|
Genetics And The Origin Of Species
''Genetics and the Origin of Species'' is a 1937 book by the Ukrainian-American evolutionary biologist Theodosius Dobzhansky. It is regarded as one of the most important works of Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis and was one of the earliest. The book popularized the work of population genetics to other biologists and influenced their appreciation for the genetics, genetic basis of evolution. In his book, Dobzhansky applied the theoretical work of Sewall Wright (1889–1988) to the study of natural populations, allowing him to address evolutionary problems in a novel way during his time. Dobzhansky implements theories of mutation, natural selection, and speciation throughout his book to explain the habits of populations and the resulting effects on their genetic behavior. The book explains evolution in depth as a process over time that accounts for the diversity of all life on Earth. The study of evolution was present, but greatly neglected at the time. Dobzhansky ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius Dobzhansky
Theodosius Grigorievich Dobzhansky (; ; January 25, 1900 – December 18, 1975) was a Russian-born American geneticist and evolutionary biologist. He was a central figure in the field of evolutionary biology for his work in shaping the modern synthesis and also popular for his support and promotion of theistic evolution as a practicing Christian. Born in the Russian Empire, Dobzhansky immigrated to the United States in 1927 at the age of 27. His 1937 work '' Genetics and the Origin of Species'' became a major influence on the modern synthesis. He was awarded the U.S. National Medal of Science in 1964 and the Franklin Medal in 1973. Biography Early life Dobzhansky was born on January 25, 1900, in Nemirov, Russian Empire (now Nemyriv, Ukraine), the only child of Grigory Dobzhansky, a mathematics teacher, and Sophia Voinarsky. He was given an unusual name, Theodosius, because he was born after his middle-aged parents prayed for a child to St. Theodosius of Chernigov. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another [and] the relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying Behavioral ecology, behavioral adaptations. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partula (gastropod)
''Partula'' is a genus of air-breathing tropical land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks in the family Partulidae.Myers, P.; Espinosa, R.; Parr, C. S.; Jones, T.; Hammond, G. S. & Dewey, T. A. (2006). The Animal Diversity Web (online). Accessed at http://animaldiversity.org. Many species of ''Partula'' are known under the general common names " Polynesian tree snail" and " Moorean viviparous tree snail". Partulids are distributed across of Pacific Ocean islands, from the Society Islands to New Guinea. Once used as decorative items in Polynesian ceremonial wear and jewelry, these small snails (averaging about one-half to three-quarters of an inch in length) gained the attention of science when Dr. Henry Crampton (along with Yoshio Kondo) spent 50 years studying and cataloging partulids, detailing their remarkable array of morphological elements, ecological niches, and behavioral aspects that illustrate adaptive radiation. Decline The partulids of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift, also known as random genetic drift, allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the Allele frequency, frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance. Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and thereby reduce genetic variation. It can also cause initially rare alleles to become much more frequent and even fixed. When few copies of an allele exist, the effect of genetic drift is more notable, and when many copies exist, the effect is less notable (due to the law of large numbers). In the middle of the 20th century, vigorous debates occurred over the relative importance of natural selection versus neutral processes, including genetic drift. Ronald Fisher, who explained natural selection using Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, held the view that genetic drift plays at most a minor role in evolution, and this remained the dominant view for several decades. In 1968, population geneticist Mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
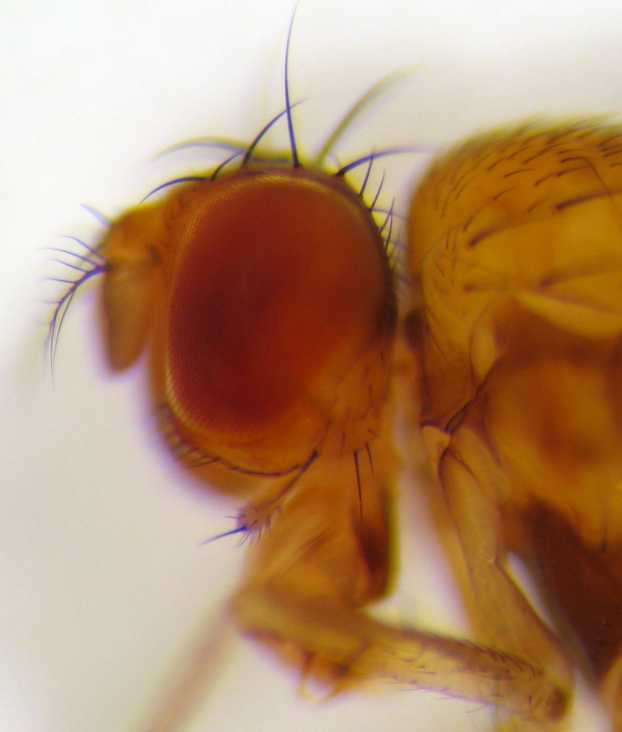
Drosophila
''Drosophila'' (), from Ancient Greek δρόσος (''drósos''), meaning "dew", and φίλος (''phílos''), meaning "loving", is a genus of fly, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many species to linger around overripe or rotting fruit. They should not be confused with the Tephritidae, a related family, which are also called fruit flies (sometimes referred to as "true fruit flies"); tephritids feed primarily on unripe or ripe fruit, with many species being regarded as destructive agricultural pests, especially the Mediterranean fruit fly. One species of ''Drosophila'' in particular, ''Drosophila melanogaster'', has been heavily used in research in genetics and is a common model organism in developmental biology. The terms "fruit fly" and "''Drosophila''" are often used synonymously with ''D. melanogaster'' in modern biological literatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
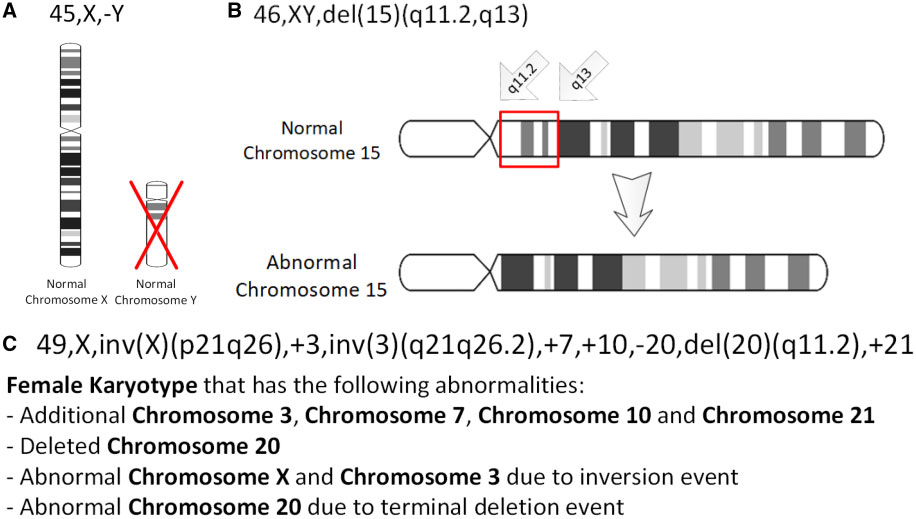
Chromosomal Inversion
An inversion is a chromosome rearrangement in which a segment of a chromosome becomes inverted within its original position. An inversion occurs when a chromosome undergoes a two breaks within the chromosomal arm, and the segment between the two breaks inserts itself in the opposite direction in the same chromosome arm. The breakpoints of inversions often happen in regions of repetitive nucleotides, and the regions may be reused in other inversions. Chromosomal segments in inversions can be as small as 1 kilobases or as large as 100 megabases. The number of genes captured by an inversion can range from a handful of genes to hundreds of genes. Inversions can happen either through ectopic recombination between Repeated sequence (DNA), repetitive sequences, or through chromosomal breakage followed by non-homologous end joining. Inversions are of two types: paracentric inversion, paracentric and pericentric inversion, pericentric. Paracentric inversions do not include the centromere, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
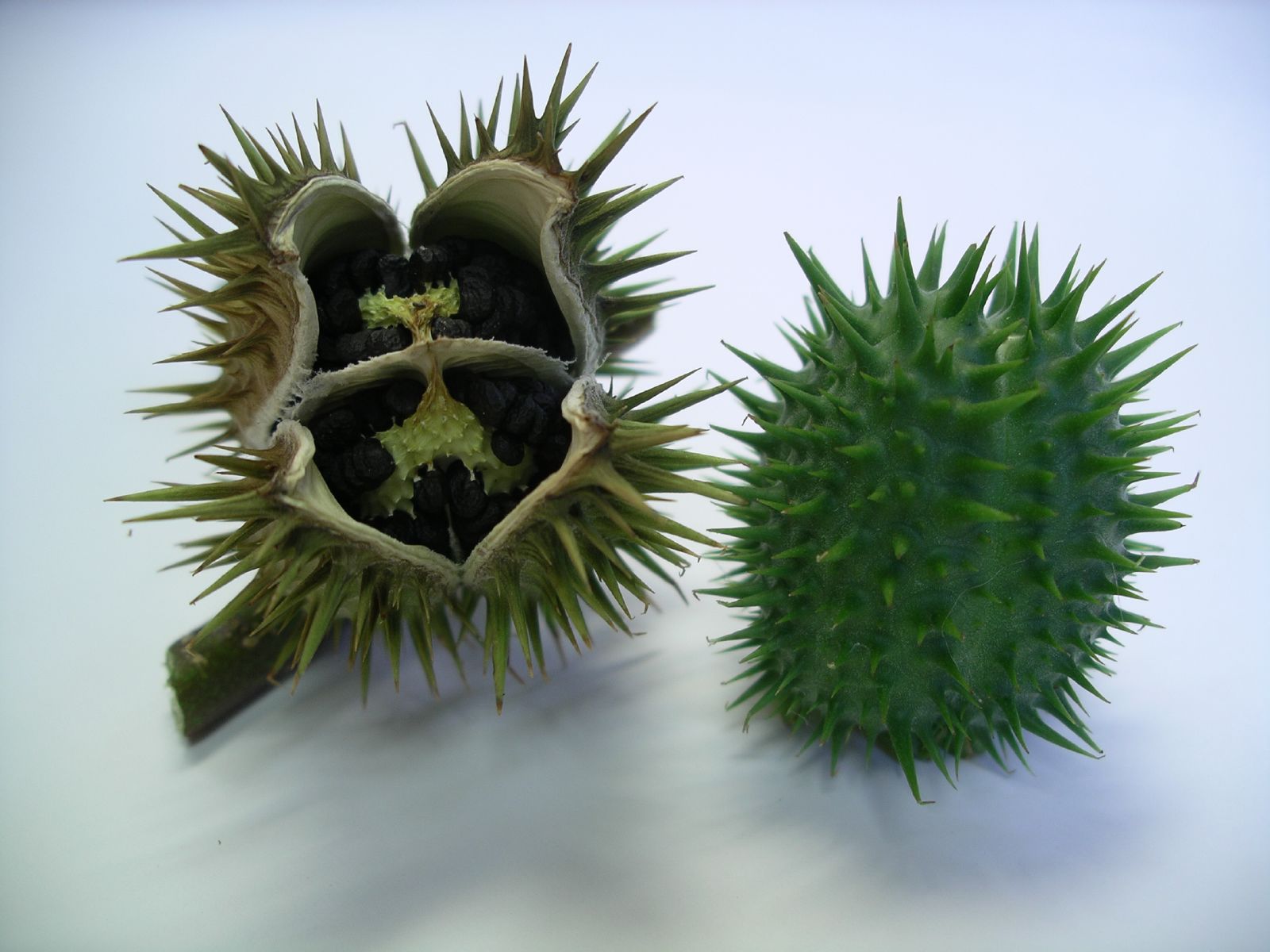
Datura Stramonium
''Datura stramonium'', known by the common names thornapple, jimsonweed (jimson weed), or devil's trumpet, is a poisonous flowering plant in the ''Datureae, Daturae'' Tribe (botany), tribe of the nightshade family Solanaceae. Its likely origin was in Central America, and it has been introduced in many world regions. It is an aggressive invasive species, invasive weed in temperate climates and tropical climates across the world. ''D. stramonium'' has frequently been employed in traditional medicine to treat a variety of ailments. It has also been used as a hallucinogen (of the anticholinergic/antimuscarinic, deliriant type), taken entheogenically to cause intense, sacred or occult visions.Schultes, Richard Evans; Albert Hofmann (1979). ''Plants of the Gods: Origins of Hallucinogenic Use'' New York: McGraw-Hill. . It is unlikely ever to become a major drug of abuse owing to effects upon both mind and body frequently perceived as being highly Dysphoria, unpleasant, giving rise to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" translocation. Reciprocal translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes. Two detached fragments of two different chromosomes are switched. Robertsonian translocation occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes get attached, meaning that given two healthy pairs of chromosomes, one of each pair "sticks" and blends together homogeneously. Each type of chromosomal translocation can result in disorders for growth, function and the development of an individuals body, often resulting from a change in their genome. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise-separated genes. It is detected on cytogenetics or a karyotype of affected cells. Translocations can be bala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most important of these proteins are the histones. Aided by chaperone proteins, the histones bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These eukaryotic chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure that has a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Normally, chromosomes are visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage occurs, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and the two copies are joined by a centromere—resulting in either an X-shaped structure if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-armed structure if the centromere is located distally; the jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is distinguished from '' genetic variability'', which describes the tendency of genetic characteristics to vary. Genetic diversity serves as a way for populations to adapt to changing environments. With more variation, it is more likely that some individuals in a population will possess variations of alleles that are suited for the environment. Those individuals are more likely to survive to produce offspring bearing that allele. The population will continue for more generations because of the success of these individuals. The academic field of population genetics includes several hypotheses and theories regarding genetic diversity. The neutral theory of evolution proposes that diversity is the result of the accumulation of neutral substitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Dunn
Leslie Clarence Dunn (November 2, 1893 in Buffalo, New York – March 19, 1974) was a developmental geneticist at Columbia University. His early work with the mouse T-locus and established ideas of gene interaction, fertility factors, and allelic distribution.American Philosophical Society (2000)"L. C. Dunn Biography" Later work with other model organisms continued to contribute to developmental genetics. Dunn was also an activist, helping fellow scientists seek asylum during World War II, and a critic of eugenics movements.Melinda Gormley"Geneticist L.C. Dunn: Politics, Activism, and Community" (2006 dissertation, Oregon State University). Biography Dunn was born in Buffalo, New York, in 1893, to Clarence Leslie Dunn and Mary Eliza Booth Dunn.Theodosius Dobzhansky''Leslie Clarence Dunn, 1893-1974: A Biographical Memoir''(National Academy of Sciences 1978) He earned a bachelor's degree from Dartmouth College in 1915. Dunn served in the Harvard Regiment in France during W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics Society Of America
The Genetics Society of America (GSA) is a scholarly membership society of more than 5,500 genetics researchers and educators, established in 1931. The Society was formed from the reorganization of the Joint Genetics Sections of the American Society of Zoologists and the Botanical Society of America. An Abridged History of the Genetics Society of America GSA members conduct fundamental and applied research using a wide variety of s to enhance understanding of living systems. Some of the systems of study include '''' (fruit flies), '' |