|
Geography Of Albania
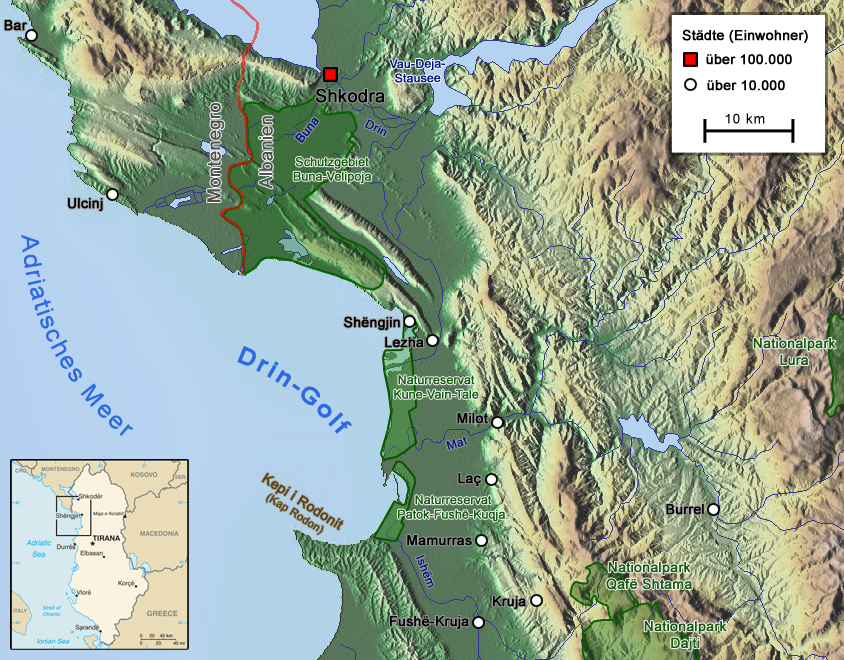
Albania is a country in southeastern Europe that lies along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, with a coastline spanning approximately . Situated on the Balkan Peninsula, it is one of the most mountainous countries in Europe. It is bounded by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the southeast and south. Most of Albania rises into mountains and hills, tending to run the length of the country from north to south, as for instance the Albanian Alps in the north, the Sharr Mountains in the northeast, the Skanderbeg Mountains in the center, the Korab Mountains in the east, the Pindus Mountains in the southeast, and the Ceraunian Mountains in the southwest. Plains and plateaus extend in the west along the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea Coast. Some of the most considerable and oldest bodies of freshwater of Europe can be found in Albania. The second largest lake of Southern Europe, the Lake of Shkodër, is located in the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharr Mountains
Dragash or Sharr ( sq-definite, Dragashi or ''Sharri;'' sr-cyr, Драгаш) is a town and municipality located in the Prizren District of Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, the municipality has 34,827 inhabitants. The Albanian name ''Sharri'' is a reference to the Šar Mountains (in Albanian ''Sharr''). The Serbian name ''Dragaš'' comes from medieval Serbian lord Constantine Dragaš. History The oldest mosque in Kosovo and in the Balkans was built in 1289 and it is called Al-Aga Mosque. Dragash was named after a Serbian medieval noble family of the same name which served Dušan the Mighty (r. 1331-1355) and Uroš the Weak (r. 1355-1371). From 1877 to 1913, Dragash was part of Kosovo Vilayet in the Ottoman Empire. From 1929 to 1941, Dragash was part of the Vardar Banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In 1941, Yugoslavia came under Axis invasion, and Dragash became a part of Albania; first under the Debar prefecture and later in 1943 transferred to the Kosovo p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Prespa Lake
Small Prespa Lake (, ''Limni Mikri Prespa''; ; , ''Malo Prespansko Ezero'') is a lake shared between Greece (138 km² drainage area; 42.5 km² surface area) and Albania (51 km² drainage area; 4.3 km² surface area). It is the smaller of the two Prespa Lakes. Details Small Prespa Lake in particular has been recognized as an important wetland ecosystems favoring breeding and feeding of rare water bird species. It is best known for hosting the largest breeding colony of the Dalmatian pelican in the world. The flora in the region is composed of more than 1,500 plant species of which 146 endemic species in the Lake Ohrid and 39 endemic species from the Prespa Lakes. The villages of Rakickë, Shyec, Buzliqen and Tren surround the Albanian portion of the lake. In Greece the villages surrounding the lake are Agios Germanos, Laimos, Milionas, Platy, Kallithea, Lefkonas, Prespes, Karyes, Mikrolimni, Oxia, Pyli and Vrontero. During 1970, significant amounts of water fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Prespa
The Lake Prespa is located on the tripoint of North Macedonia, Albania and Greece. It is a system of two lakes separated by an isthmus: the Great Prespa Lake, divided between the three countries, and the Little Prespa Lake, mostly within Greece. They are the highest tectonic lakes in the Balkans, at an elevation of . The area contains three national parks: Galičica National Park in North Macedonia, Prespa National Park in Albania, and Prespa National Park in Greece. The largest town in the region is Resen in North Macedonia. In 2014, Ohrid-Prespa Transboundary Biosphere Reserve between Albania and North Macedonia was added to UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves. Geography The Great Prespa Lake (, ''Prespansko Ezero'', , , ''Megáli Préspa'') has the total surface of . The largest part of it, belongs to North Macedonia; to Albania; and to Greece. To the south, the Little Prespa Lake (Greek: Μικρή Πρέσπα, ''Mikri Prespa''; Albanian: ''Prespa e Vog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Peninsula
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, , in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria. The concept of the Balkan Peninsula was created by the German geographer August Zeune in 1808, who mistakenly considered the Balkan Mountains the dominant mountain system of southeastern Europe spanning from the Adriatic Sea to the Black Sea. In the 19th century the term ''Balkan Peninsula'' was a synonym for Rumelia, the parts of Europe that were provinces of the Ottoman E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Of Ohrid
Lake Ohrid is a lake which straddles the mountainous border between the southwestern part of North Macedonia and eastern Albania. It is one of Europe's deepest and oldest lakes, with a unique aquatic ecosystem of worldwide importance, with more than 200 endemic species. North Macedonia's side of Lake Ohrid was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1979, with the site being extended to also include the cultural and historic area of Ohrid in 1980. In 2010, NASA named one of Titan's lakes after it. In 2014, the Ohrid-Prespa Transboundary Reserve between Albania and North Macedonia was added to UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves. Albania's side of Lake Ohrid was also designated UNESCO world heritage status in 2019. North Macedonia's portion was designated as a protected Ramsar site in 2021, passing all nine criteria for proclamation.Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning (2021)Ramsar Information Sheet: Lake Ohrid. Ramsar Secretariat, Gland, Switzerland. In A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy, Kosovo, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France, Wallachia, southern Romania, Spain, Turkey, and Vatican City. Southern Europe is focused on the three peninsulas located in the extreme south of the European continent. These are the Iberian Peninsula, the Italian Peninsula, and the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. These three peninsulas are separated from the rest of Europe by towering mountain ranges, respectively by the Pyrenees, the Alps and the Balkan Mountains. The location of these peninsulas in the heart of the Mediterranean Sea, as well as their mountainous reliefs, provide them with very different types of climates (mainly subtropics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mineral-rich waters, such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of vascular plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Fresh water is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Ionian Sea Coast
The Albanian Ionian Sea Coast ( — ) is a coastline of the north-eastern Ionian Sea, that encompasses the south-western border of the Albania, Republic of Albania, stretching from the southern half of Karaburun Peninsula, Albania, Karaburun Peninsula, across the historical region of Labëria, the city of Sarandë, the mountains of the Ceraunian Mountains, Ceraunians, and the Albanian Riviera, to the Lake of Butrint, where the Straits of Corfu, Strait of Corfu separates the country from Greece. Albania is located in Southern Europe, Southern and Southeast Europe, South-eastern Europe in the western section of the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. It borders on Montenegro to the north-west, Kosovo to the north-east, North Macedonia to the east, Greece to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The coastline occupies a total length of and explicitly marked by a mountainous landscape supplied with deep bays, numerous islands, high cliffs, Rocky coast, rocky and sand, sandy coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast
The Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast ( — ) stretches in the south-eastern Adriatic Sea beginning at the Gulf of Drin in the north, across the port cities of Shëngjin, Durrës, and Vlorë, to the Bay of Vlorë in the south, where the Albanian Riviera and the Albanian Ionian Sea Coast begin. Albania is geographically located in Southern and South-eastern Europe within the Balkan Peninsula. It borders on Montenegro to the north-west, Kosovo to the north-east, North Macedonia to the east, Greece to the south, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. The total length of the coastline is approximately , of which are taken up by white sandy beaches and the rest by various other landforms. The Adriatic Sea is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending all the way from the Strait of Otranto in the south up to the Po Valley in the north. The sea is apportioned into two major basins, wherein Albania is entirely located within the deepest and the southernmost. The coa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceraunian Mountains
The Ceraunian Mountains (, , 'Thunderbolt Mountains') are a coastal mountain range in southwestern Albania, within the Vlorë County. The mountain range rises on the northeastern bank of the Ionian Sea and protrudes into the Adriatic Sea. It extends for approximately in a southeast-northwest direction near Sarandë, along the Albanian Riviera, close to Orikum. Geologically, the Karaburun Peninsula belongs to the Ceraunian Mountains, and is separated from the rest by the Llogara Pass () forming the western part of the Ceraunian mountain range, called Acroceraunian Mountains (). The mountains are about long and about wide. The highest peak is Çikë with an elevation of . Name In classical antiquity, the name of the mountains was recorded in Ancient Greek as ''Keraunia ore'', meaning "thunder-split peaks". The western part of the mountain chain is called ''Akrokeraunia'', meaning 'Cape Thunder' which referred to the modern Karaburun peninsula. Both names Ceraunia and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |