|
Gottesman–Kitaev–Preskill Code
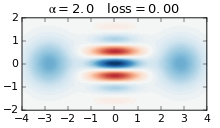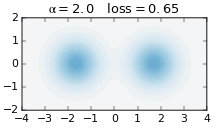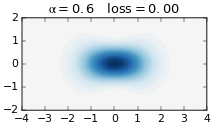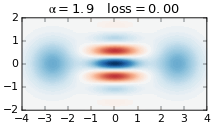
The Gottesman–Kitaev–Preskill (GKP) code is a quantum error correcting code that encodes logical qubits into the continuous degrees of freedom of a quantum system. It is named after Daniel Gottesman, Alexei Kitaev and John Preskill who published it together in 2001. The code is used in continuous variable (CV) photonic quantum computing, in which logical qubits are encoded into the field quadratures of an optical mode. This modes can be thought of as the quantum harmonic oscillator with conjugate position and momentum operators. By encoding logical qubits into a single optical mode, the GKP code demonstrates greater hardware efficiency than traditional qubit codes. Instead of needing many qubits to act as redundancy for a single qubit, the GKP code instead requires a precisely constructed optical state. GKP codes are able to protect against both small shifts in the quadratures, but also loss channels such as photon loss in a photonic system. Overview GKP codes protects ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Error Correction
Quantum error correction (QEC) is a set of techniques used in quantum computing to protect quantum information from errors due to decoherence and other quantum noise. Quantum error correction is theorised as essential to achieve fault tolerant quantum computing that can reduce the effects of noise on stored quantum information, faulty quantum gates, faulty quantum state preparation, and faulty measurements. Effective quantum error correction would allow quantum computers with low qubit fidelity to execute algorithms of higher complexity or greater circuit depth. Classical error correction often employs redundancy. The simplest albeit inefficient approach is the repetition code. A repetition code stores the desired (logical) information as multiple copies, and—if these copies are later found to disagree due to errors introduced to the system—determines the most likely value for the original data by majority vote. For instance, suppose we copy a bit in the one (on) state thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherent State
In physics, specifically in quantum mechanics, a coherent state is the specific quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator, often described as a state that has dynamics most closely resembling the oscillatory behavior of a classical harmonic oscillator. It was the first example of quantum dynamics when Erwin Schrödinger derived it in 1926, while searching for solutions of the Schrödinger equation that satisfy the correspondence principle. The quantum harmonic oscillator (and hence the coherent states) arise in the quantum theory of a wide range of physical systems.J.R. Klauder and B. Skagerstam, ''Coherent States'', World Scientific, Singapore, 1985. For instance, a coherent state describes the oscillating motion of a particle confined in a quadratic potential well (for an early reference, see e.g. Schiff's textbook). The coherent state describes a state in a system for which the ground-state wavepacket is displaced from the origin of the system. This state can be relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanadu Quantum Technologies
Xanadu Quantum Technologies is a Canadian quantum computing hardware and software company headquartered in Toronto, Ontario. The company develops cloud accessible photonic quantum computers and develops open-source software for quantum machine learning and simulating quantum photonic devices. History Xanadu was founded in 2016 by Christian Weedbrook and was a participant in the Creative Destruction Lab's accelerator program. Since then, Xanadu has raised a total of US$245M in funding with venture capital financing from Bessemer Venture Partners, Capricorn Investment Group, Tiger Global Management, In-Q-Tel, Business Development Bank of Canada, OMERS Ventures, Georgian, Real Ventures, Golden Ventures and Radical Ventures and innovation grants from Sustainable Development Technology Canada and DARPA. Technology Xanadu's hardware efforts have been focused on developing programmable Gaussian boson sampling (GBS) devices. GBS is a generalization of boson sampling, which tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homodyne Detection
In electrical engineering, homodyne detection is a method of extracting information encoded as modulation of the phase and/or frequency of an oscillating signal, by comparing that signal with a standard oscillation that would be identical to the signal if it carried null information. "Homodyne" signifies a single frequency, in contrast to the dual frequencies employed in heterodyne detection. When applied to processing of the reflected signal in remote sensing for topography, homodyne detection lacks the ability of heterodyne detection to determine the size of a static discontinuity in elevation between two locations. (If there is a path between the two locations with smoothly changing elevation, then homodyne detection may in principle be able to track the signal phase along the path if sampling is dense enough). Homodyne detection is more readily applicable to velocity sensing. In optics In optical interferometry, homodyne signifies that ''the reference radiation'' (i.e. the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Splitter
A beam splitter or beamsplitter is an optical instrument, optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as Interferometry, interferometers, also finding widespread application in fibre optic telecommunications. Designs In its most common form, a cube, a beam splitter is made from two triangular glass prism (optics), prisms which are glued together at their base using polyester, epoxy, or urethane-based adhesives. (Before these synthetic resins, natural ones were used, e.g. Canada balsam.) The thickness of the resin layer is adjusted such that (for a certain wavelength) half of the light incident through one "port" (i.e., face of the cube) is reflection (physics), reflected and the other half is transmitted due to Total internal reflection#Frustrated_TIR, FTIR (frustrated total internal reflection). polarizer, Polarizing beam splitters, such as the Wollaston prism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boson Sampling
Boson sampling is a restricted model of non-universal quantum computation introduced by Scott Aaronson and Alex Arkhipov after the original work of Lidror Troyansky and Naftali Tishby, that explored possible use of boson scattering to evaluate expectation values of permanents of matrices. The model consists of sampling from the probability distribution of identical bosons scattered by a linear interferometer. Although the problem is well defined for any bosonic particles, its photonic version is currently considered as the most promising platform for a scalable implementation of a boson sampling device, which makes it a non-universal approach to linear optical quantum computing. Moreover, while not universal, the boson sampling scheme is strongly believed to implement computing tasks that are hard to implement with classical computers by using far fewer physical resources than a full linear-optical quantum computing setup. This advantage makes it an ideal candidate for demonstrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat State
In quantum mechanics, the cat state, named after Schrödinger's cat, refers to a quantum state composed of a superposition of two other states of flagrantly contradictory aspects. Generalizing Schrödinger's thought experiment, any other quantum superposition of two macroscopically distinct states is also referred to as a cat state. A cat state could be of one or more modes or particles, therefore it is not necessarily an entangled state. Such cat states have been experimentally realized in various ways and at various scales. Oftentimes this superposition is described as the system being at ''both'' ''states'' ''at the same time'', such as the possibilities that a cat would be alive and dead at the same time. This description, however popular, is not correct, since some Neutron interferometer, experimental results depend on the interference of superposed states. For instance, in the well-known double-slit experiment, superposed states give interference fringes, whereas, had the part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
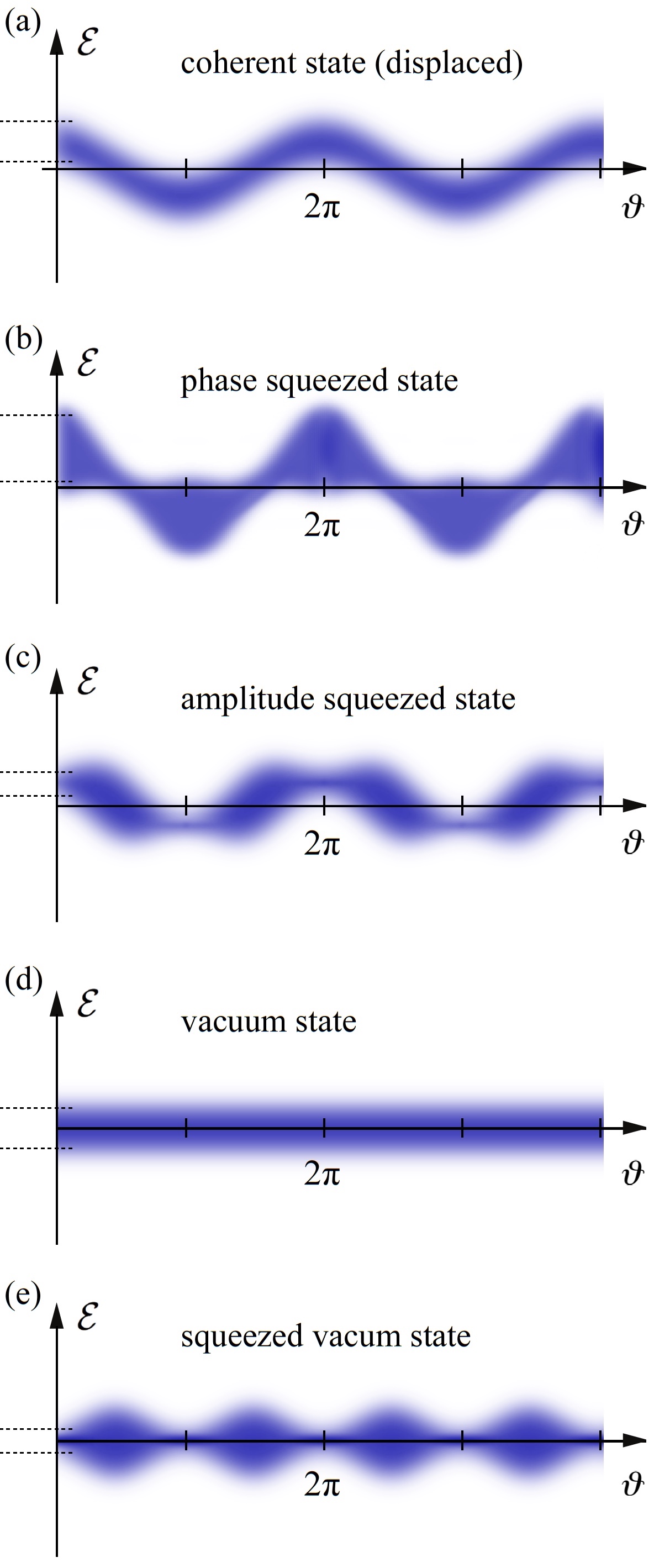
Squeezed States Of Light
In quantum physics, light is in a ''squeezed state'' if its electric field strength ''Ԑ'' for some phases \vartheta has a quantum uncertainty smaller than that of a coherent state. The term ''squeezing'' thus refers to a reduced quantum uncertainty. To obey Heisenberg's uncertainty relation, a squeezed state must also have phases at which the electric field uncertainty is ''anti-squeezed'', i.e. larger than that of a coherent state. Since 2019, the gravitational-wave observatories LIGO and Virgo employ ''squeezed'' laser light, which has significantly increased the rate of observed gravitational-wave events. Quantum physical background An oscillating physical quantity cannot have precisely defined values at all phases of the oscillation. This is true for the electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave, as well as for any other wave or oscillation (see figure right). This fact can be observed in experiments and is described by quantum theory. For electromagnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirac Comb
In mathematics, a Dirac comb (also known as sha function, impulse train or sampling function) is a periodic function, periodic Function (mathematics), function with the formula \operatorname_(t) \ := \sum_^ \delta(t - k T) for some given period T. Here ''t'' is a real variable and the sum extends over all integers ''k.'' The Dirac delta function \delta and the Dirac comb are Distribution_(mathematics)#Tempered_distributions_and_Fourier_transform, tempered distributions. The graph of the function resembles a comb (with the \deltas as the comb's ''teeth''), hence its name and the use of the comb-like Cyrillic script, Cyrillic letter Sha (Cyrillic), sha (Ш) to denote the function. The symbol \operatorname\,\,(t), where the period is omitted, represents a Dirac comb of unit period. This implies \operatorname_(t) \ = \frac\operatorname\ \!\!\!\left(\frac\right). Because the Dirac comb function is periodic, it can be represented as a Fourier series based on the Dirichlet kernel: \o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pauli Matrices
In mathematical physics and mathematics, the Pauli matrices are a set of three complex matrices that are traceless, Hermitian, involutory and unitary. Usually indicated by the Greek letter sigma (), they are occasionally denoted by tau () when used in connection with isospin symmetries. \begin \sigma_1 = \sigma_x &= \begin 0&1\\ 1&0 \end, \\ \sigma_2 = \sigma_y &= \begin 0& -i \\ i&0 \end, \\ \sigma_3 = \sigma_z &= \begin 1&0\\ 0&-1 \end. \\ \end These matrices are named after the physicist Wolfgang Pauli. In quantum mechanics, they occur in the Pauli equation, which takes into account the interaction of the spin of a particle with an external electromagnetic field. They also represent the interaction states of two polarization filters for horizontal/vertical polarization, 45 degree polarization (right/left), and circular polarization (right/left). Each Pauli matrix is Hermitian, and together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stabilizer Code
Stabilizer, stabiliser, stabilisation or stabilization may refer to: Chemistry and food processing * Stabilizer (chemistry), a substance added to prevent unwanted change in state of another substance ** Polymer stabilizers are stabilizers used specifically in plastic or other polymers * Stabilizer (food), a type of food additive * Wood stabilization, a wood preservation process to prevent distortion caused by moisture * Clarification and stabilization of wine Mathematics * Stabilization (category theory) * Stabilizer subgroup Technology * Buoyancy compensator (diving) adjusts buoyancy. * Stabilizer (aircraft), surfaces to help keep aircraft under control. Includes: ** Vertical stabilizer of airplanes ** Tailplane or horizontal stabilizer * Stabilizer (ship), fins on ships to counteract roll * Stabilizer, another name for bicycle training wheels * Stabilizers, the extendable legs mounted on a land vehicle which are folded out when stabilization is required; see Outrigger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Vacuum State
In quantum field theory, the quantum vacuum state (also called the quantum vacuum or vacuum state) is the quantum state with the lowest possible energy. Generally, it contains no physical particles. However, the quantum vacuum is not a simple empty space, but instead contains fleeting electromagnetic waves and particles that pop into and out of the quantum field. The QED vacuum of quantum electrodynamics (or QED) was the first vacuum of quantum field theory to be developed. QED originated in the 1930s, and in the late 1940s and early 1950s, it was reformulated by Feynman, Tomonaga, and Schwinger, who jointly received the Nobel prize for this work in 1965. For a historical discussion, see for example For the Nobel prize details and the Nobel lectures by these authors, see Today, the electromagnetic interactions and the weak interactions are unified (at very high energies only) in the theory of the electroweak interaction. The Standard Model is a generalization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |