|
Goatsucker Records
Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called bugeaters, their primary source of food being insects. Some New World species are called nighthawks. The English word ''nightjar'' originally referred to the European nightjar. Nightjars are found all around the world, with the exception of Antarctica, and certain island groups such as the Seychelles. They can be found in a variety of habitats, most commonly the open country with some vegetation. They usually nest on the ground, with a habit of resting and roosting on roads. The subfamilies of nightjars have similar characteristics, including small feet, of little use for walking, and long, pointed wings. Typical nightjars have rictal bristles, longer bills, and softer plumage. The colour of their plumage and their unusual perching habits help conceal them during the day. Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Eared Nightjar
The great eared nightjar (''Lyncornis macrotis'') is a species of nightjar in the family Caprimulgidae. It is found in southwest India and in parts of Southeast Asia. This very large nightjar has long barred wings, a barred tail and long ear-tufts which are often recumbent. It has a white throat band but has no white on its wings or on its tail. Taxonomy The great eared nightjar was formally described in 1831 by the Irish zoologist Nicholas Aylward Vigors based on a sample collected in the neighbourhood of Manila in the Philippines. Vigors coined the binomial name ''Caprimulgus macrotis''. The great eared nightjar was formerly placed in the genus ''Eurostopodus''. It and the closely related Malaysian eared nightjar were moved to the resurrected genus '' Lyncornis'' based on the results of a molecular phylogenetic study published in 2010 that found large genetic differences between the great eared nightjar and other species in ''Eurostopodus''. The genus name ''Lyncornis'' combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potoo
Potoos (family (biology), family Nyctibiidae) are a group of birds related to the nightjars and frogmouths. They are sometimes called poor-me-ones, after their haunting bird vocalization, calls. The family Nyctibiidae was formerly included with the nightjars in the order Caprimulgiformes but is now placed in a separate order, Nyctibiiformes. There are seven species in two genera in tropical Central America, Central and South America. Fossil evidence indicates that they also inhabited Europe during the Paleogene. Potoos are nocturnal insectivores that lack the bristles around the mouth found in the true nightjars. They hunt from a perch like a shrike or Old World flycatcher, flycatcher. During the day they perch upright on tree stumps, camouflaged to look like part of the stump. The single spotted egg is laid directly on the top of a stump. In Argentina, they are known as kakuy or cacuy from Quechua language, Quechua meaning 'to remain'. In Bolivia they are called ''guajojo'', fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jon E
Jonathan Whyte Potter-Mäl (born February 19, 1986), known by his stage name Jonathan Emile (or Jon E), is a Jamaican Canadian singer, rapper, record producer and cancer survivor. In October 2015, he released his debut studio album, ''The Lover/Fighter Document LP'', which incorporates elements of hip hop, reggae, jazz, R&B and electro-pop. The independent album features collaborations with Kendrick Lamar, Murs, Buckshot and others. His debut reggae album, ''Spaces-in-Between'', was released in January 2020 through his label MindPeaceLove and Tuff Gong. Life and career Early life and cancer years Jonathan Whyte Potter-Mäl was born on February 19, 1986, in the LaSalle borough of Montreal, Quebec, to a Canadian and half-American father and a Jamaican mother. He graduated from Selwyn House School in 2003. Emile was trained at the Black Theatre Workshop youth initiative in Montreal. During and after his cancer treatment, he independently developed his knowledge on studio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Sibley
Charles Gald Sibley (August 7, 1917 – April 12, 1998) was an American ornithologist and molecular biologist. He had an immense influence on the scientific classification of birds, and the work that Sibley initiated has substantially altered our understanding of the evolutionary history of modern birds. Sibley's taxonomy has been a major influence on the sequences adopted by ornithological organizations, especially the American Ornithologists' Union. Life and work Educated in California (A.B. 1940; Ph.D. 1948 in Zoology, University of California, Berkeley. Minor fields: Paleontology, Botany), he did his first fieldwork in Mexico in 1939 and 1941, then in Solomon Islands, Bismarck Archipelago, New Guinea, and the Philippines during World War II while on leave from the U.S. Navy, in which he was Ensign to Lieutenant in the Communications and Medical Service Corps. He was based for much of the war at Emirau Island, in what is now New Ireland Province of Papua New Guinea. His first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiological And Biochemical Zoology
''Ecological and Evolutionary Physiology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Society for Integrative and Comparative Biology. The journal publishes original research examining fundamental questions about how the ecological environment and/or evolutionary history interact with physiological function, as well as the ways physiology may constrain behavior. For ''EEP'', physiology denotes the study of function in the broadest sense, across levels of organization from molecules to morphology to organismal performance and on behavior and life history traits. Subdisciplines and topics covered by the journal include comparative physiology, biomechanics and functional morphology, behavioral endocrinology, ecoimmunology, ecotoxicology, ecomorphology, phenotypic plasticity, energetics, allometry and scaling, animal locomotion and muscle function, physiological foundations of behavior, physiological genetics and genomics, indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Poorwill
The common poorwill (''Phalaenoptilus nuttallii'') is a nocturnal bird of the family Caprimulgidae, the nightjars. It is found from British Columbia and southeastern Alberta, through the western United States to northern Mexico. The bird's habitat is dry, open areas with grasses or shrubs, and even stony desert slopes with very little vegetation. Many northern birds migrate to winter within the breeding range in central and western Mexico, though some remain further north. The common poorwill is the only bird known to go into torpor for extended periods (weeks to months). This happens on the southern edge of its range in the United States, where it spends much of the winter inactive, concealed in piles of rocks. Such an extended period of torpor is close to a state of hibernation and is not known among other birds. Taxonomy The common poorwill was illustrated and formally described in 1844 by the ornithologist John James Audubon from a male specimen collected on the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypsis
In ecology, crypsis is the ability of an animal or a plant to avoid observation or detection by other animals. It may be part of a predation strategy or an antipredator adaptation. Methods include camouflage, nocturnality, subterranean lifestyle and mimicry. Crypsis can involve visual, olfactory (with pheromones) or auditory concealment. When it is visual, the term cryptic coloration, effectively a synonym for animal camouflage, is sometimes used, but many different methods of camouflage are employed in nature. Overview There is a strong evolutionary pressure for prey animals to avoid predators through camouflage, and for predators to be able to detect camouflaged prey. There can be a self-perpetuating coevolution, in the shape of an evolutionary arms race, between the perceptive abilities of animals attempting to detect the cryptic animal and the cryptic characteristics of the hiding species. Methods Methods of crypsis include (visual) camouflage, nocturnality, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
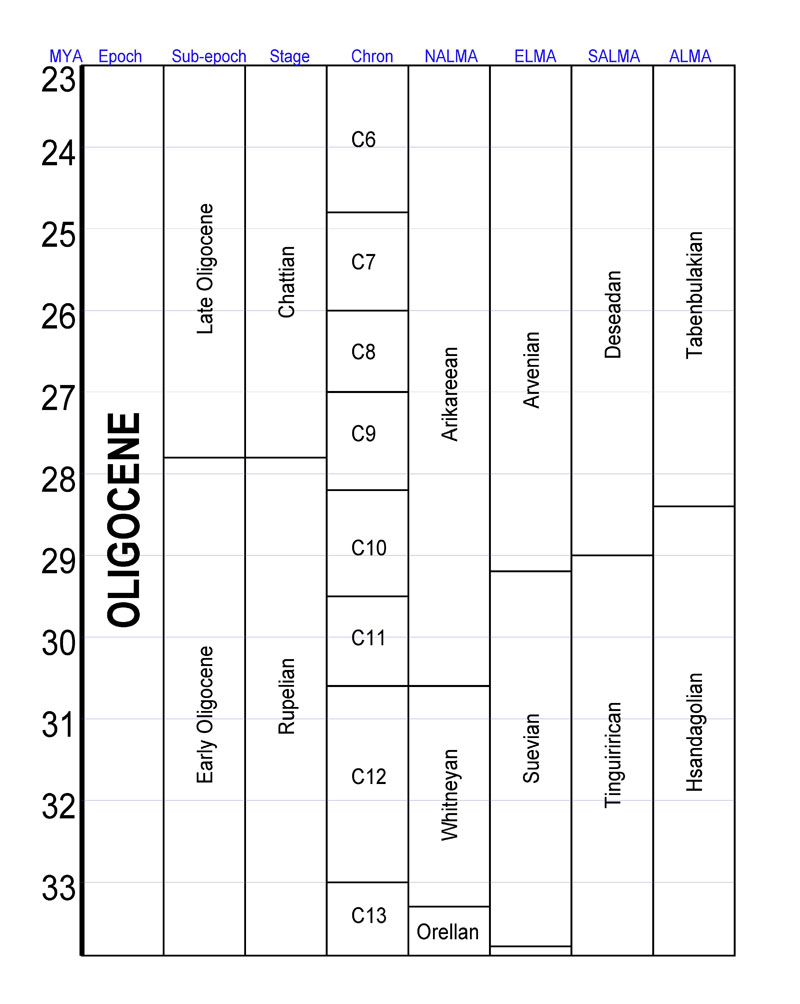
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from Ancient Greek (''olígos'') 'few' and (''kainós'') 'new', and refers to the sparsity of Neontology, extant forms of Mollusca, molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', 'Eos, Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeotrogonidae
Archaeotrogonidae is a prehistoric bird family known from the Eocene and Oligocene of Europe. They are members of Strisores, and are thought to be closely related to nightjars. The remains of '' Archaeotrogon'' have been found in the Quercy Phosphorites of France, a geological formation containing Late Eocene and Early Oligocene deposits. They are primarily known from limb bones. Four species are presently considered valid. The Middle Eocene '' Hassiavis'', a more recently described bird from the famous Messel Pit in Germany, is also a member of the family. In 2021, a new genus, '' Archaeodromus'' was described from fossils found in the Early Eocene (Ypresian) aged London Clay, which are the oldest representatives of the family. They were initially thought be prehistoric trogon. However, it is nowadays generally believed that they are not very closely related to these tropical forest birds of our time, but rather convergent. The Archaeotrogonidae actually seem to be Cypselomor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strisores
Strisores ( ), sometimes called nightbirds, is a clade of birds that includes the living family (biology), families and order (biology), orders Caprimulgidae (nightjars, nighthawks and allies), Nyctibiidae (potoos), Steatornithidae (oilbirds), Podargidae (frogmouths), Apodiformes (swifts and hummingbirds), as well as the Aegotheliformes (owlet-nightjars) whose distinctness was only recently realized. The Apodiformes (which include the "Trochiliformes" of the Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy) and the Aegotheliformes form the Apodimorphae, Daedalornithes. Description The material evidence for this group is very equivocal; the most ancient Strisores are quite nondescript tree-dwellers but already tend towards peculiarly apomorphic feet, and no Cretaceous fossils are known. Torpor and other metabolic peculiarities are frequently found in this group, perhaps more often than in any other bird lineage. The synapomorphies that define this clade are the ''ossa maxillaria'' separated by a large c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |