|
Genetic Studies On Croats
Population genetics is a scientific discipline which contributes to the examination of the human evolutionary and historical migrations. Particularly useful information is provided by the research of two uniparental markers within our genome, the Y-chromosome (Y-DNA) and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), as well as autosomal DNA. The data from Y-DNA and autosomal DNA suggests that the Croats mostly are descendants of the Slavs of the medieval migration period, according to mtDNA have genetic diversity which fits within a broader European maternal genetic landscape, and overall have a uniformity with other South Slavs from the territory of former Yugoslavia. There are many Paleolithic period sites located in the territory of Croatia, mostly ascribed to the Mousterian phase in the Middle Paleolithic period. In the Neolithic period in Southeast Europe were founded major cultures like Vinča, Varna, Starčevo. In the Bronze Age happened symbiosis between Proto-Indo-Europeans of Kurgan cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and among populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, speciation, and population stratification, population structure. Population genetics was a vital ingredient in the emergence of the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern evolutionary synthesis. Its primary founders were Sewall Wright, J. B. S. Haldane and Ronald Fisher, who also laid the foundations for the related discipline of quantitative genetics. Traditionally a highly mathematical discipline, modern population genetics encompasses theoretical, laboratory, and field work. Population genetic models are used both for statistical inference from DNA sequence data and for proof/disproof of concept. What sets population genetics apart from newer, more phenotypic approaches to modelling evolution, such as evolutionary game theory and evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
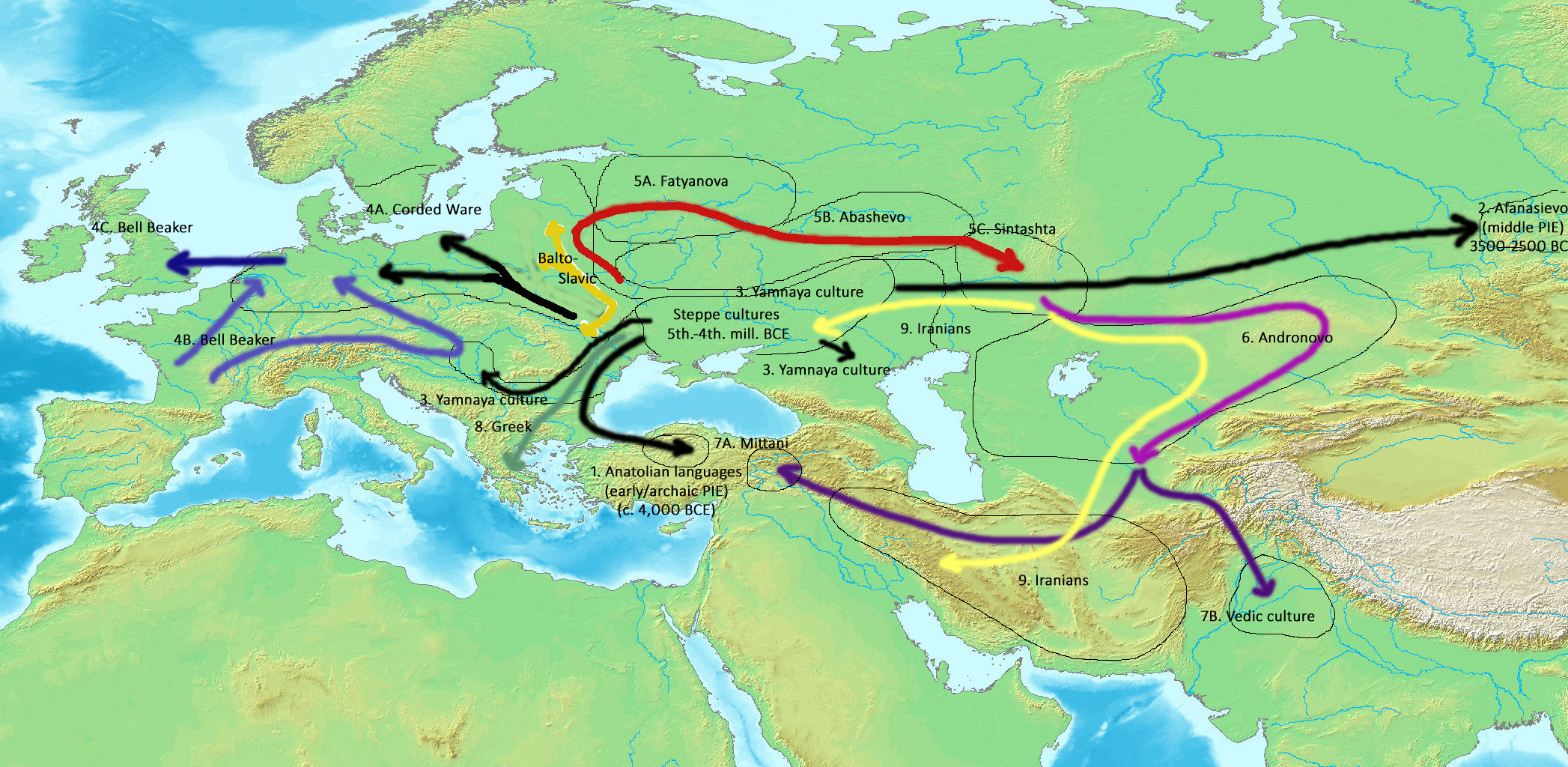
Kurgan Hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Turkic word ''kurgan'' (), meaning tumulus or burial mound. The steppe theory was first formulated by Otto Schrader (1883) and V. Gordon Childe (1926), then systematized in the 1950s by Marija Gimbutas, who used the term to group various prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and its relationship with other cultures as a point of reference. Gimbutas defined the Kurgan culture as composed of four successive periods, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osijek
Osijek () is the fourth-largest city in Croatia, with a population of 96,848 in 2021. It is the largest city and the economic and cultural centre of the eastern Croatian region of Slavonia, as well as the administrative centre of Osijek-Baranja County. Osijek is on the right bank of the Drava River, upstream of its confluence with the Danube, at an elevation of . Name The name was given to the city due to its position on elevated ground, which prevented the city being flooded by the local swamp waters. Its name ''Osijek'' derives from the Croatian word ''oseka'' ' ebb tide'. Due to its history within the Habsburg monarchy and briefly in the Ottoman Empire, as well as the presence of German, Hungarian, and Serbian minorities throughout its history, Osijek has (or had) its names in other languages: Hungarian: ''Eszék'', German: , or , , and English: ''Esgek''. Its Roman name was ''Aelia Mursa'', ''Mursa'', and later ''Mursa Major'', which may be a form of the pre-existing na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beli Manastir
Beli Manastir ( sr-Cyrl, Бели Манастир, ) is a town in eastern Croatia. It is the principal town of the Croatian part of Baranja, located in the Osijek-Baranja County. Name The name means "white monastery" in Serbo-Croatian. Originally called Monoštor, the current name was adopted in 1923. It is also known as ''Pélmonostor'' in Hungarian, and ''Manoster'' in German. The name Beli Manastir was first mentioned in 1227, when Moys de Daro, Hungarian Palatine, built a monastery on his estate in Pelu. Other names formerly used for the town were: ''Pél'', ''Bell'', and ''Monostor''. All names are connected with monasteries that existed in history at this location. The first monastery was built in the 9th century during the rule of Slavic duke Kocelj but was later razed, and all that remained of it was ''pil'' (''obelisk'' in English), hence the later Hungarian name ''Pél'', which was a version of the Slavic word. History In the 9th century, this area was part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup C-V20
Haplogroup C-V20 (also known as Haplogroup C1a2) is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two primary branches of Haplogroup C1a (Y-DNA), Haplogroup C1a, one of the descendants of Haplogroup C-F3393, Haplogroup C1 (The other is Haplogroup C-M8, C1a1 in Japan with an average amount of 5%). Haplogroup C-V20 is now distributed in Europe, North Africa, West Asia, and South Asia with very low frequency. History and Distribution Haplogroup C1a2 (V20) has been discovered in the remains of Palaeolithic people in Czech Republic (30,000 years ago), Belgium (35,000 years ago), and the Sunghir archaeological site near Vladimir, Russia, Vladimir, Russia. Regarding more recent prehistory, Haplogroup C-V20 has been found in the remains of a male (died ''ca.'' 7,000 years ago) associated with a late group of the Alföld Linear Pottery culture at Kompolt-Kigyósér, Hungary whose mtDNA belonged to haplogroup J (mtDNA), haplogroup J1c1, the remains of a male (died ''ca.'' 7,000 years ago) associ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardium Pottery
Cardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the '' Corculum cardissa'', a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery are in turn used to define the Neolithic culture which produced and spread them, commonly called the "Cardial culture". The alternative name, impressed ware, is given by some archaeologists to define this culture, because impressions can be made with sharp objects other than cockle shells, such as a nail or comb. Impressed pottery is much more widespread than the Cardial. Impressed ware is found in the zone "covering Italy to the Ligurian coast" as distinct from the more western Cardial extending from Provence to western Portugal. The sequence in prehistoric Europe has traditionally been supposed to start with widespread Cardial ware, and then to develop other methods of impression locally, termed "epi-Cardial". However the widespread Cardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, Genographic Project, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid advancements in DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinkovci
Vinkovci () is a city in Slavonia, in the Vukovar-Syrmia County in eastern Croatia. The city settlement's population was 28,111 in the 2021 census, while the total population was 30,842, making it the largest town of the county. It is a local transport hub, particularly because of its railways. Name The name comes from the Croatian name, Croatian given name Vinko, cognate to the name Vincent. It has been in use following a dedication of the oldest town church of Saint Elijah () to Saint Vincent the Deacon () in the Middle Ages. The name of the city in Croatian language, Croatian is plural. It was called in antiquity. There is no known Latin or Greek etymology for , so it is assumed to be inherited from an earlier time. ''Cibale'' is a toponym derived from geomorphology, from Indo-European meaning "ascension" or "head". It is assumed that the root is in Proto-Indo-European (head), in the sense of a hill, meaning a place that was protected from the flooding of Bosut (river), B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PCA And Admixture Of The Croatian Neolithic Potočani Samples
PCA may refer to: Medicine and biology * Patient-controlled analgesia * Plate count agar in microbiology * Polymerase cycling assembly, for large DNA oligonucleotides * Posterior cerebral artery * Posterior cortical atrophy, a form of dementia *Prostate cancer * Protein-fragment complementation assay, to identify protein–protein interactions * Protocatechuic acid, a phenolic acid. * Personal Care Assistant, also known as unlicensed assistive personnel *Procainamide Military and government * EU-Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (PCA agreement between Armenia and the EU) * Parks Canada Agency * Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (EU) * Permanent change of assignment in US armed forces Organizations Business * Packaging Corporation of America * Peanut Corporation of America, former company * Pennsylvania Central Airlines 1936-1948 Education * Pacific Coast Academy, fictional school in TV series ''Zoey 101'' * Parents and citizens associations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Slavs
The early Slavs were speakers of Indo-European languages, Indo-European dialects who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe and established the foundations for the Slavs, Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the Early Middle Ages, Early and High Middle Ages. The Slavs' original homeland is still a matter of debate due to a lack of historical records; however, scholars generally place it in Eastern Europe, with Polesia being the most commonly accepted location. It is generally agreed that ancient Roman writers referred to the ancestors of Slavs as Vistula Veneti, Venedi. The proto-Slavic term ''Slav'' shares roots with Slavic terms for ''speech'', ''word'' , and perhaps was used by early Slavic people themselves to denote other people, who spoke languages similar to Slavs (ethnonym), theirs. The first written use of the name "S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |