|
Graphite
Graphite () is a Crystallinity, crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked Layered materials, layers of graphene, typically in excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on a large scale (1.3million metric tons per year in 2022) for uses in many critical industries including refractories (50%), lithium-ion batteries (18%), foundries (10%), and lubricants (5%), among others (17%). Graphite converts to diamond under extremely high pressure and temperature. Graphite's low cost, thermal and chemical inertness and characteristic conductivity of heat and electricity finds numerous applications in high energy and high temperature processes. Types and varieties Graphite can occur naturally or be produced synthetically. Natural graphite is obtained from naturally occurring geologic deposits and synthetic graphite is produced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is a carbon allotrope consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, honeycomb planar nanostructure. The name "graphene" is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, indicating the presence of double bonds within the carbon structure. Graphene is known for its exceptionally high Ultimate tensile strength, tensile strength, Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity, Transparency and translucency, transparency, and being the thinnest two-dimensional material in the world. Despite the nearly transparent nature of a single graphene sheet, graphite (formed from stacked layers of graphene) appears black because it absorbs all visible light wavelengths. On a microscopic scale, graphene is the strongest material ever measured. The existence of graphene was first theorized in 1947 by P. R. Wallace, Philip R. Wallace during his research on graphite's electronic properties, while the term ''graphen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium-ion Batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy density, and energy efficiency and a longer cycle life and calendar life than other types of rechargeable batteries. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991; over the following 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold. In late 2024 global demand passed per year, while production capacity was more than twice that. The invention and commercialization of Li-ion batteries has had a large impact on technology, as recognized by the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Li-ion batteries have enabled portable consumer electronics, laptop computers, cellular phones, and electric cars. Li-ion batteries also see significa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) can color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acheson Process
The Acheson process is a method of synthesizing silicon carbide (SiC) and graphite invented by Edward Goodrich Acheson and patented by him in 1896. Process The process consists of heating a mixture of silicon dioxide">Acheson founded the Carbor ... and patented by him in 1896. Process The process consists of heating a mixture of silicon dioxide (SiO2), in the form of silica or quartz sand, and carbon, in its chemical element, elemental form as powdered coke (fuel), coke, in an iron bowl. In the furnace, the silicon dioxide, which sometimes also contains other additives along with ferric oxide and saw dust is melted surrounding a graphite rod, which serves as a core. These rods are inserted in such a way that they are held in contact with each other through the particles of coke, which is commonly called coke bed. An electric current is passed through the graphite rods which heats the mixture to 1700–2500 °C. The result of the carbothermic reaction is a layer of si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphitization
Graphitization is a process of transforming a carbonaceous material, such as coal or the carbon in certain forms of iron alloys, into graphite. Process The graphitization process involves a restructuring of the molecular structure of the carbon material. In the initial state, these materials can have an amorphous structure or a crystalline structure different from graphite. Graphitization generally occurs at high temperatures (up to ), and can be accelerated by catalysts such as iron or nickel. When carbonaceous material is exposed to high temperatures for an extended period of time, the carbon atoms begin to rearrange and form layered crystal planes. In the structure of graphite, carbon atoms are arranged in flat hexagonal sheets that are stacked on top of each other. These crystal planes give graphite its characteristic flake structure, giving it specific properties such as good electrical and thermal conductivity, low friction and excellent lubrication. Interest Graphiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
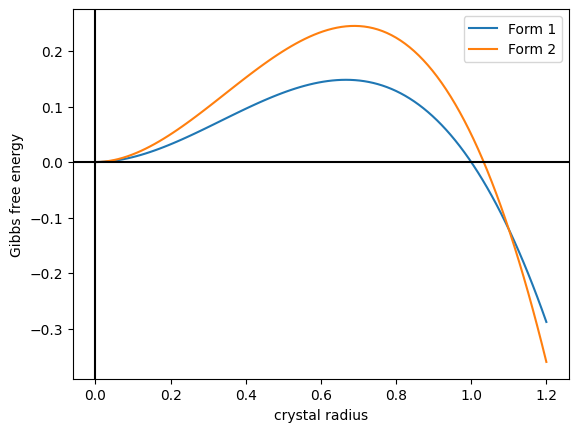
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricants
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking ( oils and fats in use in frying pans and baking to prevent food sticking), to reduce rusting and friction in machinery, through the use of motor oil and grease, bioapplications on humans (e.g., lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better, more efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractories
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the ''refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, or as component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is a type of fossil fuel, formed when dead plant matter decays into peat which is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its Electricity generation, electricity. Some iron and steel-maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedimentation is any process that causes these particles to settle in place. Geological detritus originates from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus is formed by bodies and parts (mainly shells) of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies ( marine snow). Sedimentation may also occur when dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution. The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive (73% of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |