|
Golay Detector
The Golay cell is a type of opto-acoustic detector mainly used for infrared spectroscopy. It consists of a gas-filled enclosure with an infrared absorbing material and a flexible diaphragm or membrane. When infrared radiation is absorbed, it heats the gas, causing it to expand. The resulting increase in pressure deforms the membrane. Light reflected off the membrane is detected by a photodiode A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ..., and motion of the membrane produces a change in the signal on the photodiode. The concept was originally described in 1947 by Marcel J. E. Golay, after whom it came to be named. The Golay cell has high sensitivity and a flat response over a very broad range of frequencies. The response time is modest, of order 10 ms. The detector performanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Golay Cell Schematic
{{disam ...
Golay may refer to: * Jeanne Golay (born 1962), bicycle professional * Helen Golay (born 1931), American woman who murdered two homeless men for life insurance money * Marcel J. E. Golay (1902–1989), mathematician, physicist and information theorist * Dolphy (1928-2012), Filipino actor and comedian, used Golay as his screen name in 1944. Several devices and systems were named after Marcel J. E. Golay: * Golay cell, a detector for infrared spectroscopy * Savitzky–Golay filter, a signal processing filter * Binary Golay code, an error-correcting code * Ternary Golay code, an error-correcting code Places: * Golay, Kutch, a village in Kutch, Gujarat, India See also * Gola (other) * Golay code (other) Golay code may refer to: * Binary Golay code, an error-correcting code used in digital communications * Ternary Golay code * (Golay) complementary sequences : ''For complementary sequences in biology, see complementarity (molecular biology). For i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Diaphragm (mechanical Device)
In mechanics, a diaphragm is a sheet of a semi-flexible material anchored at its periphery and most often round in shape. It serves either as a barrier between two chambers, moving slightly up into one chamber or down into the other depending on differences in pressure, or as a device that vibrates when certain frequencies are applied to it. A diaphragm pump uses a diaphragm to pump a fluid. A typical design is to have air on one side constantly vary in pressure, with fluid on the other side. The increase and decrease in volume caused by the action of the diaphragm alternately forces fluid out the chamber and draws more fluid in from its source. The action of the diaphragm is very similar to the action of a plunger with the exception that a diaphragm responds to changes in pressure rather than the mechanical force of the shaft. A diaphragm pressure tank is a tank which has pressurant sealed inside on one side of the diaphragm. It is favored in certain applications due to its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and even by industry. Further, both spellings are often used ''within'' a particular industry or country. Industries in British English-speaking countries typically use the "gauge" spelling. is the pressure relative to the ambient pressure. Various #Units, units are used to express pressure. Some of these derive from a unit of force divided by a unit of area; the International System of Units, SI unit of pressure, the Pascal (unit), pascal (Pa), for example, is one newton (unit), newton per square metre (N/m2); similarly, the Pound (force), pound-force per square inch (Pound per square inch, psi, symbol lbf/in2) is the traditional unit of pressure in the imperial units, imperial and United States customary units, US customary systems. Pressure ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers. Principle of operation A photodiode is a PIN diode, PIN structure or p–n junction. When a photon of sufficient energy strikes the diode, it creates an electron–electron hole, hole pair. This mechanism is also known as the inner photoelectric effect. If the absorption occurs in the junction's depletion region, or one diffusion length away from it, these carriers are swept from the junction by the built-in electric field of the depletion region. Thus holes move toward the anode, and electrons toward the cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Marcel J
Marcel may refer to: People * Marcel (given name), people with the given name Marcel * Marcel (footballer, born August 1981), Marcel Silva Andrade, Brazilian midfielder * Marcel (footballer, born November 1981), Marcel Augusto Ortolan, Brazilian striker * Marcel (footballer, born 1983), Marcel Silva Cardoso, Brazilian left back * Marcel (footballer, born 1992), Marcel Henrique Garcia Alves Pereira, Brazilian midfielder * Marcel (singer), American country music singer * Étienne Marcel (died 1358), provost of merchants of Paris * Gabriel Marcel (1889–1973), French philosopher, Christian existentialist and playwright * Jean Marcel (died 1980), Madagascan Anglican bishop * Jean-Jacques Marcel (1931–2014), French football player * Rosie Marcel (born 1977), English actor * Sylvain Marcel (born 1974), Canadian actor * Terry Marcel (born 1942), British film director * Claude Marcel (1793-1876), French diplomat and applied linguist Other uses * Marcel (''Friends''), a fic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
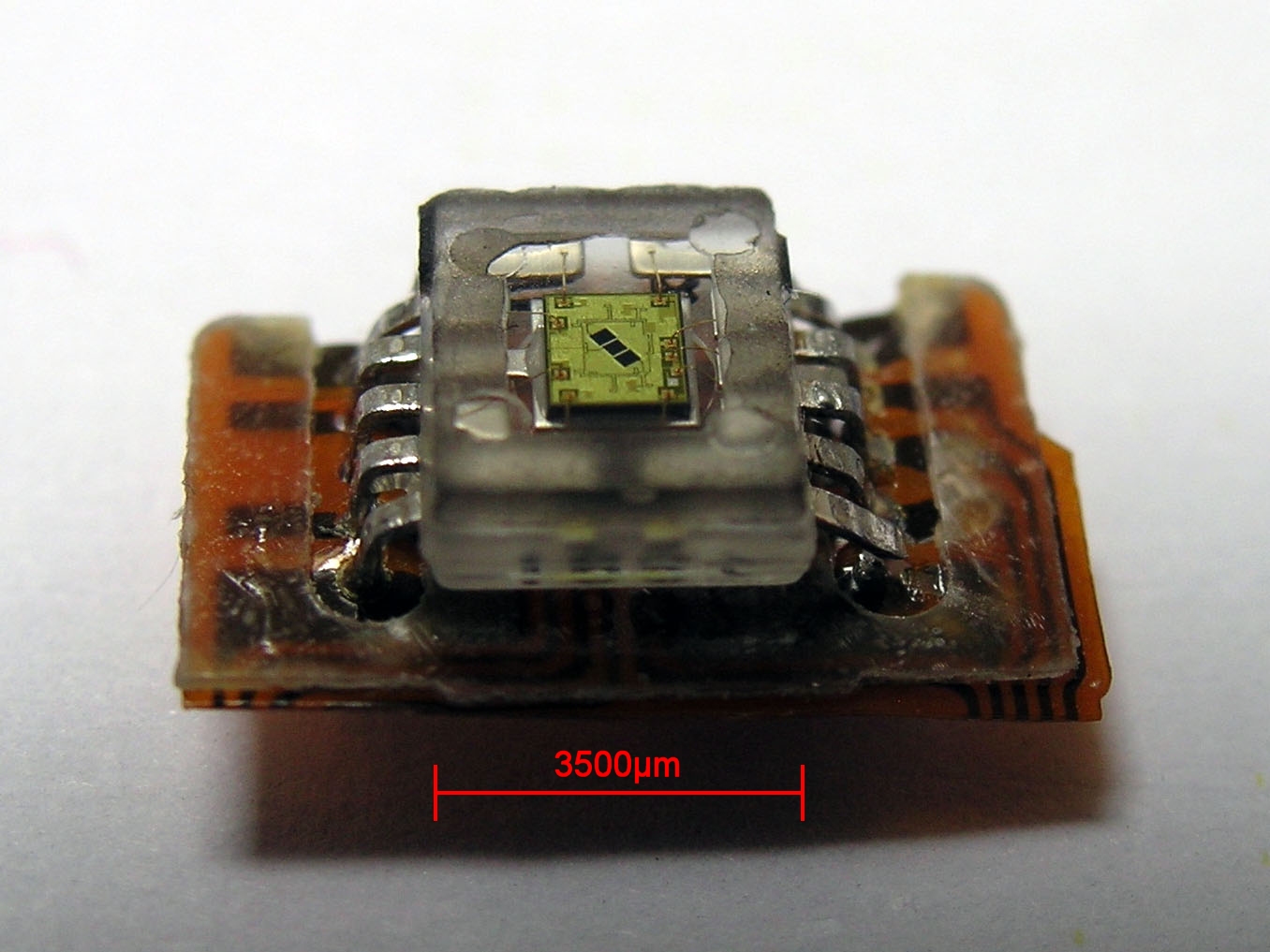 |
Photodetectors
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical communication to scientific research and industrial automation. Photodetectors can be classified by their mechanism of detection, such as the photoelectric effect, photochemical reactions, or thermal effects, or by performance metrics like spectral response. Common types include photodiodes, phototransistors, and photomultiplier tubes, each suited to specific uses. Solar cells, which convert light into electricity, are also a type of photodetector. This article explores the principles behind photodetectors, their various types, applications, and recent advancements in the field. History The development of photodetectors began with the discovery of the photoelectric effect by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, later explained by Albert Einstein i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |