|
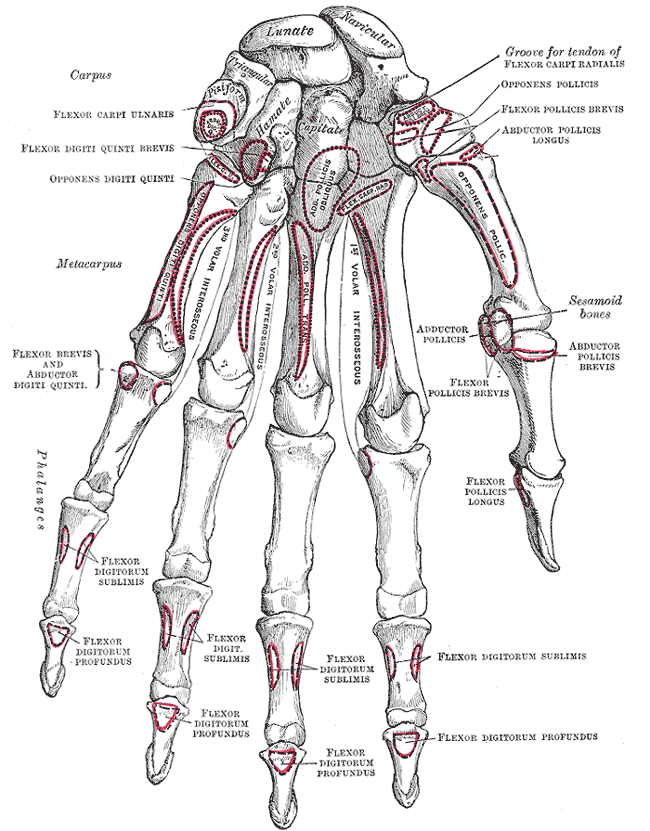
Gray's Anatomy
''Gray's Anatomy'' is a reference book of human anatomy written by Henry Gray, illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter and first published in London in 1858. It has had multiple revised editions, and the current edition, the 42nd (October 2020), remains a standard reference, often considered "the doctors' bible". Earlier editions were called ''Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical'', ''Anatomy of the Human Body'' and ''Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied'', but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, ''Gray's Anatomy''. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject. Publication history Origins The English anatomist Henry Gray was born in 1827. He studied the development of the endocrine glands and spleen and in 1853 was appointed Lecturer on Anatomy at St George's Hospital Medical School in London. In 1855, he approached his colleague Henry Vandyke Carter with his idea to produce an inexpensive and access ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Gray
Henry Gray (1827 – 13 June 1861) was a British anatomist and surgery, surgeon most notable for publishing the book ''Gray's Anatomy''. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society (FRS) at the age of 25. Biography Gray was born in Belgravia, London, in 1827 and lived most of his life in London. In 1842, he entered as a student at St George's Hospital, St. George's Hospital, London (then situated in Belgravia, now moved to Tooting), and he is described by those who knew him as a most painstaking and methodical worker, and one who learned his anatomy by the slow but invaluable method of making dissections for himself. While still a student, Gray secured the triennial prize of Royal College of Surgeons of England, Royal College of Surgeons in 1848 for an essay entitled ''The Origin, Connexions and Distribution of nerves to the human eye and its appendages, illustrated by comparative dissections of the eye in other vertebrate animals.'' In 1852, at the early age of 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy Act 1832
The Anatomy Act 1832 ( 2 & 3 Will. 4. c. 75), also known as the Warburton Anatomy Act 1832 is an act of Parliament of the United Kingdom that gave free licence to doctors, teachers of anatomy and bona fide medical students to dissect donated bodies. It was enacted in response to public revulsion at the illegal trade in corpses. Background The 19th century ushered in a new-found medical interest in detailed anatomy thanks to an increase in the importance of surgery. In order to study anatomy, human cadavers were needed and thus ushered in the practice of grave robbing. Before 1832, the Murder Act 1752 stipulated that only the corpses of executed murderers could be used for dissection. By the early 19th century, the rise of medical science – coinciding with a reduction in the number of executions – had caused demand to outstrip supply. Around 1810, an anatomical society was formed to impress upon the government the necessity for altering the law. Among its members were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Anthony Spitzka
Edward Anthony Spitzka (June 17, 1876 – September 4, 1922) was an American anatomist who autopsied (29 Oct 1901) the brain of Leon Czolgosz, the assassin of president William McKinley. (In 1881, his father Edward Charles Spitzka, a famous neurologist and medical specialist in mental diseases, testified to the insanity of Charles Guiteau, the assassin of President James A. Garfield, at Guiteau's murder trial.) Dr. Edward Anthony Spitzka was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 1908. He was the author of 40 papers on brain anatomy. Widely recognized as one of the world's leading brain anatomists, he directed the Baugh Institute of Anatomy until 1914. Dr. Spitzka performed post mortem examinations of the brains of many distinguished American men, including Prof. Edward Drinker Cope, Prof. Joseph Leidy, Prof. Harrison Allen, Dr. William Pepper, George Francis Train, and Major John Wesley Powell. Publications *Co-edited (with J.C. DaCosta) ''Seventeenth Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Pickering Pick
Thomas Pickering Pick (13 June 1841 – 6 September 1919) was a British surgeon and author. He edited the tenth through fourteenth editions of ''Gray's Anatomy'', succeeding Timothy Holmes as editor. His other notable books include ''Fractures and Dislocations'' (Cassell & Co, 1885), '' A Treatise on Surgery'' (1875), and ''Surgery'' (1899). Pickering Pick's father was a Liverpool merchant. At 16, he came to London and trained at St George's Hospital. He qualified for the Fellowship of the Royal College of Surgeons Fellowship of the Royal Colleges of Surgeons (FRCS) is a professional qualification to practise as a senior surgeon in Ireland or the United Kingdom. It is bestowed on an intercollegiate basis by the four Royal Colleges of Surgeons (the Roya ... in 1866 and was elected as the hospital's assistant surgeon in 1869. From 1878 to 1898 he held the office of surgeon, then became a consulting surgeon prior to his 1900 retirement. For many years he was Inspector of An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Williams Keen
William Williams Keen Jr. (January 19, 1837June 7, 1932) was an American physician and the first brain surgeon in the United States. During his lifetime, Keen worked with six American presidents. Early life and education Keen was born in Philadelphia on January 19, 1837, to William Williams Keen Sr. (1797–1882) and Susan Budd. He attended Saunders's Academy and Philadelphia's Central High School. Keen graduated from Brown University, with an A.B. in 1859. He then obtained a degree in medicine from Jefferson Medical College in 1862. During the American Civil War Keen served as a surgeon for the Fifth Massachusetts Militia Regiment and then for the Union Army during the American Civil War. While serving, Keen built a reputation for his work with patients who had neurological wounds, mainly because most surgeons refrained from treating neurological wounds.Bingham, W. F. (1986). W. W. Keen and the dawn of American neurosurgery. Journal of Neurosurgery, 64(5), 705–712. He als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (, 1743July 4, 1826) was an American Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was the primary author of the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence. Jefferson was the nation's first United States Secretary of State, U.S. secretary of state under George Washington and then the nation's second vice president of the United States, vice president under John Adams. Jefferson was a leading proponent of democracy, republicanism, and Natural law, natural rights, and he produced formative documents and decisions at the state, national, and international levels. Jefferson was born into the Colony of Virginia's planter class, dependent on slavery in the colonial history of the United States, slave labor. During the American Revolution, Jefferson represented Virginia in the Second Continental Congress, which unanimously adopted the Declaration of Independence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robley Dunglison
Robley Dunglison (4 January 1798 – 1 April 1869) was an English-American physician, medical educator and author who served as the first full-time professor of medicine in the United States at the newly founded University of Virginia from 1824 to 1833. He authored multiple medical textbooks and is considered the "Father of American Physiology" after the publication of his landmark textbook ''Human Physiology'' in 1832. He was the personal physician to Thomas Jefferson, James Madison and James Monroe. He consulted in the treatment of Andrew Jackson and was in attendance at Jefferson's death. He served as chair of materia medica, therapeutics, hygiene and medical jurisprudence at the University of Maryland School of Medicine from 1833 to 1836 and chair of the Institutes of Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence at Jefferson Medical College from 1836 to 1868. He assisted William Beaumont in some of his experiments on gastric digestion and published the first description of Huntington' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lea & Febiger
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW) is an American imprint of the American Dutch publishing conglomerate Wolters Kluwer. It was established by the acquisition of Williams & Wilkins and its merger with J.B. Lippincott Company in 1998. Under the LWW brand, Wolters Kluwer, through its Health Division, publishes scientific, technical, and medical content such as textbooks, reference works, and over 275 scientific journals (most of which are medical or other public health journals). Publications are aimed at physicians, nurses, clinicians, and students. Overview LWW grew out of the gradual consolidation of various earlier independent publishers by Wolters Kluwer. Predecessor Wolters Samson acquired Raven Press of New York in 1986. Wolters Samson merged with Kluwer in 1987. The merged company bought J. B. Lippincott & Co. of Philadelphia in 1990; it merged Lippincott with the Raven Press to form Lippincott-Raven in 1995. In 1997 and 1998, Wolters Kluwer acquired Thomson Science (owne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchill Livingstone
Churchill Livingstone is an academic publisher. It was formed in 1971 from the merger of Longman's medical list, E & S Livingstone (Edinburgh, Scotland) and J & A Churchill (London, England) and was owned by Pearson. Harcourt acquired Churchill Livingstone in 1997. It is now integrated as an imprint in Elsevier's health science The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to health sciences: Health sciences – those sciences that focus on health, or health care, as core parts of their subject matter. Health sciences relate to multiple ... division after Elsevier acquired Harcourt in 2001. In the past it published a number of classic medical texts, including Sir William Osler's textbook '' The Principles and Practice of Medicine, Gray's Anatomy,'' and '' Myles' Textbook for Midwives.'' In the 1980s, in addition to new texts in all areas of clinical medicine, it published an extensive list of medical and nursing textbooks in low-cost e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Education
Pearson Education, known since 2011 as simply Pearson, is the educational publishing and services subsidiary of the international corporation Pearson plc. The subsidiary was formed in 1998, when Pearson plc acquired Simon & Schuster's educational business and combined it with Pearson's existing education company Addison-Wesley Longman. Pearson Education was restyled as simply Pearson in 2011. In 2016, the diversified parent corporation Pearson plc rebranded to focus entirely on education publishing and services; further, as of 2023, Pearson Education is Pearson plc's main subsidiary. In 2019, Pearson Education began phasing out the prominence of its hard-copy textbooks in favor of digital textbooks, which cost the company far less, and can be updated frequently and easily. As of 2023, Pearson Education has testing/teaching centers in over 55 countries worldwide; the UK and the U.S. have the most centers. The headquarters of parent company Pearson plc are in London, England. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longman
Longman, also known as Pearson Longman, is a publisher, publishing company founded in 1724 in London, England, which is owned by Pearson PLC. Since 1968, Longman has been used primarily as an imprint by Pearson's Schools business. The Longman brand is also used for the Longman Schools in China and the ''Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, Longman Dictionary''. History Beginnings The Longman company was founded by Thomas Longman (1699–1755), Thomas Longman (1699 – 18 June 1755), the son of Ezekiel Longman (died 1708), a gentleman of Bristol. Thomas was apprenticed in 1716 to John Osborn, a London bookseller, and at the expiration of his apprenticeship married Osborn's daughter. In August 1724, he purchased the stock and household goods of William Taylor (bookseller), William Taylor, the first publisher of ''Robinson Crusoe'', for 9s 6d. Taylor's two shops in Paternoster Row, London, were known respectively as the ''Black Swan (St. Paul's Churchyard), Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making smallpox the only human disease to have been eradicated to date. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was transmitted from one person to another primarily through prolonged face-to-face contact with an infected person or rarely via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medications could poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |