|
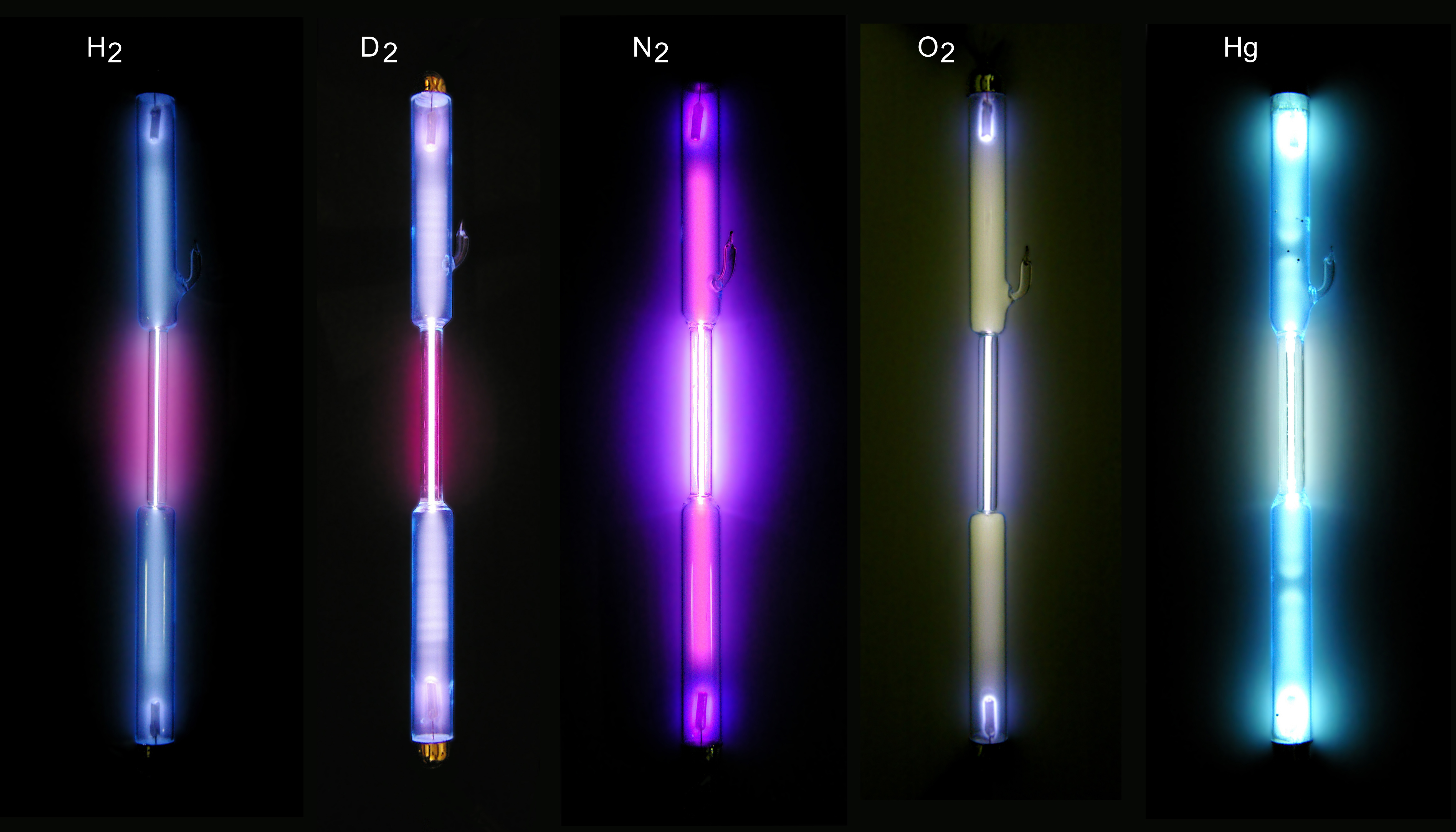
Gas-filled Tube
A gas-filled tube, also commonly known as a discharge tube or formerly as a Julius Plücker, Plücker tube, is an arrangement of electrodes in a gas within an dielectric, insulating, temperature-resistant envelope. Gas-filled tubes exploit phenomena related to electric discharge in gases, and operate by ionisation, ionizing the gas with an applied voltage sufficient to cause electrical conduction by the underlying phenomena of the Townsend discharge. A gas-discharge lamp is an electric light using a gas-filled tube; these include fluorescent lamps, metal-halide lamps, sodium-vapor lamps, and neon lights. Specialized gas-filled tubes such as krytrons, thyratrons, and ignitrons are used as switching devices in electric devices. The voltage required to initiate and sustain discharge is dependent on the pressure and composition of the fill gas and geometry of the tube. Although the envelope is typically glass, power tubes often use ceramics, and military tubes often use glass-line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas-filled tube used as a high-power electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Thyratrons can handle much greater currents than similar hard-vacuum tubes. Electron multiplication occurs when the gas becomes ionized, producing a phenomenon known as a Townsend discharge. Gases used include mercury vapor, xenon, neon, and (in special high-voltage applications or applications requiring very short switching times) hydrogen. Unlike a vacuum tube (valve), a thyratron cannot be used to amplify signals linearly. In the 1920s, thyratrons were derived from early vacuum tubes such as the UV-200, which contained a small amount of argon gas to increase its sensitivity as a radio signal detector, and the German LRS relay tube, which also contained argon gas. Gas rectifiers, which predated vacuum tubes, such as the argon-filled General Electric " Tungar bulb" and the Cooper-Hewitt mercury-pool rectifier, also provided an influence. Irving Langmuir and G. S. Meikle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossatron
In electronics, a crossatron is a high-power pulsed modulator device that consists of a cold cathode gas-filled tube that combines features of thyratrons, vacuum tubes, and power semiconductor switches. This switch is capable of operating with voltages in excess of 100 kilovolts by the use of deuterium gas fill to increase the Paschen breakdown voltage, axial molybdenum cathode corrugations to provide a higher current capability, and a Paschen shield that is formed from molybdenum. The terminal curvature of the Paschen shield and of the adjacent portion of the anode are selected to establish a voltage stress at the curved Paschen shield surface within the approximate range of 90–150 kV/cm in response to a 100 kV differential. The cold cathode gives the crossatron an advantage of achievable lifetime and reliability in comparison to a hydrogen-filled thyratron. It features fast start-up speeds and operates well when enduring high temperatures, high radiation, electromagnetic pul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Generator
Neutron generators are neutron source devices which contain compact linear particle accelerators and that produce neutrons by fusing isotopes of hydrogen together. The nuclear fusion, fusion reactions take place in these devices by accelerating either deuterium, tritium, or a mixture of these two isotopes into a metal hydride target which also contains deuterium, tritium or a mixture of these isotopes. Fusion of deuterium atoms (D + D) results in the formation of a helium-3 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 2.5 MeV. Fusion of a deuterium and a tritium atom (D + T) results in the formation of a helium-4 ion and a neutron with a kinetic energy of approximately 14.1 MeV. Neutron generators have applications in medicine, security, and materials analysis. The basic concept was first developed by Ernest Rutherford's team in the Cavendish Laboratory in the early 1930s. Using a linear accelerator driven by a Cockcroft–Walton generator, Mark Oliphant l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. These inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. The photons of ultraviolet have greater energy than those of visible light, from about 3.1 to 12 electron volts, around the minimum energy required to ionize atoms. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack sufficient energy, it can induce chemical reactions and cause many substances to glow or fluoresce. Many practical applications, including chemical and biological effects, are derived from the way that UV radiation can interact with organic molecules. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterium
Deuterium (hydrogen-2, symbol H or D, also known as heavy hydrogen) is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen; the other is protium, or hydrogen-1, H. The deuterium nucleus (deuteron) contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common H has no neutrons. The name ''deuterium'' comes from Greek '' deuteros'', meaning "second". American chemist Harold Urey discovered deuterium in 1931. Urey and others produced samples of heavy water in which the H had been highly concentrated. The discovery of deuterium won Urey a Nobel Prize in 1934. Nearly all deuterium found in nature was synthesized in the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, forming the primordial ratio of H to H (~26 deuterium nuclei per 10 hydrogen nuclei). Deuterium is subsequently produced by the slow stellar proton–proton chain, but rapidly destroyed by exothermic fusion reactions. The deuterium–deuterium reaction has the second-lowest energy threshold, and is the most astrophysically acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen (H−), a hydrogen ion with two electrons. In modern usage, this is typically only used for ionic bonds, but it is sometimes (and has been more frequently in the past) applied to all chemical compound, compounds containing covalent bond, covalently bound H atoms. In this broad and potentially archaic sense, water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. In covalent compounds, it implies hydrogen is attached to a less electronegative chemical element, element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form Binary compounds of hydrogen, binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being helium, He, neon, Ne, argon, Ar, krypton, Kr, promethium, Pm, osmium, Os, iridium, Ir, radon, Rn, francium, Fr, and radium, Ra. exotic atom#exotic molecules, Exotic molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dekatron
In electronics, a Dekatron (or Decatron, or generically three-phase gas counting tube or glow-transfer counting tube or cold cathode tube) is a gas-filled decade counting tube. Dekatrons were used in computers, calculators, and other counting-related products during the 1950s and 1960s. "Dekatron" was the brand name used by Ericsson Telephones Limited (ETL), of Beeston, Nottingham (not to be confused with the Swedish TelefonAB Ericsson of Stockholm) and has since become a generic trademark. The device was invented by John Reginald Acton, with the patent assigned to Ericsson. US2651004A The dekatron was useful for computing, calculating, and frequency-dividing purposes because one complete revolution of the neon dot in a dekatron usually means 10 pulses on the guide electrode(s), and a signal can be derived from one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
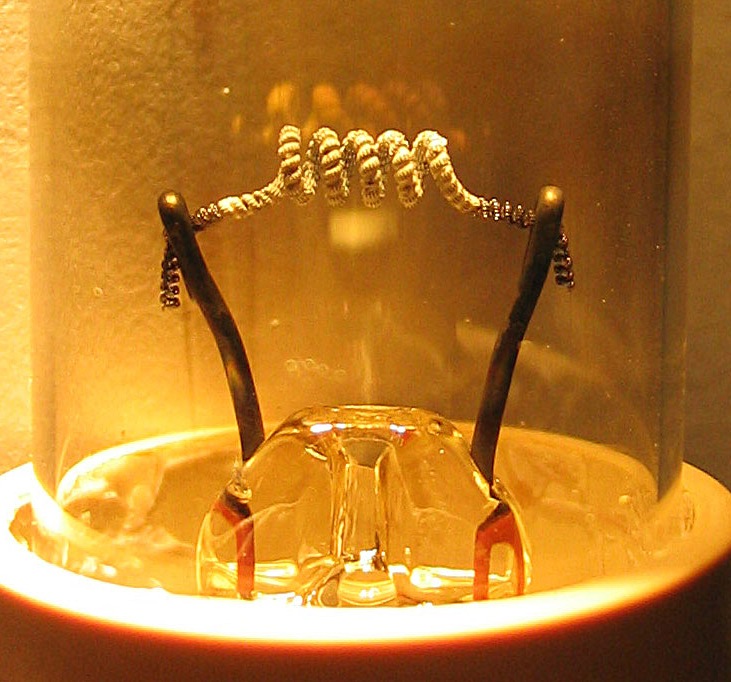
Cold Cathode
A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a Electrical filament, filament.A negatively charged electrode emits electrons or is the positively charged terminal. For more, see field emission. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more electrons than can be supplied by thermionic emission alone. It is used in Gas discharge lamp, gas-discharge lamps, such as neon lamps, discharge tubes, and some types of vacuum tube. The other type of cathode is a hot cathode, which is heated by electric current passing through a Electrical filament, filament. A cold cathode does not necessarily operate at a low temperature: it is often heated to its operating temperature by other methods, such as the current passing from the cathode into the gas. Cold-cathode devices A cold-cathode vacuum tube does not rely on external heating of an electrode to provide thermionic emission of electrons. Early cold-cathode devices included the Geissler tube and Julius Plücker, Plucker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Cathode
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |