|
Glutamic Protease
Glutamic proteases are a group of proteolytic enzymes containing a glutamic acid residue within the active site. This type of protease was first described in 2004 and became the sixth catalytic type of protease. Members of this group of protease had been previously assumed to be an aspartate protease, but structural determination showed it to belong to a novel protease family. The first structure of this group of protease was scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the active site of which contains a catalytic dyad, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), which give rise to the name eqolisin. This group of proteases are found primarily in pathogenic fungi affecting plant and human. Distribution and types There are two independent families of glutamic proteases (G1 and G2), and have a limited distribution. They were originally thought to be limited to filamentous fungi mainly in the Ascomycota phylum. Subsequently, however, glutamic proteases have been identified in bacteria and archaea. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
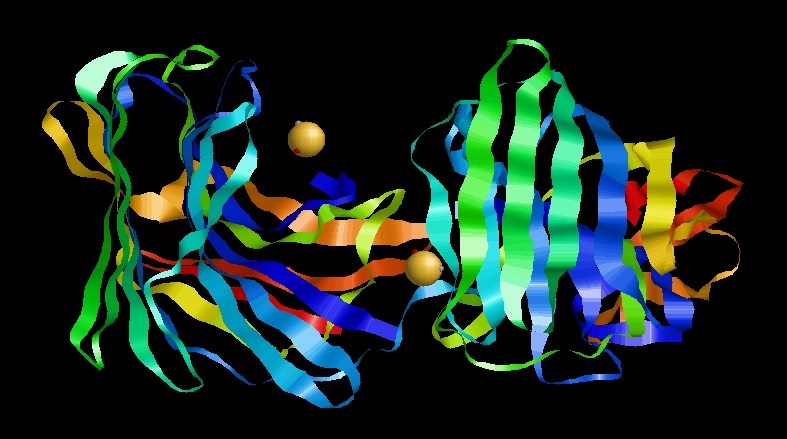
Scytalidoglutamic Peptidase
Scytalidocarboxyl peptidase B, also known as Scytalidoglutamic peptidase and Scytalidopepsin B (, obsolete names include ''Scytalidium aspartic proteinase B'', ''Ganoderma lucidum carboxyl proteinase'', ''Ganoderma lucidum aspartic proteinase'', ''Scytalidium lignicolum aspartic proteinase B'', ''SLB'') is a proteolytic enzyme. It was previously thought to be an aspartic protease, but determination of its molecular structure showed it to belong a novel group of proteases, glutamic protease. The protease has a unique structure and a novel catalytic dyad (E136 and Q53) in its active site. The active-site residues, glutamic acid (E) and glutamine (Q), was used to coin the name of the family of proteases, eqolisins, to which Scytalidoglutamic peptidase B belongs. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : Hydrolysis of proteins with broad specificity, cleaving Phe24-Phe and Tyr26–Thr but not Leu15-Tyr and Phe25-Tyr in the B chain of insulin. It also cleaves the His6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of '' Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartic Protease
Aspartic proteases are a catalytic type of protease enzymes that use an activated water molecule bound to one or more aspartate residues for catalysis of their peptide substrates. In general, they have two highly conserved aspartates in the active site and are optimally active at acidic pH. Nearly all known aspartyl proteases are inhibited by pepstatin. Aspartic endopeptidases of vertebrate, fungal and retroviral origin have been characterised. More recently, aspartic endopeptidases associated with the processing of bacterial type 4 prepilin and archaean preflagellin have been described. Eukaryotic aspartic proteases include pepsins, cathepsins, and renins. They have a two-domain structure, arising from ancestral duplication. Retroviral and retrotransposon proteases (retroviral aspartyl proteases) are much smaller and appear to be homologous to a single domain of the eukaryotic aspartyl proteases. Each domain contributes a catalytic Asp residue, with an extended active ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, polar amino acid. It is non-essential and conditionally essential in humans, meaning the body can usually synthesize sufficient amounts of it, but in some instances of stress, the body's demand for glutamine increases, and glutamine must be obtained from the diet. It is encoded by the codons CAA and CAG. In human blood, glutamine is the most abundant free amino acid. The dietary sources of glutamine include especially the protein-rich foods like beef, chicken, fish, dairy products, eggs, vegetables like beans, beets, cabbage, spinach, carrots, parsley, vegetable juices and also in wheat, papaya, Brussels sprouts, celery, kale and fermented foods like miso. Functions Glutamine plays a role in a variety of biochemical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine Protease
Serine proteases (or serine endopeptidases) are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 16 superfamilies (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evolution of the catalytic mechanism. The majority belong to the S1 family of the PA clan (superfamily) of proteases. For superfamilies, P: superfamily, containing a mixture of nucleophile class families, S: purely serine proteases. superfamily. Within each superfamily, families are designated by their catalytic nucleophile, (S: serine proteases). Substrate specificity Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepstatin
Pepstatin is a potent inhibitor of aspartyl proteases. It is a hexa-peptide containing the unusual amino acid statine (Sta, (3S,4S)-4-amino-3-hydroxy-6-methylheptanoic acid), having the sequence Isovaleryl-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta (Iva-Val-Val-Sta-Ala-Sta). It was originally isolated from cultures of various species of Actinomyces due to its ability to inhibit pepsin at picomolar concentrations. Pepstatin A is well known to be an inhibitor of aspartic proteases such as pepsin, cathepsins D and E. Except for its role as a protease inhibitor, however, the pharmacological action of pepstatin A upon cells remain unclear. Pepstatin A suppresses receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)–induced osteoclast differentiation. Pepstatin A suppresses the formation of multinuclear osteoclasts dose-dependently. This inhibition of the formation only affected osteoclast cells, i.e., not osteoblast-like cells. Furthermore, pepstatin A also suppresses differentiation from pre-osteoclast cells to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily related proteins. In many cases, a protein family has a corresponding gene family, in which each gene encodes a corresponding protein with a 1:1 relationship. The term "protein family" should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy. Proteins in a family descend from a common ancestor and typically have similar three-dimensional structures, functions, and significant sequence similarity. The most important of these is sequence similarity (usually amino-acid sequence), since it is the strictest indicator of homology and therefore the clearest indicator of common ancestry. A fairly well developed framework exists for evaluating the significance of similarity between a group of sequences using sequence alignment methods. Proteins that do not share a common ancestor are very unlikely to show statistically significant sequence similarity, making sequence alignment a powerful tool for identifying the members of protein families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspergilloglutamic Peptidase
Aspergilloglutamic peptidase, also called aspergillopepsin II (, ''proctase A'', '' Aspergillus niger acid proteinase A'', ''Aspergillus niger var. macrosporus aspartic proteinase'') is a proteolytic enzyme. The enzyme was previously thought be an aspartic protease, but it was later shown to be a glutamic protease with a catalytic Glu residue at the active site, and was therefore renamed aspergilloglutamic peptidase. Determination of its molecular structure showed it to be a unique two-chain enzyme with a light chain and a heavy chain bound non-covalently with each other. The C-terminal region of the light chain of one molecule binds to the active site cleft of another molecule in the manner of a substrate. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : Preferential cleavage in B chain of insulin: Asn3-Gln, Gly13-Ala, Tyr26-Thr This enzyme is isolated from ''Aspergillus niger ''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
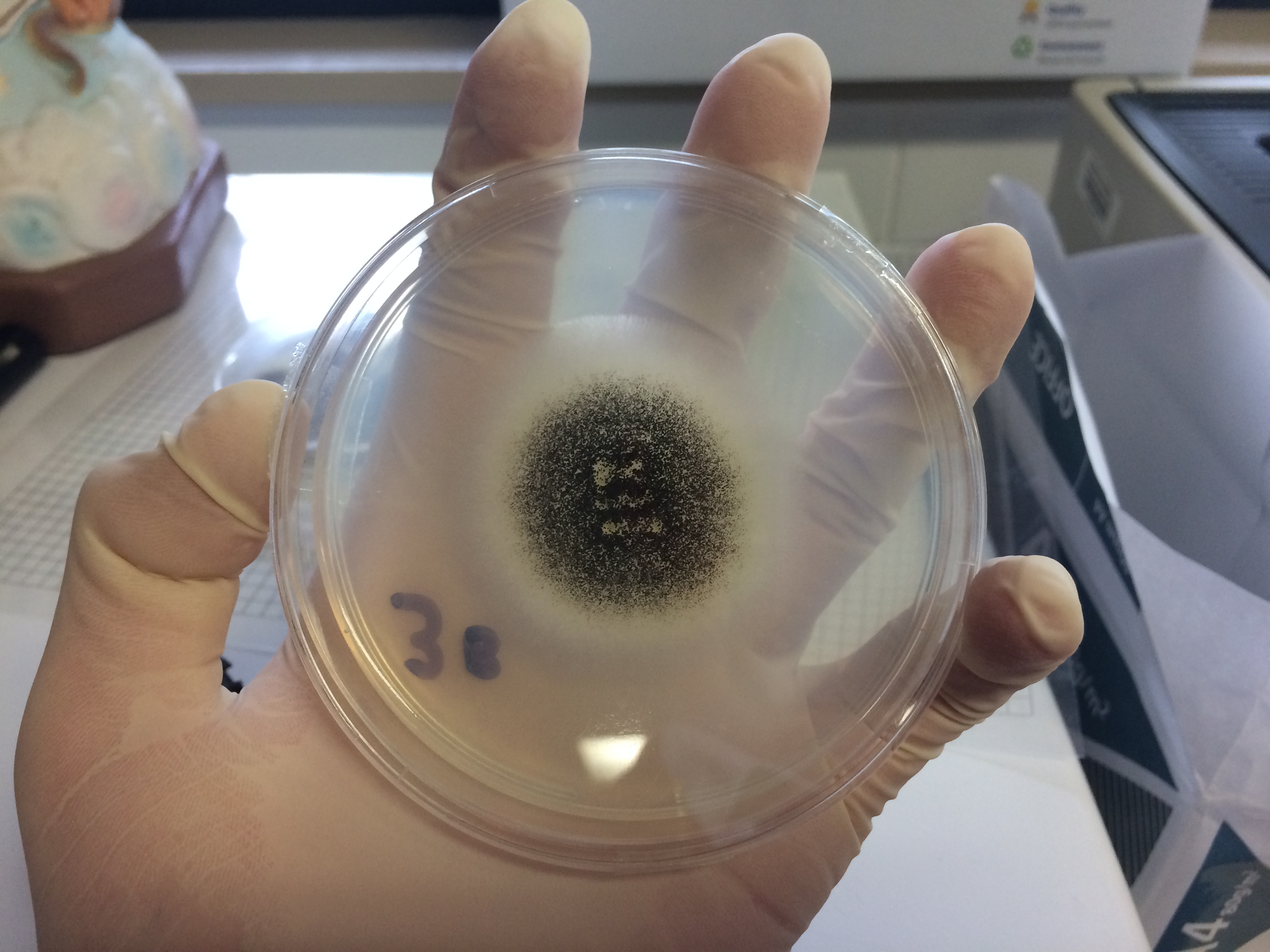
Aspergillus Niger
''Aspergillus niger'' is a mold classified within the ''Nigri'' section of the ''Aspergillus'' genus. The ''Aspergillus'' genus consists of common molds found throughout the environment within soil and water, on vegetation, in fecal matter, on decomposing matter, and suspended in the air. Species within this genus often grow quickly and can sporulate within a few days of germination. A combination of characteristics unique to ''A. niger'' makes the microbe invaluable to the production of many acids, proteins and bioactive compounds. Characteristics including extensive metabolic diversity, high production yield, secretion capability, and the ability to conduct post-translational modifications are responsible for ''A. niger's'' robust production of secondary metabolites. ''A. niger's'' capability to withstand extremely acidic conditions makes it especially important to the industrial production of citric acid. ''A. niger'' causes a disease known as "black mold" on certain fruits an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)