|
Gated Commit
A gated commit, gated check-in or pre-tested commit is a software integration pattern that reduces the chances for breaking a build (and often its associated tests) by committing changes into the main branch of version control. This pattern can be supported by a continuous integration (CI) server. To perform a gated commit the software developer must request a gated commit from the CI server before committing the actual changes to a central location. The CI server merges the local changes with the head of the master branch and performs the validations (build and tests) that make up the gate. So the developer can see if his or her changes break the build without actually committing the changes. A commit to the central location will only be allowed if the gates are cleared. As an alternative this pattern can be realized using different branches in version control. For instance, GitHub can force all commits to a branch B to be merge commits from pull requests which have successfully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Studio
Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) developed by Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs including web site, websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms including Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), Microsoft Store and Microsoft Silverlight. It can produce both machine code, native code and managed code. Visual Studio includes a code editor supporting IntelliSense (the code completion component) as well as code refactoring. The integrated debugger works as both a source-level debugger and as a machine-level debugger. Other built-in tools include a Profiling (computer programming), code profiler, designer for building GUI applications, web designer, class (computing), class designer, and database schema designer. It accepts plug-ins that expand the functionality at almost every level—including adding support for source control systems (like Subver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Pattern
A design pattern is the re-usable form of a solution to a design problem. The idea was introduced by the architect Christopher Alexander and has been adapted for various other disciplines, particularly software engineering. The " Gang of Four" book. Details An organized collection of design patterns that relate to a particular field is called a pattern language. This language gives a common terminology for discussing the situations designers are faced with. Documenting a pattern requires explaining why a particular situation causes problems, and how the components of the pattern relate to each other to give the solution. Christopher Alexander describes common design problems as arising from "conflicting forces"—such as the conflict between wanting a room to be sunny and wanting it not to overheat on summer afternoons. A pattern would not tell the designer how many windows to put in the room; instead, it would propose a set of values to guide the designer toward a deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Build
A software build is the process of converting source code files into standalone artifact (software development), software artifact(s) that can be run on a computer, or the result of doing so. In software production, builds optimize software for performance and distribution, packaging into formats such as '.''exe'; '.deb'; '.apk. The build process often employs specialized tools such as CMake, Make, or Gradle, and integrates with automation systems including Jenkins (software), Jenkins or Git Actions. Despite advancements, challenges such as dependency conflicts, platform compatibility, and long compile times, remain problems. Software development In software development, building software is an end-to-end process that involves many distinct functions. Some of these functions are described below. Version control The version control function carries out activities such as workspace creation and updating, baselining and reporting. It creates an environment for the build process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version Control
Version control (also known as revision control, source control, and source code management) is the software engineering practice of controlling, organizing, and tracking different versions in history of computer files; primarily source code text files, but generally any type of file. Version control is a component of software configuration management. A ''version control system'' is a software tool that automates version control. Alternatively, version control is embedded as a feature of some systems such as word processors, spreadsheets, collaborative groupware, web docs, and content management systems, e.g., Help:Page history, Wikipedia's page history. Version control includes viewing old versions and enables Reversion (software development), reverting a file to a previous version. Overview As teams develop software, it is common to Software deployment, deploy multiple versions of the same software, and for different developers to work on one or more different versions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
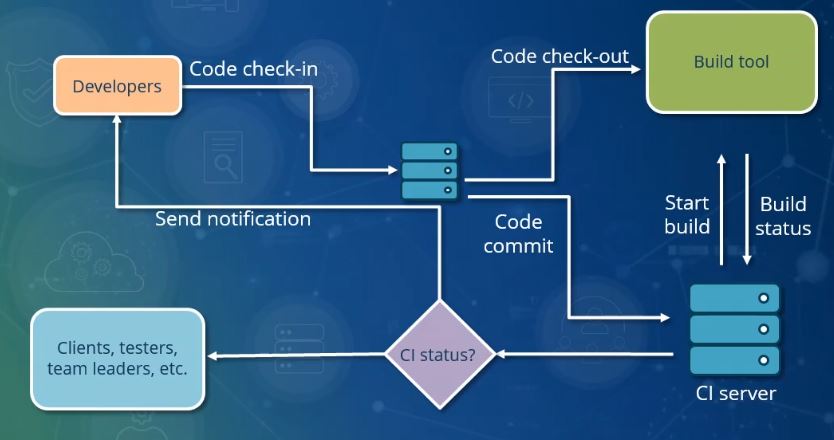
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branching (version Control)
Branching, in version control and software configuration management, is the duplication of an object under version control (such as a source code file or a directory tree). Each object can thereafter be modified separately and in parallel so that the objects become different. In this context the objects are called branches. The users of the version control system can branch any branch. Branches are also known as ''trees'', ''streams'' or ''codelines''. The originating branch is sometimes called the ''parent branch'', the ''upstream branch'' (or simply ''upstream'', especially if the branches are maintained by different organizations or individuals), or the ''backing stream''. Trunk ''Child branches'' are branches that have a parent; a branch without a parent is referred to as the ''trunk'' or the ''mainline''. The trunk is also sometimes loosely referred to as HEAD, but properly head refers not to a branch, but to the most recent commit on a given branch, and both the trunk and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pull Request
In software development, distributed version control (also known as distributed revision control) is a form of version control in which the complete codebase, including its full history, is mirrored on every developer's computer. Compared to centralized version control, this enables automatic management branching and merging, speeds up most operations (except pushing and fetching), improves the ability to work offline, and does not rely on a single location for backups. Git, the world's most popular version control system, is a distributed version control system. In 2010, software development author Joel Spolsky described distributed version control systems as "possibly the biggest advance in software development technology in the astten years". Distributed vs. centralized Distributed version control systems (DVCS) use a peer-to-peer approach to version control, as opposed to the client–server approach of centralized systems. Distributed revision control synchronizes reposi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TeamCity
TeamCity is a build management and continuous integration server from JetBrains. It was first released on October 2, 2006 and is commercial software and licensed under a proprietary license: a freemium license for up to 100 build configurations and three free Build Agent licenses are available. open-source projects may request a free license. Features * Gated commits (prevents developers from breaking sources in a version control system by running the build remotely for local changes prior to commit) *Build Grid. Allows running multiple builds and tests under different platforms and environments simultaneously *Integrated code coverage, inspections and duplicates search *Integration with IDEs: Eclipse, IntelliJ IDEA, Visual Studio *Platforms supported: Java, .NET and Ruby Version control systems TeamCity supports the following version control systems: * Git * Mercurial (hg) *Subversion (svn) * Perforce *Concurrent Versions System (CVS) * StarTeam * ClearCase (Base and UC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |