|
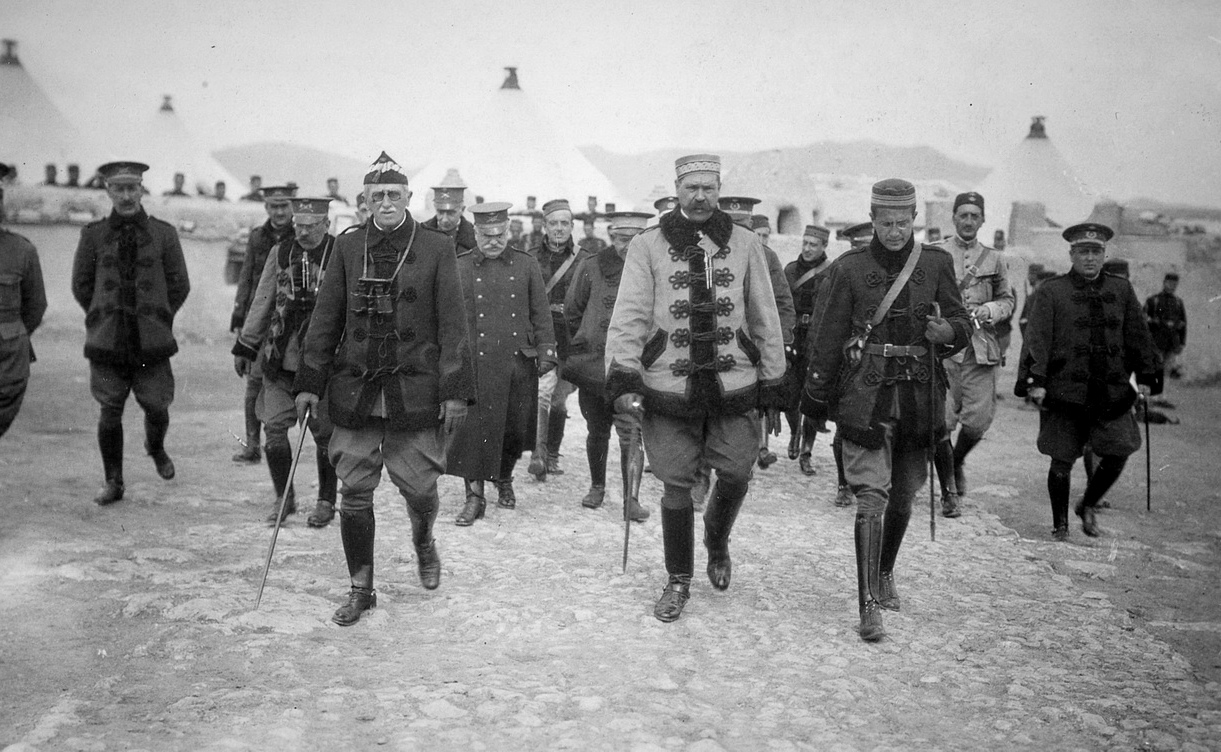
General De Lattre
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny (2 February 1889 – 11 January 1952) was a French ''général d'armée'' during World War II and the First Indochina War. He was posthumously elevated to the dignity of Marshal of France in 1952. As an officer during World War I, he fought in various battles, including at Verdun, and was wounded five times, surviving the war with eight citations, the Legion of Honour, and the Military Cross. During the Interwar period, he took part in the Rif War in Morocco, where he was again wounded in action. He went on to serve in the Ministry of War and the staff of ''Conseil supérieur de la guerre'' under the vice president ''Général d'armée'' Maxime Weygand. Early in World War II, from May to June 1940, he was the youngest French general. He led the 14th Infantry Division during the Battle of France in the battles of Rethel, Champagne-Ardenne, and Loire, until the Armistice of 22 June 1940. During the Vichy Regime he remained in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshal Of France
Marshal of France (, plural ') is a French military distinction, rather than a military rank, that is awarded to General officer, generals for exceptional achievements. The title has been awarded since 1185, though briefly abolished (1793–1804) and for a period dormant (1870–1916). It was one of the Great Officers of the Crown of France during the and Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration, and one of the Grand Dignitaries of the French Empire, Grand Dignitaries of the Empire during the First French Empire (when the title was Marshal of the Empire, not Marshal of France). A Marshal of France displays seven stars on each shoulder strap. A marshal also receives a Baton (military), baton – a blue cylinder with stars, formerly fleur-de-lis, fleurs-de-lis during the monarchy and French Imperial Eagle, eagles during the First French Empire. The baton bears the Latin inscription of ', which means "terror in war, ornament in peace". Between the end of the 16th century a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
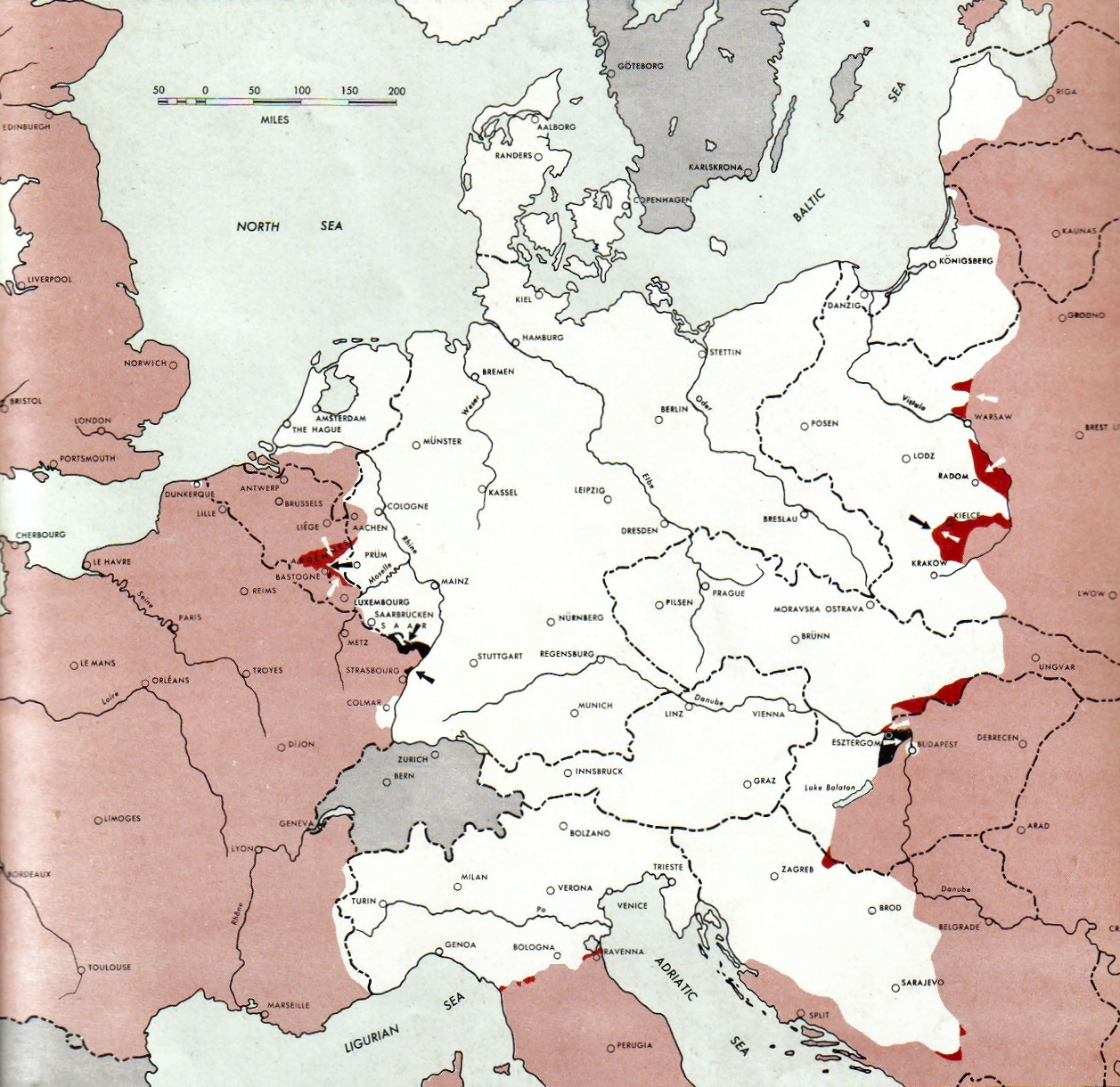
Colmar Pocket
The Colmar Pocket (; ) was the area held in central Alsace, France, by the German Nineteenth Army from November 1944 to February 1945, against the U.S. 6th Army Group (6th AG) during World War II. It was formed when 6th AG liberated southern and northern Alsace and adjacent eastern Lorraine, but could not clear central Alsace. During Operation Nordwind in December 1944, the 19th Army attacked north out of the Pocket in support of other German forces attacking south from the Saar into northern Alsace. In late January and early February 1945, the French First Army (reinforced by the U.S. XXI Corps) cleared the Pocket of German forces. Background Formation of the Pocket A German bridgehead on the west bank of the Rhine long and deep was isolated in November 1944 when the German defenses in the Vosges Mountains The Vosges ( , ; ; Franconian (linguistics), Franconian and ) is a range of medium mountains in Eastern France, near its France–Germany border, border with G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Dragoon
Operation Dragoon (initially Operation Anvil), known as Débarquement de Provence in French ("Provence Landing"), was the code name for the landing operation of the Allies of World War II, Allied invasion of Provence (Southern France) on 15August 1944. Although initially designed to be executed in conjunction with Operation Overlord, the June 1944 Normandy landings, Allied landing in Normandy, the lack of enough resources led to the cancellation of the second landing. By July 1944 the landing was reconsidered, as the clogged-up ports in Normandy did not have the capacity adequately to supply the Allied forces. Concurrently, the high command of the French Liberation Army pushed for a revival of the operation, which would involve large numbers of French troops. As a result, the operation was finally approved in July to be executed in August. The invasion sought to secure the vital ports on the French Mediterranean coast and increase pressure on the German forces by opening another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Elba
The invasion of Elba, codenamed Operation Brassard, was part of the Italian campaign during the Second World War. The invasion was carried out from 17 to 19 June 1944 by Free French Forces supported by British and American ships and aircraft. According to the testimony of captured Germans, Allied activity had been observed on Corsica, thus the defenders were aware of the impending invasion 24 hours in advance. They resisted for two days before being given permission to withdraw to the mainland. Background Elba The Island of Elba is from the Italian mainland, opposite the coastal town of Piombino in Tuscany. The island is the third largest Italian island after Sicily and Sardinia and the largest of the Tuscan Archipelago. The island is long and varies from wide at the east and west ends to in the middle, The island is dry and mountainous, Monte Capanne, the highest point at , is in the west and the coast has steep cliffs with deep semicircular bays. The population, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands) and French Third Republic, France. The plan for the invasion of the Low Countries and France was called (Case Yellow or the Manstein plan). (Case Red) was planned to finish off the French and British after the Dunkirk evacuation, evacuation at Dunkirk. The Low Countries and France were defeated and occupied by Axis troops down to the Demarcation line (France), Demarcation line. On 3 September 1939, French declaration of war on Germany (1939), France and United Kingdom declaration of war on Germany (1939), Britain declared war on Nazi Germany, over the German invasion of Poland on 1 September. In early September 1939, the French army began the limited Saar Offensive but by mid-October had withdrawn to the start line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rif War (1920)
The Rif War (, , ) was an armed conflict fought from 1921 to 1926 between Spain (joined by History of France, France in 1924) and the Berbers, Berber tribes of the mountainous Rif region of northern Morocco. Led by Abd el-Krim, the Riffians at first inflicted several defeats on the Spanish forces by using guerrilla tactics and with the help of captured European weapons. After France's military intervention against Abd el-Krim's forces and the major landing of Spanish troops at Alhucemas landing, Al Hoceima, considered the first Amphibious warfare, amphibious landing in history to involve the use of tanks and aircraft, Abd el-Krim surrendered to the French and was taken into exile. In July 1909, Spanish workers constructing a rail-bridge providing access to iron mines near Melilla were attacked by Riffian tribesmen. This incident led to the summoning of reinforcements from Spain itself. A series of skirmishes over the following weeks cost the Spanish over a thousand casualties. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Battle Of The Aisne
The Third Battle of the Aisne () was part of the German spring offensive during World War I that focused on capturing the Chemin des Dames Ridge before the American Expeditionary Forces arrived completely in French Third Republic, France. It was one of a series of offensives, known as the German spring offensive, ''Kaiserschlacht'', launched by the Germans in the spring and summer of 1918. Background The massive surprise attack (named ''Blücher-Yorck'' after two Prussian generals of the Napoleonic Wars) lasted from 27 May until 4 June 1918 and was the first full-scale German offensive following the Battle of the Lys (1918), Lys Offensive in Flanders in April. The Germans held the Chemin des Dames Ridge from the First Battle of the Aisne in September 1914 to 1917, when General Charles Mangin, Mangin captured it during the Second Battle of the Aisne (in the Nivelle Offensive). Operation Blücher-Yorck was planned primarily by General Erich Ludendorff, the First Quartermaster g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun ( ; ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front in French Third Republic, France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north of Verdun. The German 5th Army (German Empire), 5th Army attacked the defences of the Fortified Region of Verdun (RFV, ) and those of the French Second Army (France), Second Army on the right (east) bank of the Meuse. Using the experience of the Second Battle of Champagne in 1915, the Germans planned to capture the Meuse Heights, an excellent defensive position, with good observation for artillery-fire on Verdun. The Germans hoped that the French would commit their strategic reserve to recapture the position and suffer catastrophic losses at little cost to the German infantry. Poor weather delayed the beginning of the attack until 21 February but the Germans captured Fort Douaumont in the first three days. The advance then slowed for seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |