|
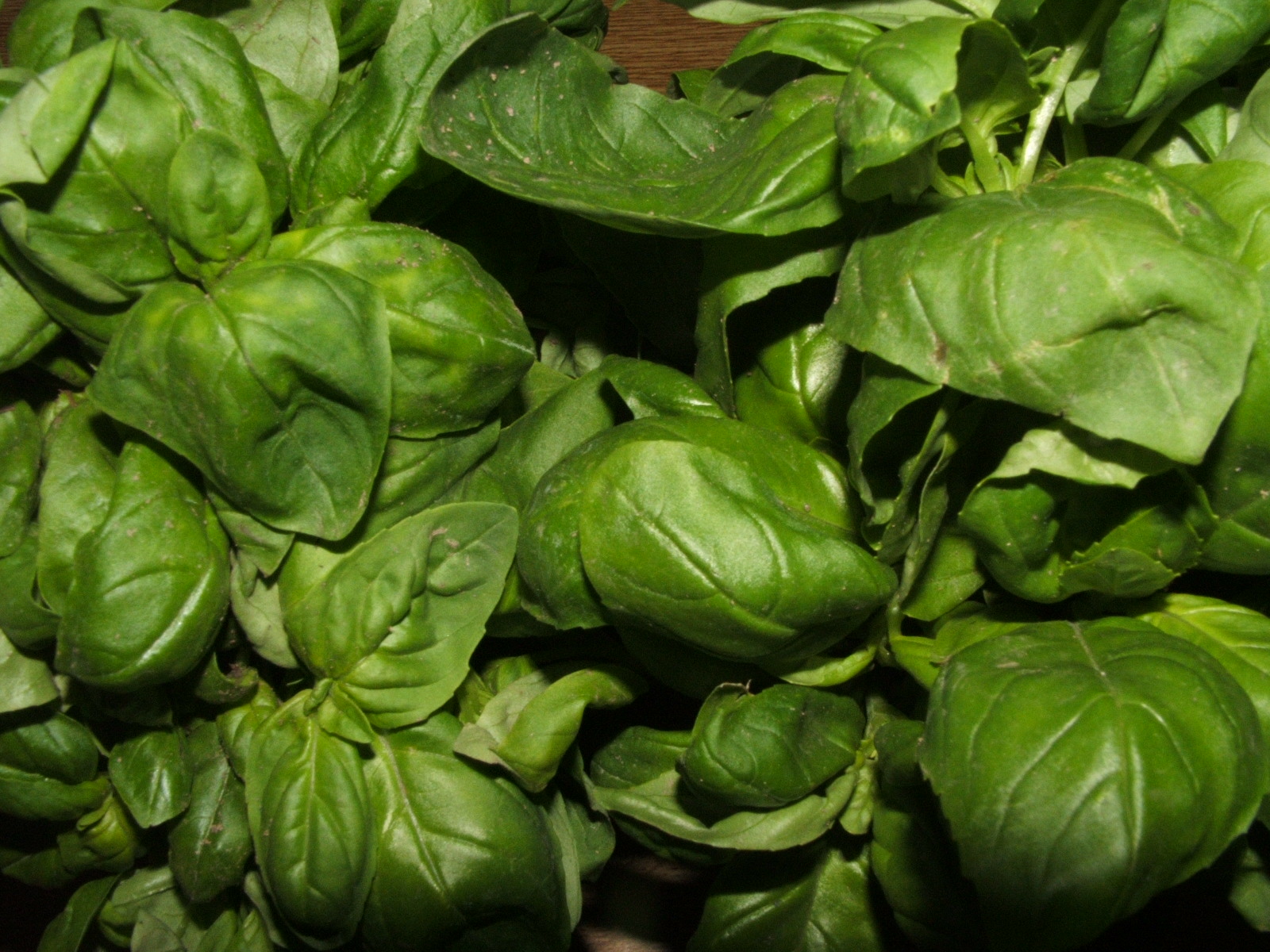
Genovese Basil
Genovese basil (in Ligurian language ''baxaicò'' or ''baxeicò'') is a cultivar of ''Ocimum basilicum'' (sweet basil). It is one of the most popular basils for culinary use, particularly for its use in pesto, the traditional Genoese sauce. The name "Basilico Genovese" is protected by the European Union with the Denominazione di Origine Protetta certification. Genoese basil is produced in the provinces of Genoa, Savona and Imperia. The best genoese basil is said to be grown in Prà, a western delegation of the city of Genoa. The nearby presence of a large steel mill from the 1950s to the 1980s threatened the cultivar, said to be necessary to produce the "real" genoese pesto. Now the threat is mostly gone with the dismissal of the mill and the conversion of the remaining lines to less polluting productions. Nomenclature and Taxonomy References See also * International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants The ''International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilico Genovese Di Prà-2
Basil (, ; ''Ocimum basilicum'' , also called great basil, is a culinary herb of the family Lamiaceae (mints). It is a tender plant, and is used in cuisines worldwide. In Western cuisine, the generic term "basil" refers to the variety also known as sweet basil or Genovese basil. Basil is native to tropical regions from Central Africa to Southeast Asia. In temperate climates basil is treated as an annual plant, however, basil can be grown as a short-lived perennial or biennial in warmer horticultural zones with tropical or Mediterranean climates. There are many varieties of basil including sweet basil, Thai basil (''O. basilicum'' var. ''thyrsiflora''), and Mrs. Burns' Lemon (''O. basilicum var. citriodora''). ''O. basilicum'' can cross-pollinate with other species of the ''Ocimum'' genus, producing hybrids such as lemon basil (''O. × citriodorum'') and African blue basil (''O. × kilimandscharicum''). Etymology The name "basil" comes from the Latin , and the Greek (), m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptophyta
Streptophyta (), informally the streptophytes (, from the Greek ''strepto'' 'twisted', for the morphology of the sperm of some members), is a clade of plants. The composition of the clade varies considerably between authors, but the definition employed here includes land plants and all green algae except the Chlorophyta and the more basal Prasinodermophyta. Classifications The composition of Streptophyta and similar groups (Streptophytina, Charophyta) varies in each classification. Some authors are more restrictive, including only the Charales and Embryophyta (e.g., Streptophyta Jeffrey 1967; Adl et al. 2012, Streptophytina Lewis & McCourt 2004), others include more groups (e.g., Charophyta Lewis & McCourt 2004; Karol et al. 2009; Adl et al. 2012, Streptophyta Bremer, 1985; de Reviers 2002; Leliaert et al. 2012, Streptobionta Kenrick & Crane 1997; some authors use this broader definition, but exclude the Embryophyta, e.g., Charophyta Cavalier-Smith 1993; Leliaert et al. 2012, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamiaceae
The Lamiaceae ( ) or Labiatae are a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint, deadnettle or sage family. Many of the plants are aromatic in all parts and include widely used culinary herbs like basil, mint, rosemary, sage, savory, marjoram, oregano, hyssop, thyme, lavender, and perilla, as well as other medicinal herbs such as catnip, salvia, bee balm, wild dagga, and oriental motherwort. Some species are shrubs, trees (such as teak), or, rarely, vines. Many members of the family are widely cultivated, not only for their aromatic qualities, but also their ease of cultivation, since they are readily propagated by stem cuttings. Besides those grown for their edible leaves, some are grown for decorative foliage. Others are grown for seed, such as '' Salvia hispanica'' (chia), or for their edible tubers, such as '' Plectranthus edulis'', '' Plectranthus esculentus'', ''Plectranthus rotundifolius'', and ''Stachys affinis'' (Chinese artichoke). Many are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamiales
The order Lamiales (also known as the mint order) are an order in the asterid group of dicotyledonous flowering plants. It includes about 23,810 species, 1,059 genera, and is divided into about 25 families. These families include Acanthaceae, Bignoniaceae, Byblidaceae, Calceolariaceae,Carlemanniaceae, Gesneriaceae, Lamiaceae, Lentibulariaceae, Linderniaceae, Martyniaceae, Mazaceae, Oleaceae, Orobanchaceae, Paulowniaceae, Pedaliaceae, Peltantheraceae, Phrymaceae, Plantaginaceae, Plocospermataceae, Schlegeliaceae, Scrophulariaceae, Stilbaceae, Tetrachondraceae, Thomandersiaceae, Verbenaceae. Being one of the largest orders of flowering plants, Lamiales have representatives found all over the world. Well-known or economically important members of this order include lavender, lilac, olive, jasmine, the ash tree, teak, snapdragon, sesame, psyllium, garden sage, and a number of table herbs such as mint, basil, and rosemary. Description Plant species within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteranae
Asterales () is an order of dicotyledonous flowering plants that includes the large family Asteraceae (or Compositae) known for composite flowers made of florets, and ten families related to the Asteraceae. While asterids in general are characterized by fused petals, composite flowers consisting of many florets create the false appearance of separate petals (as found in the rosids). The order is cosmopolitan (plants found throughout most of the world including desert and frigid zones), and includes mostly herbaceous species, although a small number of trees (such as the ''Lobelia deckenii'', the giant lobelia, and ''Dendrosenecio'', giant groundsels) and shrubs are also present. Asterales are organisms that seem to have evolved from one common ancestor. Asterales share characteristics on morphological and biochemical levels. Synapomorphies (a character that is shared by two or more groups through evolutionary development) include the presence in the plants of oligosaccharid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnoliopsida
Magnoliopsida is a valid botanical name for a class of flowering plants. By definition the class will include the family Magnoliaceae, but its circumscription can otherwise vary, being more inclusive or less inclusive depending upon the classification system being discussed. Classification Cronquist and Takhtajan systems In the Takhtajan system and the Cronquist system, the name was used for the group known as dicotyledons. The Takhtajan system used this internal taxonomy: * class Magnoliopsida dicotyledons*: subclass Magnoliidae *: subclass Nymphaeidae *: subclass Nelumbonidae *: subclass Ranunculidae *: subclass Caryophyllidae *: subclass Hamamelididae *: subclass Dilleniidae *: subclass Rosidae *: subclass Cornidae *: subclass Asteridae *: subclass Lamiidae The Cronquist system used this internal taxonomy (in the 1981 version): * class Magnoliopsida dicotyledons*: subclass Magnoliidae *: subclass Hamamelidae *: subclass Caryophyllidae *: subclass Dilleniidae * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class ( la, classis) is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name (and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'') was first introduced by the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in his classification of plants that appeared in his ''Eléments de botanique'', 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdivision (botany)
In zoological nomenclature, a subphylum is a taxonomic rank below the rank of phylum. The taxonomic rank of " subdivision" in fungi and plant taxonomy is equivalent to "subphylum" in zoological taxonomy. Some plant taxonomists have also used the rank of subphylum, for instance monocotyledons as a subphylum of phylum Angiospermae and vertebrates as a subphylum of phylum Chordata. Taxonomic rank Subphylum is: #subordinate to the phylum #superordinate to the infraphylum. Where convenient, subphyla in turn can be divided into infraphyla; in turn such an infraphylum also would be superordinate to any classes or superclasses in the hierarchy. Examples Not all fauna phyla are divided into subphyla. Those that are include: *Arthropoda: divided into subphyla Trilobitomorpha, Chelicerata, Myriapoda, Hexapoda and Crustacea, * Brachiopoda: divided into subphyla Linguliformea, Craniformea and Rhynchonelliformea, *Chordata: divided into Tunicata, Cephalochordata, and its large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. Vascular plants include the clubmosses, horsetails, ferns, gymnosperms (including conifers), and angiosperms (flowering plants). Scientific names for the group include Tracheophyta, Tracheobionta and Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Some early land plants (the rhyniophytes) had less developed vascular tissue; the term eutracheophyte has been used for all other vascular plants, including all living ones. Historically, vascular plants were known as "higher plants", as it was believed that they were further evolved than other plants due to being more complex organisms. However, this is an antiquated remnant of the obsolete scala naturae, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |