, his younger brother Gilbert was killed in an accident with a cultipacker. Gardner, who was driving the tractor during the fatal accident, carried guilt for his brother's death throughout his life, suffering nightmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Civilization
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompasses the social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, belief systems, political systems, artifacts and technologies primarily rooted in European and Mediterranean histories. A broad concept, "Western culture" does not relate to a region with fixed members or geographical confines. It generally refers to the classical era cultures of Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome that expanded across the Mediterranean basin and Europe, and later circulated around the world predominantly through colonization and globalization. Historically, scholars have closely associated the idea of Western culture with the classical era of Greco-Roman antiquity. However, scholars also acknowledge that other cultures, like Ancient Egypt, the Phoenician city-states, and sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoffrey Chaucer
Geoffrey Chaucer ( ; – 25 October 1400) was an English poet, author, and civil servant best known for ''The Canterbury Tales''. He has been called the "father of English literature", or, alternatively, the "father of English poetry". He was the first writer to be buried in what has since come to be called Poets' Corner, in Westminster Abbey. Chaucer also gained fame as a philosopher and astronomer, composing the scientific ''A Treatise on the Astrolabe'' for his 10-year-old son, Lewis. He maintained a career in public service as a bureaucrat, courtier, diplomat, and member of parliament, having been elected as Knight of the shire, shire knight for Kent. Among Chaucer's many other works are ''The Book of the Duchess'', ''The House of Fame'', ''The Legend of Good Women'', ''Troilus and Criseyde'', and ''Parlement of Foules''. He is seen as crucial in legitimising the literary use of Middle English when the dominant literary languages in England were still Anglo-Norman Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago Review
''Chicago Review'' is a student-run literary magazine founded in 1946 and published quarterly in the Humanities Division at the University of Chicago. The magazine features contemporary poetry, fiction, and criticism, often publishing works in translation and special features in double issues. Three stories published in ''Chicago Review'' have won the O. Henry Award. Work that first appeared in ''Chicago Review'' has also been reprinted in ''The Best American Poetry 2002'', '' The Best American Poetry 2004'', and '' The Best American Short Stories 2003''. Early history ''Chicago Review'' was founded in 1946 by two University of Chicago graduate students, James Radcliffe Squires and Carrolyn Dillard, in response to what they described as "an exaggerated utilitarianism on the college." They aimed to present a "contemporary standard of good writing" and demanded "that the writers do better than they thought they could." ''Chicago Review'' exclusively published work by students a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairie Schooner
''Prairie Schooner'' is a literary magazine published quarterly at the University of Nebraska–Lincoln with the cooperation of UNL's English Department and the University of Nebraska Press. It is based in Lincoln, Nebraska and was first published in 1926. It was founded by Lowry Wimberly and a small group of his students, who together formed the Wordsmith Chapter of Sigma Upsilon (a national honorary literary society). Although many assume it is a regional magazine, it is nationally and internationally distributed and publishes writers from all over the United States and the world. ''Prairie Schooner'' has garnered reprints, and honorable mentions in the Pushcart Prize anthologies and various of the ''Best American'' series, including '' Best American Short Stories'', ''Best American Essays'', ''Best American Mystery Stories'', and ''Best American Nonrequired Reading''. Editors ''Prairie Schooners current editor (2011–present) is Jamaican/Ghanaian poet and author Kwame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Existentialism
Existentialism is a family of philosophical views and inquiry that explore the human individual's struggle to lead an authentic life despite the apparent absurdity or incomprehensibility of existence. In examining meaning, purpose, and value, existentialist thought often includes concepts such as existential crises, angst, courage, and freedom. Existentialism is associated with several 19th- and 20th-century European philosophers who shared an emphasis on the human subject, despite often profound differences in thought. Among the 19th-century figures now associated with existentialism are philosophers Søren Kierkegaard and Friedrich Nietzsche, as well as novelist Fyodor Dostoevsky, all of whom critiqued rationalism and concerned themselves with the problem of meaning. The word ''existentialism'', however, was not coined until the mid 20th century, during which it became most associated with contemporaneous philosophers Jean-Paul Sartre, Martin Heidegger, Simone de Beau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon
A dragon is a Magic (supernatural), magical legendary creature that appears in the folklore of multiple cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but European dragon, dragons in Western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as winged, horned, and capable of breathing fire. Chinese dragon, Dragons in eastern cultures are usually depicted as wingless, four-legged, Snake, serpentine creatures with above-average intelligence. Commonalities between dragons' traits are often a hybridization of Reptile, reptilian, mammalian, and Bird, avian features. Etymology The word ''dragon'' entered the English language in the early 13th century from Old French , which, in turn, comes from Latin (genitive ), meaning "huge serpent, dragon", from , (genitive , ) "serpent". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
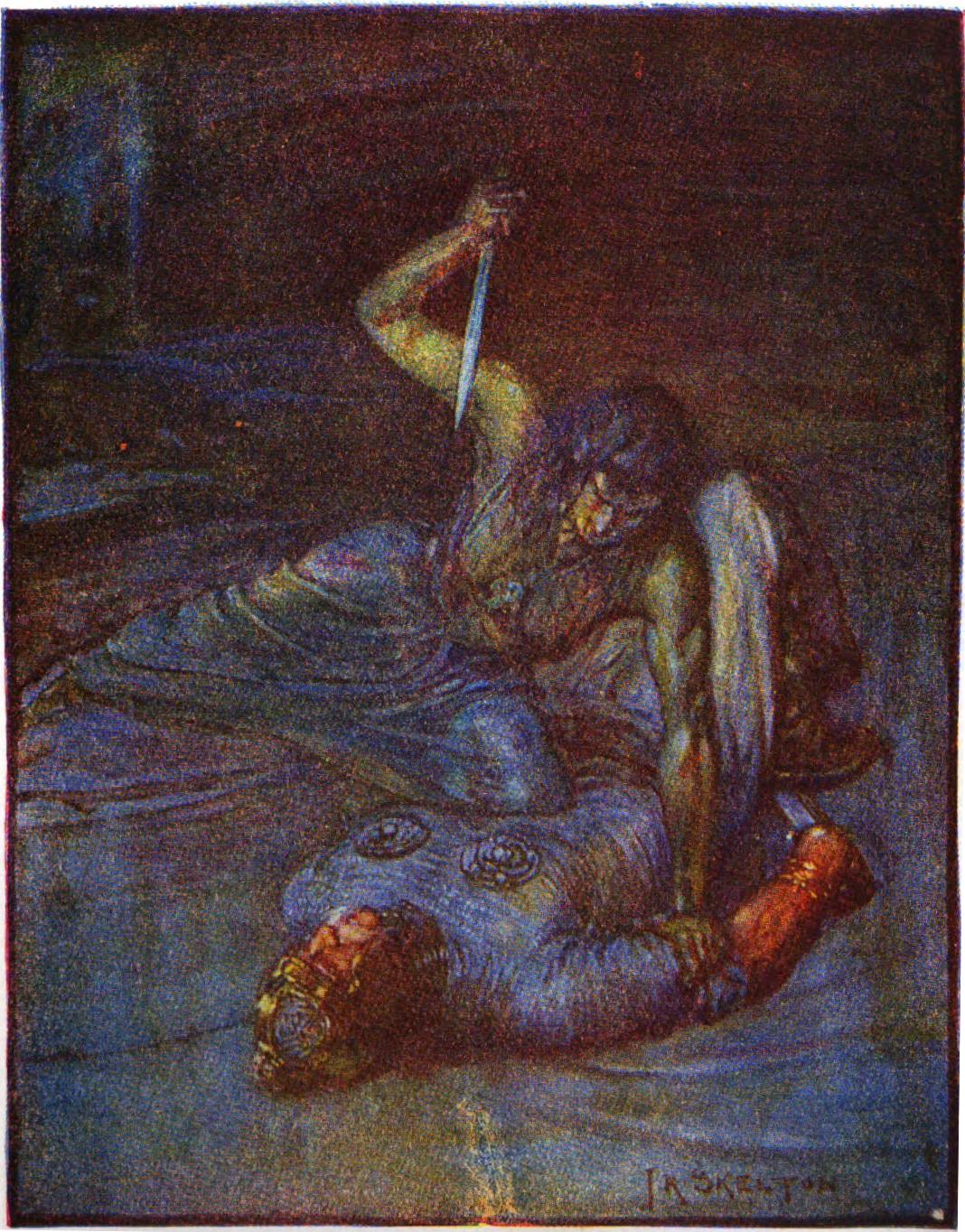
Grendel's Mother
Grendel's mother () is one of three antagonists in the anonymous Old English poem ''Beowulf'' (c. 700–1000 AD), the other two being Grendel and the dragon. Each antagonist reflects different negative aspects of both the hero Beowulf and the heroic society in which the poem is set. Grendel's mother is introduced in lines 1258b to 1259a as: "Grendles modor/ides, aglæcwif". Grendel's mother, who is never given a name in the text, is the subject of an ongoing controversy among medieval scholars. This controversy is due to the ambiguity of a few words in Old English which appear in the original ''Beowulf'' manuscript. While there is agreement over the word "modor" (mother), the phrase "ides, aglæcwif" is the subject of scholarly debate. Story The poem, ''Beowulf,'' is contained in the Nowell Codex. As noted in lines 106–114 and lines 1260–1267 of ''Beowulf,'' monsters (which include Grendel's mother and Grendel) are descendants of Cain. After Grendel is killed, Grendel's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
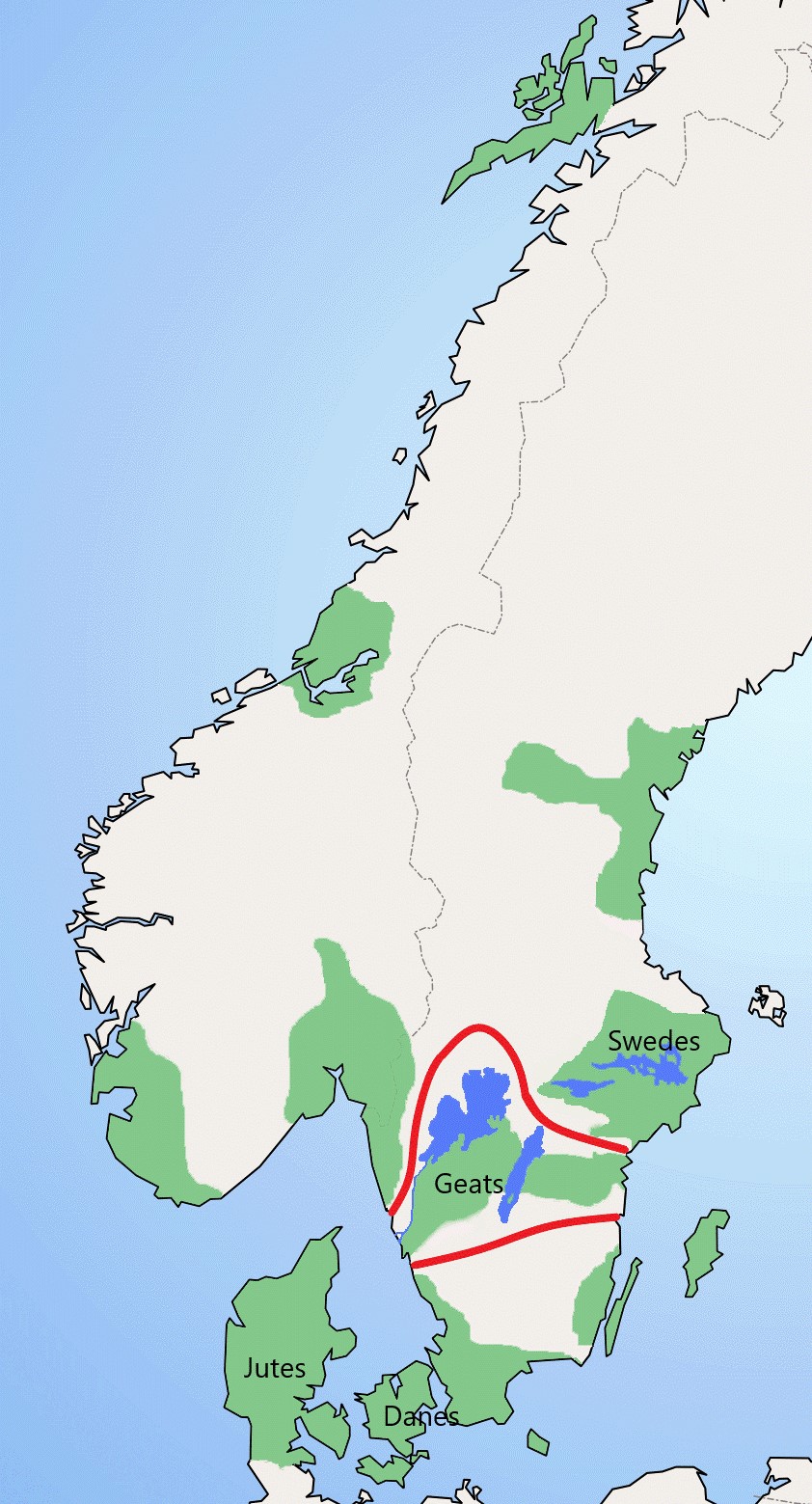
Geats
The Geats ( ; ; ; ), sometimes called ''Geats#Goths, Goths'', were a large North Germanic peoples, North Germanic tribe who inhabited ("land of the Geats") in modern southern Sweden from antiquity until the Late Middle Ages. They are one of the progenitor groups of modern Swedes, along with the tribes of Swedes (tribe), Swedes and Gutes. The name of the Geats also lives on in the Provinces of Sweden, Swedish provinces of and , the western and eastern lands of the Geats, and in many other toponyms. The Swedish dialects spoken in the areas that used to be inhabited by Geats form a distinct group, ''Götamål''. Etymology The etymology of the name ''Geat'' (Old English ', from a Proto-Germanic *''Gautaz'', plural *''Gautōz'') is similar to that of ''Goths'' and ''Gutes'' (*''Gutô'', plural *''Gutaniz''). The names derive from Indo-European ablaut, ablaut grades of the Proto-Germanic word *''geutaną'', meaning "to pour". They have the literal meaning "they who pour their se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grendel Grendel Grendel
''Grendel Grendel Grendel'' is a 1981 Australian animated film written, directed and designed by Alex Stitt, Alexander Stitt and starring Peter Ustinov. It was based on John Gardner (American writer), John Gardner's novel ''Grendel (novel), Grendel''. The music was composed and conducted by Bruce Smeaton and has been released on the 1M1 Records label. Like Gardner's novel, the film is a retelling of part of the epic poem ''Beowulf'' from the monster Grendel's point of view. Grendel (voiced by Ustinov) is by turns a thoughtful and contemplative character and a rampaging monster who attacks the mead hall of an early Danish kingdom, biting the head off of one would-be defender. This was the second full-length fully animated film ever made in Australia (coming after 1972's ''Marco Polo Junior Versus the Red Dragon''). Plot Initially narrated by the titular character through a Flashback (narrative), flashback, Grendel (Peter Ustinov), the "Great Boogey", recounts how he first left his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barry Silesky
Barry Silesky (born 1949) is a Minneapolis-native poet, biographer, and non-fiction writer. He moved to Chicago where he studied for a BA from Northwestern University and an MA from the University of Illinois. Writing career Silesky is the author of a collection of poetry, biographies, and prose, such as ''The New Tenants'', ''One Thing That Can Save Us'', ''This Disease: Poems'', ''Ferlinghetti: The Artist in His Time'', and '' John Gardner, Literary Outlaw''. He was the founding editor of ACM ('' Another Chicago Magazine'') and previously taught at the Art Institute of Chicago and Loyola University Chicago Loyola University Chicago (Loyola or LUC) is a Private university, private Society of Jesus, Jesuit research university in Chicago, Illinois, United States. Founded in 1870 by the Society of Jesus, Loyola is one of the largest Catholic Church, .... Silesky’s works are widely held in libraries worldwide. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Silesky, Barry 1949 births Living pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Being And Nothingness
''Being and Nothingness: An Essay on Phenomenological Ontology'' (), sometimes published with the subtitle ''A Phenomenological Essay on Ontology'', is a 1943 book by the philosopher Jean-Paul Sartre. In the book, Sartre develops a philosophical account in support of his existentialism, dealing with topics such as consciousness, perception, social philosophy, self-deception, the existence of "nothingness", psychoanalysis, and the question of free will. While a prisoner of war in 1940 and 1941, Sartre read Martin Heidegger's ''Being and Time'' (1927), which uses the method of Husserlian phenomenology as a lens for examining ontology. Sartre attributed the course of his own philosophical inquiries to his exposure to this work. Though influenced by Heidegger, Sartre was profoundly skeptical of any measure by which humanity could achieve a kind of personal state of fulfillment comparable to the hypothetical Heideggerian "re-encounter with Being". In Sartre's account, man is a creature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |