|
Granulomatous Mastitis
Granulomatous mastitis can be divided into idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (also known as granular lobular mastitis) and granulomatous mastitis occurring as a rare secondary complication of a great variety of other conditions such as tuberculosis and other infections, sarcoidosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Special forms of granulomatous mastitis occur as complication of diabetes. Some cases are due to silicone injection ( Silicone-induced granulomatous inflammation) or other foreign body reactions. Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM) is defined as granulomatous mastitis without any other attributable cause such as those above mentioned. It occurs on average two years and, almost exclusively, up to six years after pregnancy, usual age range is 17 to 42 years. Some cases have been reported that were related to drug induced hyperprolactinemia. It has been exceptionally rarely diagnosed during pregnancy and in men. Primary presentation of any of these conditions as mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gynecology
Gynaecology or gynecology (see American and British English spelling differences) is the area of medicine concerned with conditions affecting the Female reproductive system, female reproductive system. It is often paired with the field of obstetrics, which focuses on pregnancy and childbirth, thereby forming the combined area of obstetrics and gynaecology (OB-GYN). Gynaecology encompasses both Primary care, primary and Preventive healthcare, preventative care of issues related to female reproduction and sexual health, such as the uterus, vagina, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and breasts; subspecialties include family planning; minimally invasive surgery; pediatric and adolescent gynecology; and pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery. While gynaecology has traditionally centered on Cisgender, cisgender women, it increasingly encompasses anyone with female organs, including transgender, intersex, and Non-binary gender, nonbinary individuals; however, many non-cis women face acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
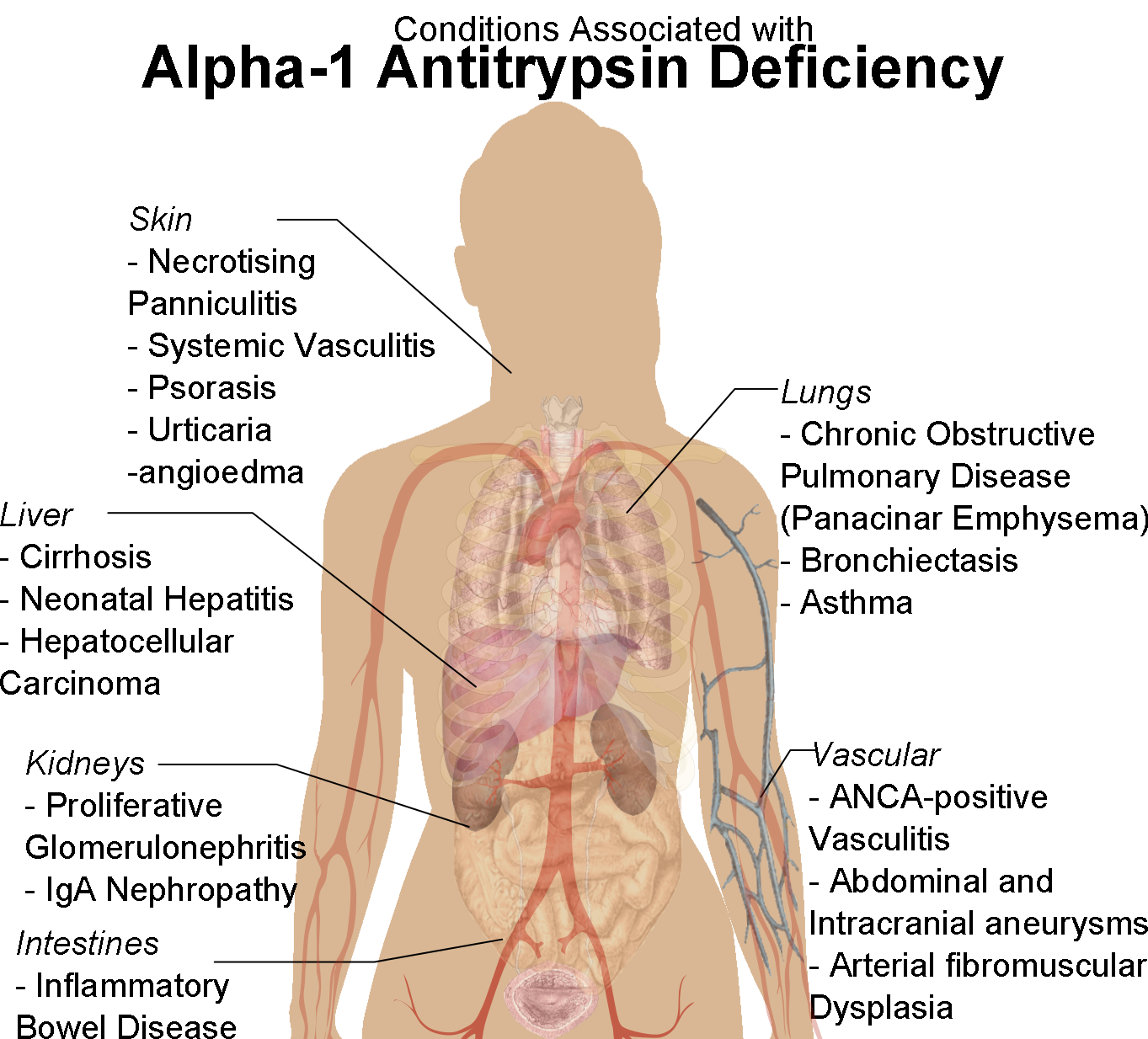
Alpha 1-antitrypsin Deficiency
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency (A1AD or AATD) is a genetic disorder that may result in lung disease or liver disease. Onset of lung problems is typically between 20 and 50 years of age. This may result in shortness of breath, wheezing, or an increased risk of lung infections. Complications may include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cirrhosis, neonatal jaundice, or panniculitis. A1AD is due to a mutation in the SERPINA1 gene that results in not enough alpha-1 antitrypsin (A1AT). Risk factors for lung disease include tobacco smoking and environmental dust. The underlying mechanism involves unblocked neutrophil elastase and buildup of abnormal A1AT in the liver. It is autosomal co-dominant, meaning that one defective allele tends to result in milder deficiency than two defective alleles; for example, carriers with an MS (or SS) allele combination usually produce enough alpha-1 antitrypsin to protect the lungs, while those with MZ alleles have a slightly increase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabergoline
Cabergoline, sold under the brand name Dostinex among others, is a dopaminergic medication used in the treatment of high prolactin levels, prolactinomas, Parkinson's disease, and for other indications. It is taken by mouth. Cabergoline is an ergot derivative and a potent dopamine D2 receptor agonist. Cabergoline was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses * Lactation suppression * HyperprolactinemiaUK electronic Medicines CompendiuDostinex TabletsLast Updated on eMC Dec 23, 2013 * Adjunctive therapy of prolactin-producing pituitary gland tumors (prolactinomas); * Monotherapy of Parkinson's disease in the early phase; * Combination therapy, together with levodopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor such as carbidopa, in progressive-phase Parkinson's disease; * In some countries also: ablactation and dysfunctions associated with hyperprolactinemia (amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, anovu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromocriptine
Bromocriptine, originally marketed as Parlodel and subsequently under many brand names, is an ergoline derivative and dopamine agonist that is used in the treatment of pituitary tumors, Parkinson's disease, hyperprolactinaemia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and, as an adjunct, Diabetes mellitus type 2, type 2 diabetes. It was patented in 1968 and approved for medical use in 1975. Medical uses Bromocriptine is used to treat acromegaly and conditions associated with hyperprolactinemia like amenorrhea, infertility, hypogonadism, and prolactin-secreting adenomas. It is also used to prevent ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome For label updates seFDA index page for NDA 017962 and to treat Parkinson's disease. Since the late 1980s it has been used, off-label, to reduce the symptoms of cocaine withdrawal but the evidence for this use is poor. Bromocriptine has been successfully used in cases of galactorrhea precipitated by dopamine antagonists like risperidone. A quick-release formul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including stress response, immune response, and regulation of inflammation, carbohydrate metabolism, protein catabolism, blood electrolyte levels, and behavior. Some common naturally occurring steroid hormones are cortisol (), corticosterone (), cortisone () and aldosterone () (cortisone and aldosterone are isomers). The main corticosteroids produced by the adrenal cortex are cortisol and aldosterone. The etymology of the '' cortico-'' part of the name refers to the adrenal cortex, which makes these steroid hormones. Thus a corticosteroid is a "cortex steroid". Classes * Glucocorticoids such as cortisol affect carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism, and have anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids are broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/ unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-shaped"). They are widely distributed in nature in the microbiota of animals (including the human microbiota) and are mostly innocuous, most commonly existing in commensal relationships with their hosts. Some, such as '' C. glutamicum'', are commercially and industrially useful. Others can cause human disease, including, most notably, diphtheria, which is caused by '' C. diphtheriae''. Like various species of microbiota (including their relatives in the genera '' Arcanobacterium'' and '' Trueperella''), they are usually not pathogenic, but can occasionally capitalize opportunistically on atypical access to tissues (via wounds) or weakened host defenses. Taxonomy The genus ''Corynebacterium'' was created by Lehmann and Neumann in 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
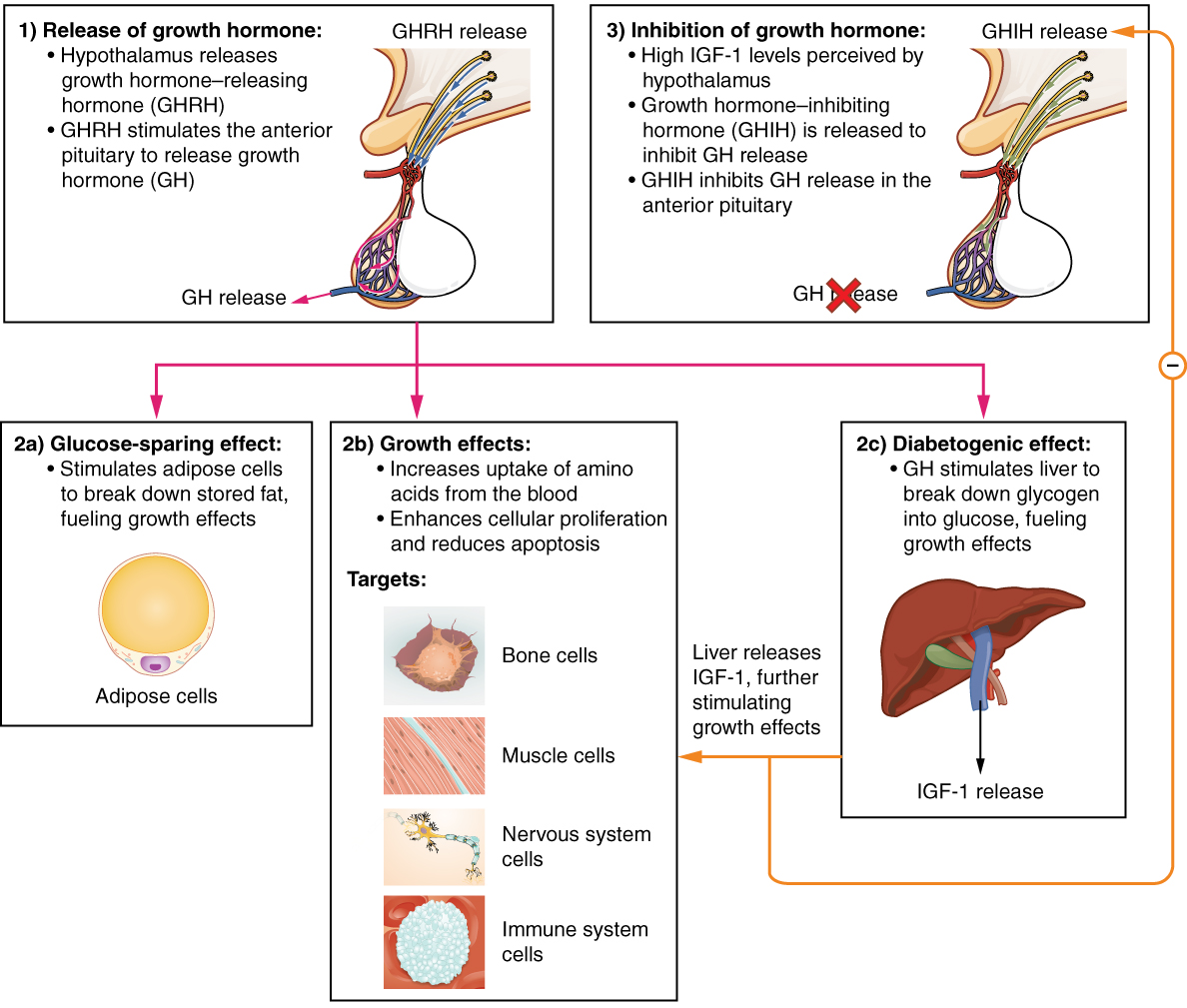
IGF-1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults. In the 1950s IGF-1 was called " sulfation factor" because it stimulated sulfation of cartilage in vitro, and in the 1970s due to its effects it was termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" (NSILA). IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGF1'' gene. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 has a molecular weight of 7,649 daltons. In dogs, an ancient mutation in IGF1 is the primary cause of the toy phenotype. IGF-1 is produced primarily by the liver. Production is stimulated by growth hormone (GH). Most of IGF-1 is bound to one of 6 binding proteins (IGF-BP). IGFBP-1 is regulated by insulin. IGF-1 is produced throughout life; the highest rates of IGF-1 production occur during the pubertal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms. Obesity increases the rate of pre-eclampsia, cesarean sections, and embryo macrosomia, as well as gestational diabetes. Babies born to individuals with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of macrosomia, of having hypoglycemia after birth, and of jaundice. If untreated, diabetes can also result in stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy because of insulin resistance or reduced production of insulin. Risk factors include being overweight, previously having gestational diabetes, a family history of type 2 diabetes, and having polycystic ovarian syndrome. Diagnosis is by blood tests. For those at normal risk, Screening (medicine), screening is recommended betw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological response in which cells in insulin-sensitive tissues in the body fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin or downregulate insulin receptors in response to hyperinsulinemia. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood sugar). Insulin is released by the pancreas in response to carbohydrates consumed in the diet. In states of insulin resistance, the same amount of insulin does not have the same effect on glucose transport and blood sugar levels. There are many causes of insulin resistance and the underlying process is still not completely understood. Risk factors for insulin resistance include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, family history of diabetes, various health conditions, and certain medications. Insulin resistance is considered a component of the metabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance can be improved or reversed with lifestyle approaches, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |