|
Gaelic Psalm
Gaelic psalm singing, or Gaelic psalmody (), is a tradition of exclusive psalmody in the Scottish Gaelic language found in Presbyterian churches in the Western Isles of Scotland. It is a form of Gaelic music. Structure and style The psalms are sung unaccompanied, in a style known as "lining out" or "precenting the line," in which the leader of the performance, or "precentor," sings a line, after which the rest of the congregation follows, with each member allowed to embellish the melody as they wish, in a free heterophonic fashion. The style of Gaelic psalm singing is influenced by piobaireachd music native to the Scottish Highlands, with frequent and distinctive use of ornamentation and grace notes. History The practice of lining out psalms was common in England and lowland Scotland in the 17th century. In 1644, the Westminster Assembly mandated its use as an official form of worship but there is evidence that it was a folk custom in English Protestant churches even before then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Ruff
Willie Henry Ruff Jr. (September 1, 1931 – December 24, 2023) was an American jazz musician, specializing in the French horn and double bass, and a music scholar and educator, primarily as a Yale professor from 1971 to 2017. Personal life Willie Henry Ruff Jr. was born in Sheffield, Alabama on September 1, 1931. He attended the Yale School of Music as an undergraduate (Bachelor of Music, 1953) and graduate student (Master of Music, 1954). Ruff died in Killen, Alabama on December 24, 2023, at the age of 92. Professional career Performing Ruff played in the Mitchell-Ruff Duo with pianist Dwike Mitchell for over 50 years. Mitchell and Ruff first met in 1947, when they were teenaged servicemen stationed at the former Lockbourne Air Force Base in Ohio; Mitchell recruited Ruff to play bass with his unit band for an Air Force radio program. Mitchell and Ruff later played in Lionel Hampton's band but left in 1955 to form their own group. Together as the Mitchell-Ruff Duo, they pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martyn Bennett
Martyn Bennett (17 February 1971 – 30 January 2005) was a Canadian-Scottish musician who was influential in the evolution of modern Celtic fusion, a blending of traditional Celtic music, Celtic and modern music. He was a piper, violinist, composer and producer. Diagnosis of serious illness at the age of thirty curtailed his live performances, although he completed a further two albums in the studio. He died from cancer in 2005, fifteen months after the release of his fifth album ''Grit (Martyn Bennett album), Grit''. Early life He was born Martyn Bennett-Knight in St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. His father, Ian Knight, was a Welsh geologist and musician. His mother was Margaret Bennett (writer), Margaret Bennett, a singer and folklorist who was born on Skye. His grandfather, George Bennett, was also an enthusiastic piper. Martyn Bennett spent the first five years of his life in the Codroy Valley, where Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic and traditional music were parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capercaillie (band)
Capercaillie are a Scottish folk band, founded in 1984 by Donald Shaw and led by Karen Matheson, and which performs traditional Gaelic and contemporary songs in English. The group adapts traditional Gaelic music and traditional lyrics with modern production techniques and instruments such as electric guitar and bass guitar, though rarely synthesizers or drum machines. They have sold over a million albums world-wide, including "three silver and one gold album in the UK". The BBC notes that the band has "achieved enormous global success both as a group and as individual musicians." Origins Originating from Argyll, a region of western Scotland, the band is named after the western capercaillie, sometimes called a wood grouse, a native Scottish bird. Career Their first album, ''Cascade'', was recorded in 1984. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the band gave their last performance on 17 August 2019 at the Festival des Filets Bleus in Concarneau, Brittany, France. They performed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cutter And The Clan
''The Cutter and the Clan'' is the fifth studio album by Scottish Celtic rock band Runrig. Released on 1 December 1987, it was the band's breakthrough album, taking them from cottage industry to the international stage. Initially, it peaked at number seven on the UK Independent Albums Chart in 1988, however, a re–release in 1995 saw it debut at number forty-five on the UK Albums Chart as well as a debut appearance of number thirty one on the Scottish Albums Chart. A further re–release in 2024 saw it reach a new peak in their native Scotland of number twelve. It was also the first Runrig album to feature keyboard player Pete Wishart – forming the "classic" line-up of the band through what would be their most commercially successful period. A 1995 re–release produced the single "An Ubhal as Àirde (The Highest Apple)", which made history by becoming the first song to be performed in Scottish Gaelic to chart in the United Kingdom. Background and release ''The Cutter and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Runrig
Runrig were a Scottish Celtic rock band formed on the Isle of Skye in 1973. From its inception, the band's line-up included brothers and songwriters Rory MacDonald (musician), Rory MacDonald (bass, vocals) and Calum MacDonald (musician), Calum MacDonald (percussion). The line-up during most of the 1980s and 1990s, which was the band's most successful period commercially, also included Donnie Munro (vocals), Malcolm Jones (guitar), Iain Bayne (drums), and Pete Wishart (keyboards). At the height of their success during the 1980s and 1990s, Runrig were described by ''Billboard (magazine), Billboard'' as one of the "most celebrated" Gaelic language bands in Scotland. Their 1995 single "An Ubhal as Àirde (The Highest Apple)" made history by becoming the first song to be sung in Scottish Gaelic to chart on the UK Singles Charts. In 2007, they re–released their 1983 debut single "Loch Lomond (Runrig song), Loch Lomond" with the Tartan Army, entitled "Loch Lomond (Runrig song), Loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
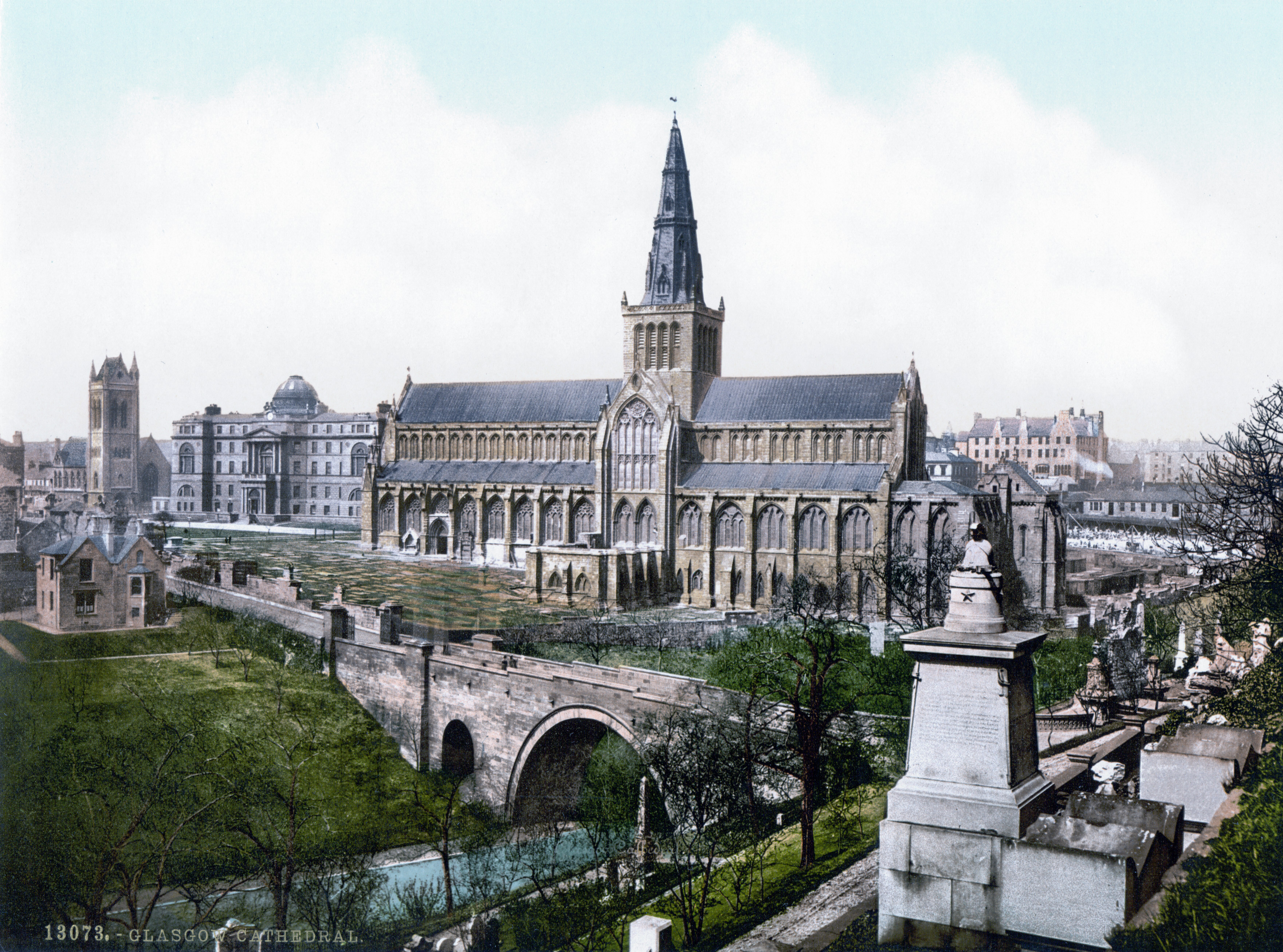
Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom and the 27th-most-populous city in Europe, and comprises Wards of Glasgow, 23 wards which represent the areas of the city within Glasgow City Council. Glasgow is a leading city in Scotland for finance, shopping, industry, culture and fashion, and was commonly referred to as the "second city of the British Empire" for much of the Victorian era, Victorian and Edwardian eras. In , it had an estimated population as a defined locality of . More than 1,000,000 people live in the Greater Glasgow contiguous urban area, while the wider Glasgow City Region is home to more than 1,800,000 people (its defined functional urban area total was almost the same in 2020), around a third of Scotland's population. The city has a population density of 3,562 p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partick
Partick (, Scottish Gaelic: ''Partaig'') is an area of Glasgow on the north bank of the River Clyde, just across from Govan. To the west lies Whiteinch, to the east Yorkhill and Kelvingrove Park (across the River Kelvin), and to the north Broomhill, Glasgow, Broomhill, Hyndland, Dowanhill, Hillhead, areas which form part of the Glasgow#West End, West End of Glasgow. Partick was a Police burgh from 1852 until 1912 when it was incorporated into the city.Second City of The Empire: 1830s to 1914 from theglasgowstory.com. Retrieved 22 December 2011. Partick is the area of the city most connected with the Scottish Highlands, Highlands, and several Gaelic agencies, such as the Gaelic Books Council (Scottish Gaelic: ''Comhairle nan Leabhraichean'') are located in the area. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
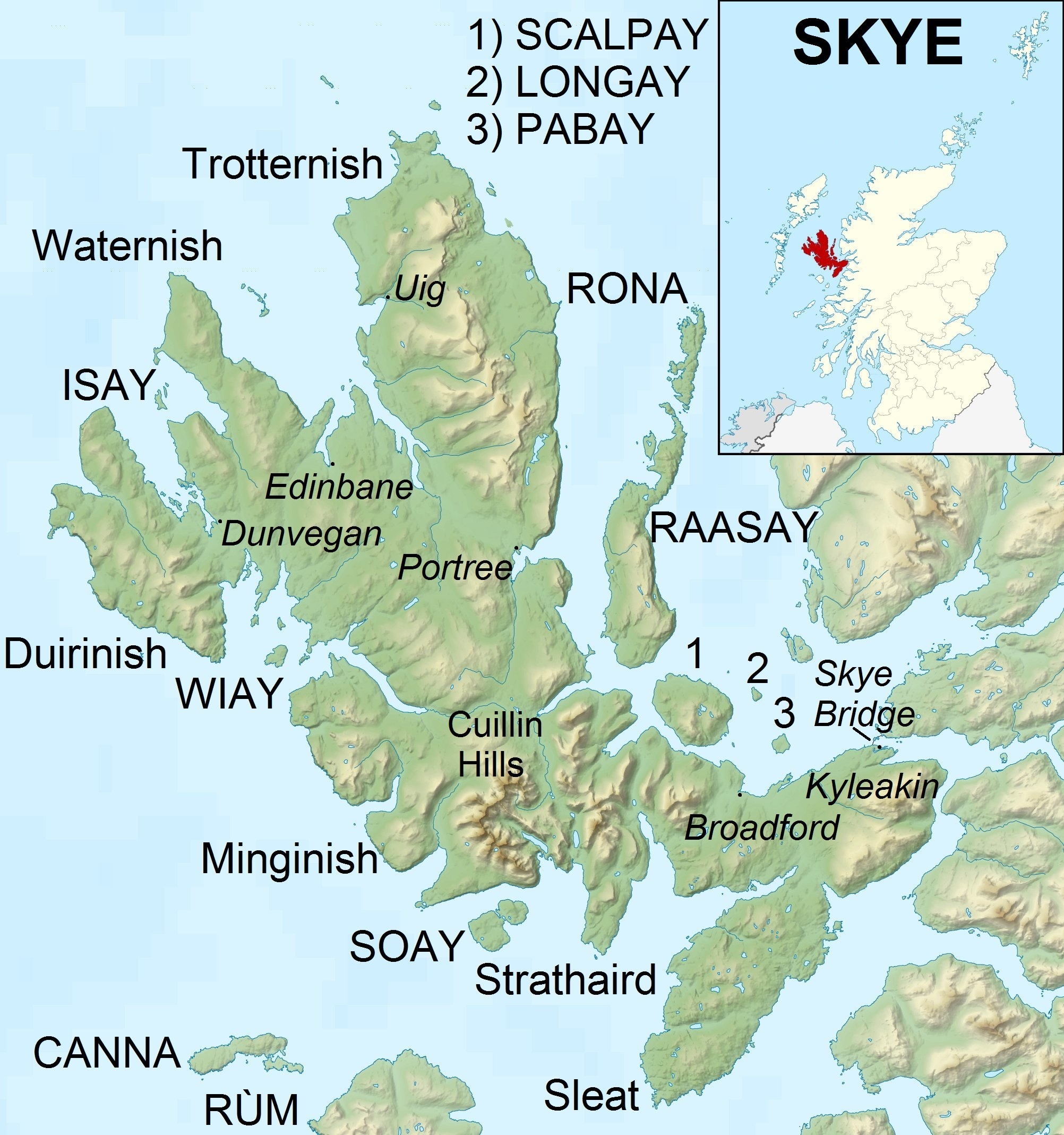
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benbecula
Benbecula ( ; or ) is an island of the Outer Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Scotland. In the 2011 census, it had a resident population of 1,283 with a sizable percentage of Roman Catholics. It is in a zone administered by or the Western Isles Council. The island is about from west to east and a similar distance from north to south. It lies between the islands of North Uist and South Uist and is connected to both by road causeways. Benbecula's main settlement and administrative centre is Balivanich (Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Mhanaich'', meaning "Town of the Monk"). In 1746, Bonnie Prince Charlie was caught in a storm and forced to land on Benbecula. The population of Benbecula were sympathetic to the Jacobite rising of 1745, Jacobite cause, and smuggled him off the island to safety, as the The Skye Boat Song, song has it: "over the sea to Skye". In 2006, local residents took control of parts of the island in a community buy-out. The previous landowners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Uist
North Uist (; ) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. Etymology In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula and South Uist are described as one island of ''Ywst'' (Uist). Starting in the south of this 'island', he described the division between South Uist and Benbecula where "the end heirof the sea enters, and cuts the countrey be ebbing and flowing through it". Further north of Benbecula he described North Uist as "this countrey is called Kenehnache of Ywst, that is in Englishe, the north head of Ywst".''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides''; Monro, Donald, 1549 Some have taken the etymology of Uist from Old Norse, meaning "west", much like Westray in Orkney. Another speculated derivation of Uist from Old Norse is ', derived from ' meaning "an abode, dwelling, domicile". A Gaelic etymology is also possible, with ' meaning "Crossings-island" or "Fords-isl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isle Of Harris
Harris (, ) is the southern and more mountainous part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. Although not an island itself, Harris is often referred to in opposition to the ''Isle of Lewis'' as the Isle of Harris, which is the former postal county and the current post town for Royal Mail postcodes starting HS3 or HS5. The civil parish of Harris is considered to include St Kilda, a now uninhabited archipelago west-northwest of North Uist, and the uninhabited islet Rockall, which is west of North Uist. Etymology The Vikings arrived in the British Isles from the late 700s, and in the Northern Isles and Western Isles of Scotland they named places as part of their conquest. Documents from several centuries ago show the Isle of Harris being referred to as Haray or Harray, Here or Herre, Herrie, and the plural Harreis; as well as possibly related place names such as Harris on the isle of Rum; Herries in Dumfries; Harray on Orkney; and Harrastadh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |