|
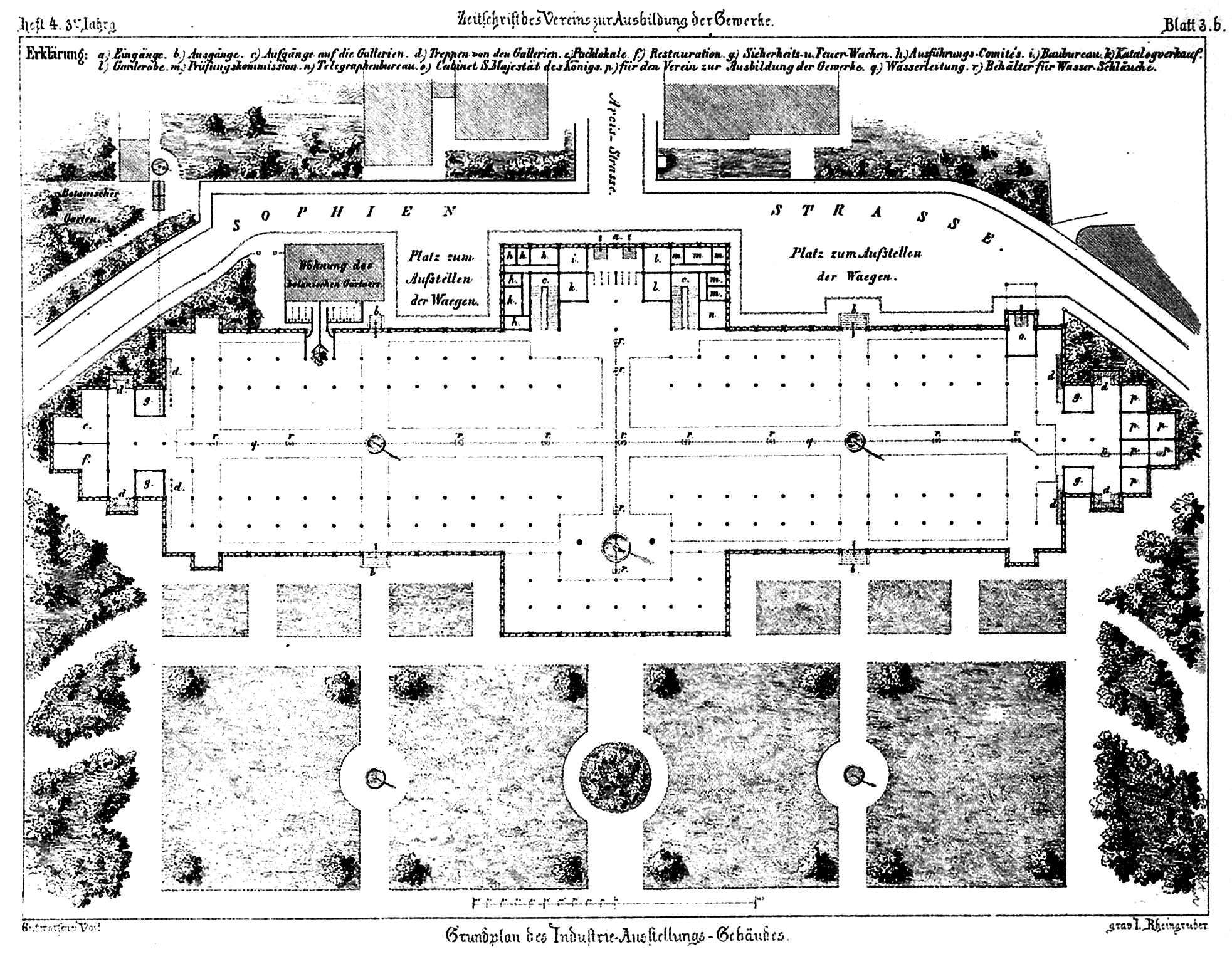
Glaspalast (Munich)
The ''Glaspalast'' (Glass Palace) was a glass and iron exhibition building located in the Alter Botanischer Garten (Munich), Old botanical garden in Munich modeled after the Crystal Palace in London. The Glaspalast opened for the first General German Industrial Exhibition on 15 July 1854. Planning Following other examples around Europe, the ''Glaspalast'' was ordered by Maximilian II of Bavaria, Maximilian II, King of Bavaria, in order to hold the ''Erste Allgemeine Deutsche Industrieausstellung'' (First General German Industrial Exhibition) on 15 July 1854. Originally it was planned to erect the building on . However, the relevant Commission decision preferred an area near the railway station. Designed by architect August von Voit and built by MAN SE, MAN AG, the building was built in 1854 to the north of the Old Botanical Garden close to the Stachus. Construction Following the completion of 1853 and the planned and conservatory of Munich Residence, a glass with cast iron d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Munich
Munich is the capital and most populous city of Bavaria, Germany. As of 30 November 2024, its population was 1,604,384, making it the third-largest city in Germany after Berlin and Hamburg. Munich is the largest city in Germany that is not a state of its own. It ranks as the 11th-largest city in the European Union. The metropolitan area has around 3 million inhabitants, and the broader Munich Metropolitan Region is home to about 6.2 million people. It is the List of EU metropolitan regions by GDP#2021 ranking of top four German metropolitan regions, third largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. Munich is located on the river Isar north of the Alps. It is the seat of the Upper Bavaria, Upper Bavarian administrative region. With 4,500 people per km2, Munich is Germany's most densely populated municipality. It is also the second-largest city in the Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect area after Vienna. The first record of Munich dates to 1158. The city ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miesbach
Miesbach () is a Town#Germany, town in Bavaria, Germany, and is the capital of the Miesbach (district), Miesbach district. The district is at an altitude of 697 metres above sea level. It covers an area of approximately 863.50 km2 of alpine climate, alpine headlands and in 2017 had a population of 11,477. The town is located 48 km southeast of Munich. Lake Schliersee and Lake Tegernsee, around which are the internationally renowned spas, Bad Wiessee, Rottach-Egern and Tegernsee, are nearby. Miesbach was founded around the year 1000 and was for hundreds of years the seat of the County of Hohenwaldeck. In the 19th century, it became the centre of the conservation movement for the traditional costumes, the Tracht. Miesbach also has a rich history as a pilgrimage and a mining village, which can still be seen in the city landscape. On September 16, 1882, Miesbach became the starting point for the first long-distance transmission of electric power in the world. A 1,343 voltag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi
Nazism (), formally named National Socialism (NS; , ), is the far-right politics, far-right Totalitarianism, totalitarian socio-political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Germany. During Hitler's rise to power, it was frequently referred to as Hitler Fascism () and Hitlerism (). The term "neo-Nazism" is applied to other far-right groups with similar ideology, which formed after World War II, and after Nazi Germany collapsed. Nazism is a form of fascism, with disdain for liberal democracy and the parliamentary system. Its beliefs include support for dictatorship, fervent antisemitism, anti-communism, anti-Slavism, anti-Romani sentiment, scientific racism, white supremacy, Nordicism, social Darwinism, homophobia, ableism, and the use of eugenics. The ultranationalism of the Nazis originated in pan-Germanism and the ethno-nationalist ''Völkisch movement, Völkisch'' movement which had been a prominent aspect of German nationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaspalast München Extinguishing Works , an indoor arena in Sindelfingen
{{Disambiguation ...
Glaspalast may refer to: *Glaspalast (Munich), Glaspalast in Munich modeled after The Crystal Palace *Glaspalast Sindelfingen Glaspalast Sindelfingen is an indoor arena, in Sindelfingen, Germany. The arena holds 5,250 people. It is primarily used for indoor athletics and concerts. KISS performed at the arena during their Lick It Up Tour on November 4, 1983. World M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neues Wiener Tagblatt
The ''Neues Wiener Tagblatt'' was a daily newspaper published in Vienna from 1867 to 1945. It was one of the highest-circulation newspapers in Austria before 1938. History The newspaper was founded by Eduard Mayer as a successor to the Wiener Journal. The first issue appeared on 10 March 1867, the year of the Compromise with Hungary and the enactment of the so-called December Constitution, valid until 1918. As early as 13 July 1867 the publisher Moritz Szeps, who had left the Morgen-Post newspaper in a dispute, took over. From 1870 he supported Josef Schöffel with a campaign in his successful fight for the Vienna Woods. Szeps' connection to Crown Prince Rudolf meant that anonymous political texts by the crown prince could repeatedly appear in the paper, in which he advocated the liberal, progressive development of Austria. Szeps remained the sole owner and publisher of the paper until 15 May 1872, then contributed the paper to the Steyrermühl-Verlag publishing house, which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Otto Runge
Philipp Otto Runge (; 1777–1810) was a German artist, draftsman, painter, and color theorist. Runge and Caspar David Friedrich are often regarded as the leading painters of the German Romantic movement.Koerner, Joseph Leo. 1990. ''Caspar David Friedrich and the Subject of Landscape.'' Yale University Press. New Haven, Connecticut. 256 pp. Rauch, Alexander. 2000. ''Neoclassicism and the Romantic Movement: Painting in Europe between Two Revolutions 1789 – 1848.'' pages 318–479. in Tomam, Rolf, editor. ''Neoclassicism and Romanticism: Architecture, Sculpture, Painting, Drawings, 1750-1848.'' Könemann, Verlagsgesellschaft. Cologne. 520 pp. He is frequently compared with William Blake by art historians, although Runge's short ten-year career is not easy to equate to Blake's career.Connelly, Frances S. 1993. ''Poetic Monsters and Nature Hieroglyphics: The Precocious Primitivism of Philipp Otto Runge.'' Art Journal. 52(2): 31-39. By all accounts he had a brilliant mind and was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Blechen
Carl Eduard Ferdinand Blechen (29 July 1798 – 23 July 1840) was a German landscape painter and a professor at the Academy of Arts, Berlin. His distinctive style was characteristic of the Romantic ideals of natural beauty. Life Blechen was born in Cottbus. His father was a minor tax official from Regensburg, and his mother was a Sorb. From 1805 to 1815 he attended the Lyceum at the Oberkirche St.Nikolai in Cottbus. His parents could not afford to pay for any further education, so they apprenticed him to a banker and he was engaged in that profession until 1822, when an increasing interest in art led him to the Berlin Academy. After a short study trip to Dresden and Saxon Switzerland, he returned to Berlin and obtained a position as a decorator for the Royal Theater on the Alexanderplatz. He married in 1824 and became a member of the Berlin Artists' Association in 1827. Later that year, he was dismissed from the Theater because of an ongoing dispute with singer Henriette Son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Von Schwind
image:Moritz von Schwind 2.jpg, 200px, Moritz von Schwind, c. 1860. Moritz von Schwind (21 January 1804 – 8 February 1871) was an Austrian painter, born in Vienna. Schwind's genius was lyrical—he drew inspiration from chivalry, folklore, and the songs of the people. Schwind died in Pöcking in Bavaria, and was buried in the Alter Südfriedhof in Munich. Life and career Moritz von Schwind received rudimentary training and spent a happy and carefree youth in Vienna. Among his companions was the composer Franz Schubert, Schubert, some of whose songs he illustrated. In 1828, the year of Schubert's death, he moved to Munich, where he befriended the painter Julius Schnorr von Karolsfeld, Schnorr and enjoyed the guidance of Peter von Cornelius, Cornelius, then director of the Academy. In 1834, he was commissioned to decorate Ludwig I of Bavaria, King Ludwig's new palace with wall paintings illustrating the works of the poet Tieck. He also found in the same place congenial sport for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
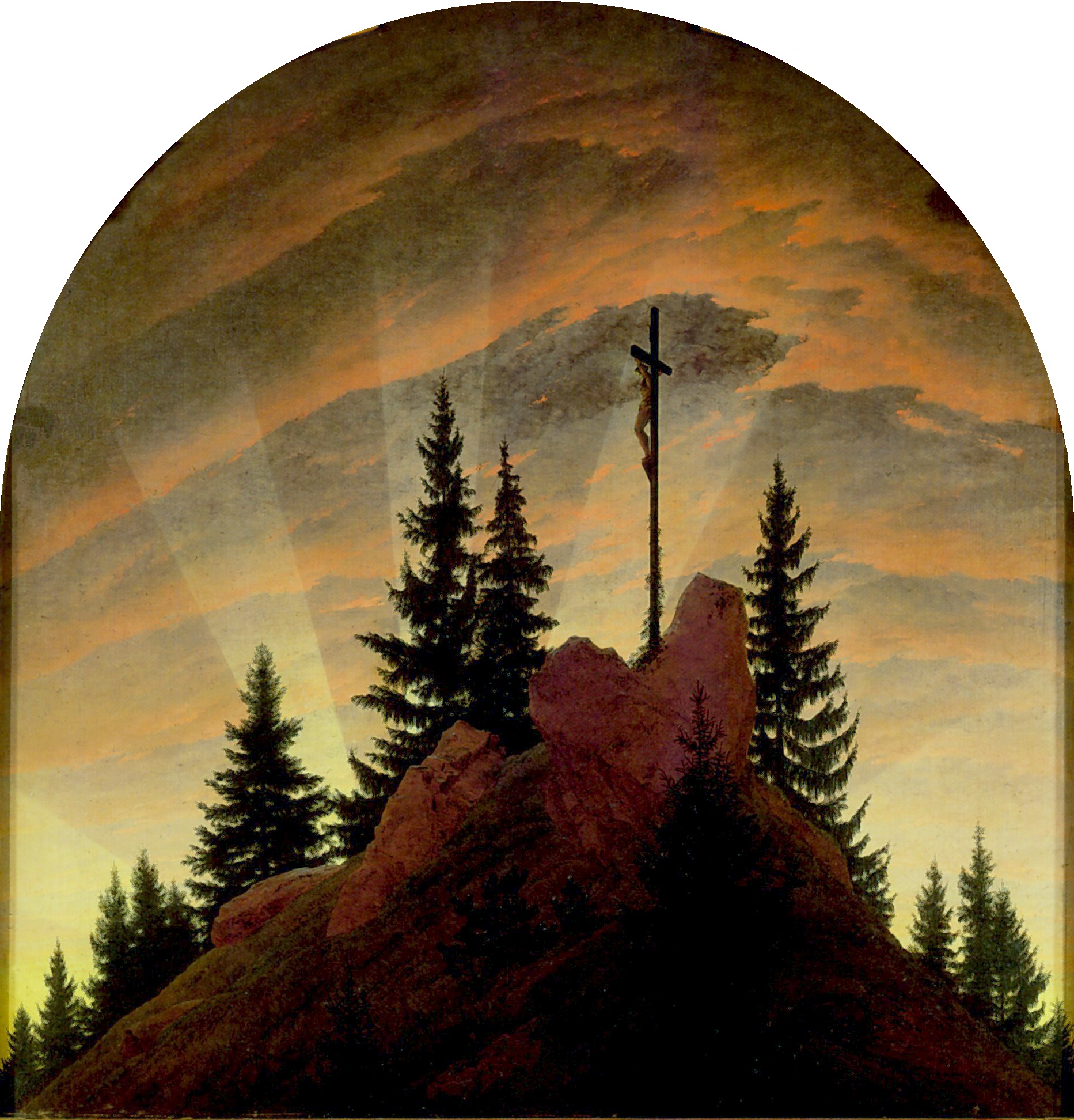
Caspar David Friedrich
Caspar David Friedrich (; 5 September 1774 – 7 May 1840) was a German Romanticism, German Romantic Landscape painting, landscape painter, generally considered the most important German artist of his generation, whose often symbolic, and anti-Classicism, classical work, conveys a subjective, emotional response to the natural world. Friedrich's paintings often set contemplative human figures silhouetted against night skies, morning mists, barren trees or Gothic architecture, Gothic ruins. Art historian Christopher John Murray described their presence, in diminished perspective, amid expansive landscapes, as reducing the figures to a scale that directs "the viewer's gaze towards their metaphysical dimension". Friedrich was born in the town of Greifswald on the Baltic Sea in what was at the time Swedish Pomerania. He studied in Copenhagen 1794–1798, before settling in Dresden. He came of age during a period when, across Europe, a growing disillusionment with materialistic socie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arson
Arson is the act of willfully and deliberately setting fire to or charring property. Although the act of arson typically involves buildings, the term can also refer to the intentional burning of other things, such as motor vehicles, watercraft, or forests. The crime is typically classified as a felony, with instances involving risk to human life or property carrying a stricter penalty. Arson that results in death can be further prosecuted as manslaughter or murder. A common motive for arson is to commit insurance fraud. In such cases, a person destroys their own property by burning it and then lies about the cause in order to collect against their insurance policy. Arson is also often committed to conceal another crime, such as murder or burglary. A person who commits arson is referred to as an arsonist, or a serial arsonist if the person has committed arson several times. Arsonists normally use an accelerant (such as gasoline or kerosene) to ignite, propel, and direct fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspar David Friedrich 046 (Monk In The Snow)
Caspar is a masculine given name. It may refer to: People * Caspar (magus), a name traditionally given to one of the Three Magi in the Bible who brought the baby Jesus gifts * Caspar Austa (born 1982), Estonian cyclist *Caspar Badrutt (1848–1904), Swiss businessman and pioneer of alpine resorts * Caspar Barlaeus (1584–1648), Dutch polymath, Renaissance humanist, theologian, poet and historian *Caspar Bartholin the Elder (1585–1629), Danish theologian and medical professor *Caspar Bartholin the Younger (1655–1738), Danish anatomist *Caspar Buberl (1834–1899), American sculptor * Caspar del Bufalo (1786–1837), Italian priest and saint *Caspar Commelijn (1668–1731), Dutch botanist * Caspar de Crayer (1582–1669), Flemish painter *Caspar Cruciger the Younger (1525–1597), German theologian, son of Caspar Creuziger * Caspar Creuziger or Caspar Cruciger the Elder (1504–1548), German humanist, professor of theology and preacher *Caspar Detlef Gustav Müller (1927–2003), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |