|
Gambia River
The Gambia River (formerly known as the River Gambra, French language, French: ''Fleuve Gambie'', Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Rio Gâmbia'') is a major river in West Africa, running from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigability, navigable for about half that length. The river is strongly associated with The Gambia, the smallest country in mainland Africa, which occupies the downstream half of the river and its two banks. Geography The Gambia River runs a total length of . From the Fouta Djallon, it runs northwest into the Tambacounda Region of Senegal, where it flows through the Parc National du Niokolo Koba, then is joined by the Nieri Ko and and passing through the Barrakunda Falls before entering the Gambia at Koina. At this point, the river runs generally west, but in a meandering course with a number of Oxbow lake, oxbows, and about from its mouth it gradually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niokolo-Koba National Park
The Niokolo-Koba National Park (, PNNK) is a World Heritage Site and natural protected area in southeastern Senegal, near the Guinea border. It is served by Niokolo-Koba Airport, an unpaved airstrip. National park Established as a reserve in 1925, Niokolo-Koba was declared a Senegalese national park on 1 January 1954. Expanded in 1969, it was inscribed as a World Heritage Site in 1981 as a UNESCO-MAB Biosphere Reserve. In 2007, it was added to the UNESCO List of Endangered World Heritage sites. It was removed from the list in 2024, following improvements in the park's state of conservation. Since 2005, the protected area is considered a West African lion, Lion Conservation Unit. Geography The park lies in an upland region through which the upper stretch of the Gambia River flows, towards the northwestern border of Guinea. The biosphere park itself covers some 9,130 square kilometres, in a great arc running from Upper Casamance/Kolda Region at the Guinea-Bissau border into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxbow Lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or stream pool, pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is meander cutoff, cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. The word "oxbow" can also refer to a U-shaped bend in a river or stream, whether or not it is cut off from the main stream. It takes its name from an oxbow which is part of a harness for oxen to pull a plough or cart. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called ''resaca (channel), resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are called billabongs. Geology An oxbow lake forms when a meandering river erodes through the neck of one of its meanders. This takes place because meanders tend to grow and become more curved over time. The river then follows a shorter course that bypasses the meander. The entrances to the abandoned meander eventually silt up, forming an oxbow lake. Oxbow lakes are stillwater lakes, with no current flowing through them, which causes the lake bed to gradually accumulate silt, becoming a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jola People
The Jola or Diola (endonym: Ajamat) are an ethnic group found in Senegal, the Gambia, and Guinea-Bissau. Most Jola live in small villages scattered throughout southern Senegal, especially in the Lower Casamance region. The main dialect of the Jola language, Fogni, is one of the six national languages of Senegal. Their economy has been based on wet rice cultivation for at least one thousand years. This system has been characterised "one of the most significant examples of 'agrarian civilizations' in West Africa". However, the Jola probably reached the Lower Casamance region in the 14th century, assimilating the previous Bainuk people and their rice tradition. In colonial times, the Jola began to cultivate peanuts as a cash crop in the drier forests. Other activities include palm wine tapping, honey collecting, livestock rearing and the production of other crops such as sweet potatoes, yams and watermelon. The traditional religion of the Jola is animism, which is practise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
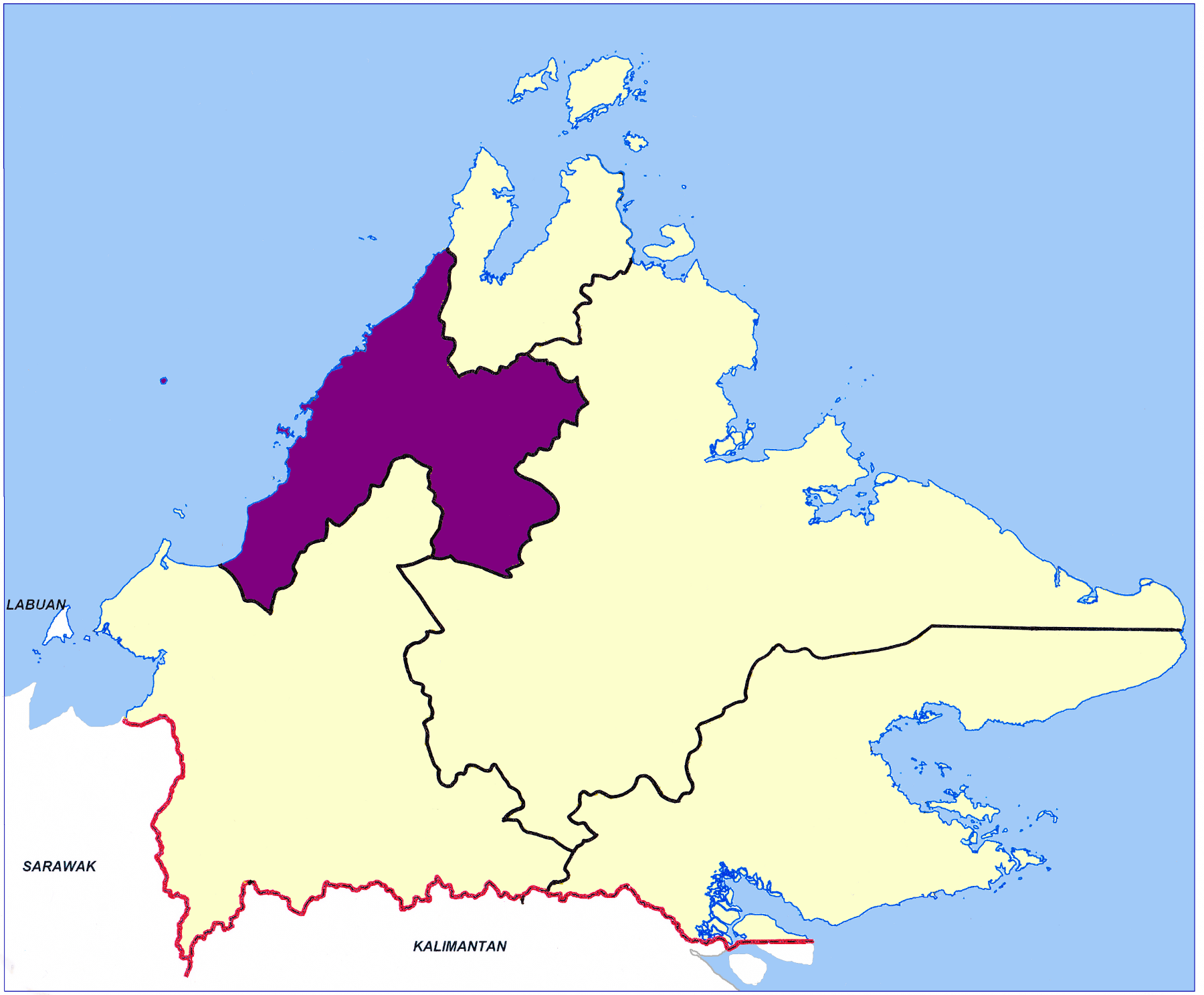
West Coast Division
West Coast Division () is an administrative Divisions of Malaysia, division of Sabah, Malaysia. It occupies the northwest portion of Sabah. With an area of 7,588 square kilometres, it occupies 10.3% of Sabah's territory. It also has approximately 30% of Sabah's total population, with the main indigenous inhabitants comprising the Bajau people, Bajau, Bisaya (Borneo), Bisaya, Bruneian Malay people, Bruneian Malay, Dusun people, Dusun, Illanun people, Illanun, Kadazan people, Kadazan and Kedayan, as well with a significant numbers of Malaysian Chinese, Chinese. The division is divided into the Districts of Malaysia, districts of Ranau District, Ranau, Kota Belud District, Kota Belud, Tuaran District, Tuaran, Penampang District, Penampang, Papar District, Papar, Putatan District, Putatan and the state capital Kota Kinabalu District, Kota Kinabalu. The main towns are as in the names of the districts, plus other towns including Petagas, Lok Kawi, Menggatal, Inanam, Telipok, Tamparuli, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower River Division
Lower River Division is one of the five administrative divisions of the Gambia. Its capital is Mansa Konko. The city and area council elections were held during April 2002, when Wally S.M. Sanneh, an APRC candidate became the Mayor, winning unopposed. The council was led by Alliance for Patriotic Reorientation and Construction (APRC), which won all the 12 seats. Per 2013 census, the region had a population of 82,361 with a population density of 051. The total number of households was 8,474 as of 2003. As of 2003, the total area of the region is 1618 km2. The infant mortality rate was 96 for every thousand births and the under-five mortality was 137 per every thousand births. Geography The Gambia is the smallest country in mainland Africa, and the width of the strip-like structure never exceeds . It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean on the west, and is otherwise surrounded by Senegal. The Gambia River flows throughout the country and is the principal source of water and tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central River Division
Central River is the largest of the five administrative divisions of the Gambia. Its capital is Janjanbureh (formerly Georgetown), on MacCarthy Island. The largest settlement is Bansang, with an estimated population in 2008 of 8,381. Until 1995 the division was known as MacCarthy Island Division, which had been established as one of five administrative areas of Gambia Protectorate in the early 20th century. It is located on both sides of the Gambia River, and its total population according to the 2013 census is 226,018. The total number of households is 17,399 as of 2003. As of 2003, the total area of the region is 2894.3 km2. Geography The Gambia is the smallest country in Africa and the width of the strip like structure never exceeding . It is bordered by Atlantic Ocean to the West, and otherwise surrounded by Senegal. The Gambia River flows throughout the country and is the principal source of water and transport medium. The banks of the river has swampy beaches, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barra, Gambia
Barra, traditionally known as Niumi, is a city in The Gambia, located in the district of Lower Niumi. The predominant languages of the city are Serer and Wolof. Although Mandinka-speaking Africans always referred to the state along the north bank of the Gambia River's estuary as Niumi, not everyone did. For a long time it was called "Barra" in the creolized trade language of the river, and between the seventeenth and nineteenth centuries British British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ... and French records use "Barra" or "Bar" more frequently than "Niumi". See also * Niumi National Park References External links Lower Niumi Populated places in the Gambia Gambia River Serer country {{Gambia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatoto
Fatoto is a small town in eastern The Gambia, Gambia on the Gambia River. It is located in Kantora District in the Upper River Division. As of 2009, it had an estimated population of 1,685. Fatoto was a major market town in the Upper River Region by at least 1921, attracting business from neighboring Senegal. A bridge over the Gambia river, funded by the Chinese government, opened in October 2021. Climate References Populated places in the Gambia Upper River Division {{Gambia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basse Santa Su
Basse Santa Su, usually known as Basse, is a town in the Gambia, lying on the south bank of the River Gambia. The easternmost major town in the nation, it is known for its important market. Basse is the capital of the Upper River Division, which is coterminous with the Basse Local Government Areas of the Gambia, Local Government Area. As of 2009, the town has an estimated population of 18,414. According to the 2013 census, the Basse LGA has 243,791 residents. Famous people include Adama Barrow, the president of Gambia. History According to oral histories, the first Mandinka people, Mandinka immigrants to the Gambia area, the Fati clan, settled in Tumana, Gambia, Tumana near Basse. They subsequently acted as hosts and/or agents for future migrants, potentially including Tiramakhan Traore. Basse was at this point a hub in regional trade networks bringing kola nuts and Guinea pepper north from what is now Guinea-Bissau and salt and salted fish up the river from the coast. A bridge o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper River Division
Upper River was one of the five Subdivisions of the Gambia, Divisions of the Gambia. Its capital was Basse Santa Su. It was subsequently reorganised as the Basse (Gambia), Basse Local Government Area, without any change in the area covered. Per 2013 census, the region had a population of 239,916 with a population density of 116. The total number of households was 12,454 as of 2003. As of 2003, the total area of the region is 2069.5 km2. The infant mortality rate was 82 for every thousand births and the under-five mortality was 110 per every thousand births. The poverty gap ratio was 25.9 per cent as of 2003 and the literacy rate was 49.5 per cent. Geography The Gambia is the smallest country in Africa and the width of its strip-like territory never exceeds . It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and otherwise surrounded by Senegal. The Gambia River flows throughout the country and is the principal source of water and transport medium. The banks of the river have swamp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casamance
Casamance is the area of Senegal south of the Gambia, including the Casamance River. It consists of the Lower Casamance (, —i.e. Ziguinchor Region) and the Upper Casamance (, —i.e. Kolda and Sédhiou Regions). The largest city of Casamance is Ziguinchor. Etymology Because this southern region of Senegal boasts a coastline that was early visited by Portuguese navigators, there has long been speculation about a Lusophone influence in its name. In his Wolof-French Dictionary published in 1923 by the Catholic Mission of Dakar, Aloyse Kobès provides the following definition: "Kasamansa (Casamance), derived from (Portuguese), meaning house, dwelling, and ''mansa'' ( Mandingo), meaning king, chief." Peoples Casamance is mainly inhabited by the Jola and Bainuk. Significant minority populations include the Balanta, Mande and Fulani. Casamance is religiously diverse, with the inhabitants practicing Islam, Christianity, and traditional African religions. History Accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-Gambia Highway
The Trans-Gambia Highway is a major highway in The Gambia, running across the centre of the nation in a north–south direction. Within the Gambia, the highway consists of two main stretches, the North Bank Road and South Bank Road, each corresponding to the parts of the country on either side of the Gambia River. The two roads are connected via the Senegambia bridge between Farafenni and Soma, as well as bridges at Basse Santa Su and Fatoto, at the far eastern end of the country. Prior to the building of these bridge, the crossings were served by a ferry. Aside from a short four-lane section in Kombo, both the North Bank and South Bank roads are paved two lane highways. The road is also economically important for Senegal, in which it is designated as the N4 road. Geography The Gambia is an elongated state forming a country that is almost surrounded by Senegal (but not an enclave, as it also borders the Atlantic Ocean). The Gambia almost separates the Casamance region fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |