|
GWAS In Allergy
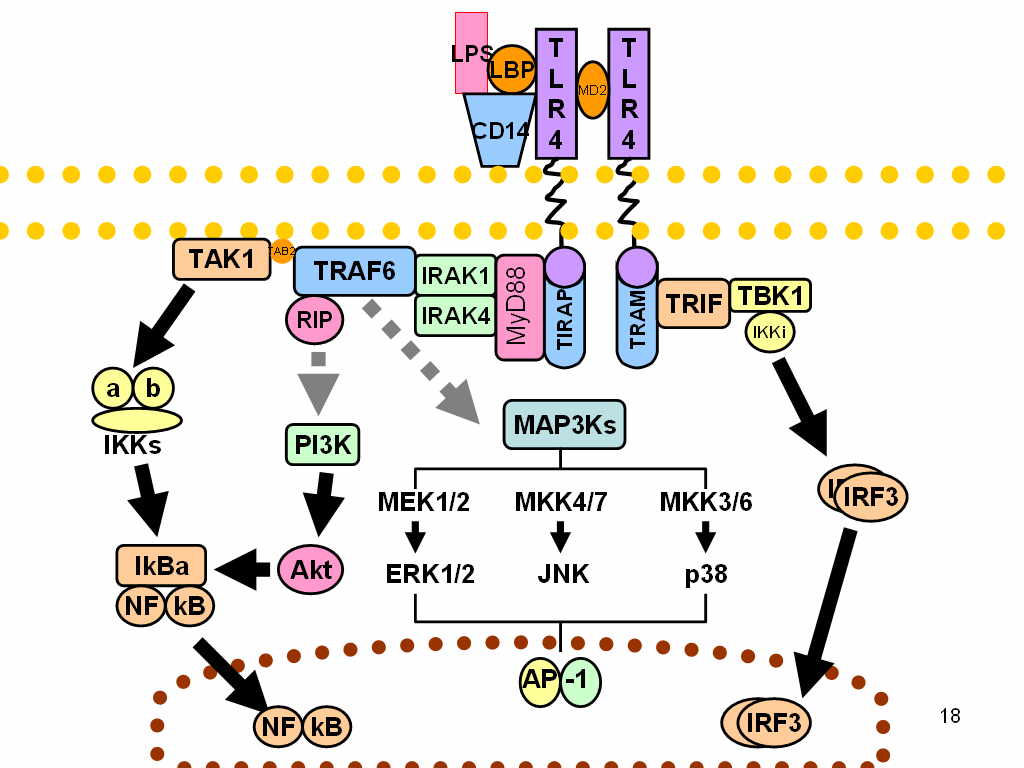
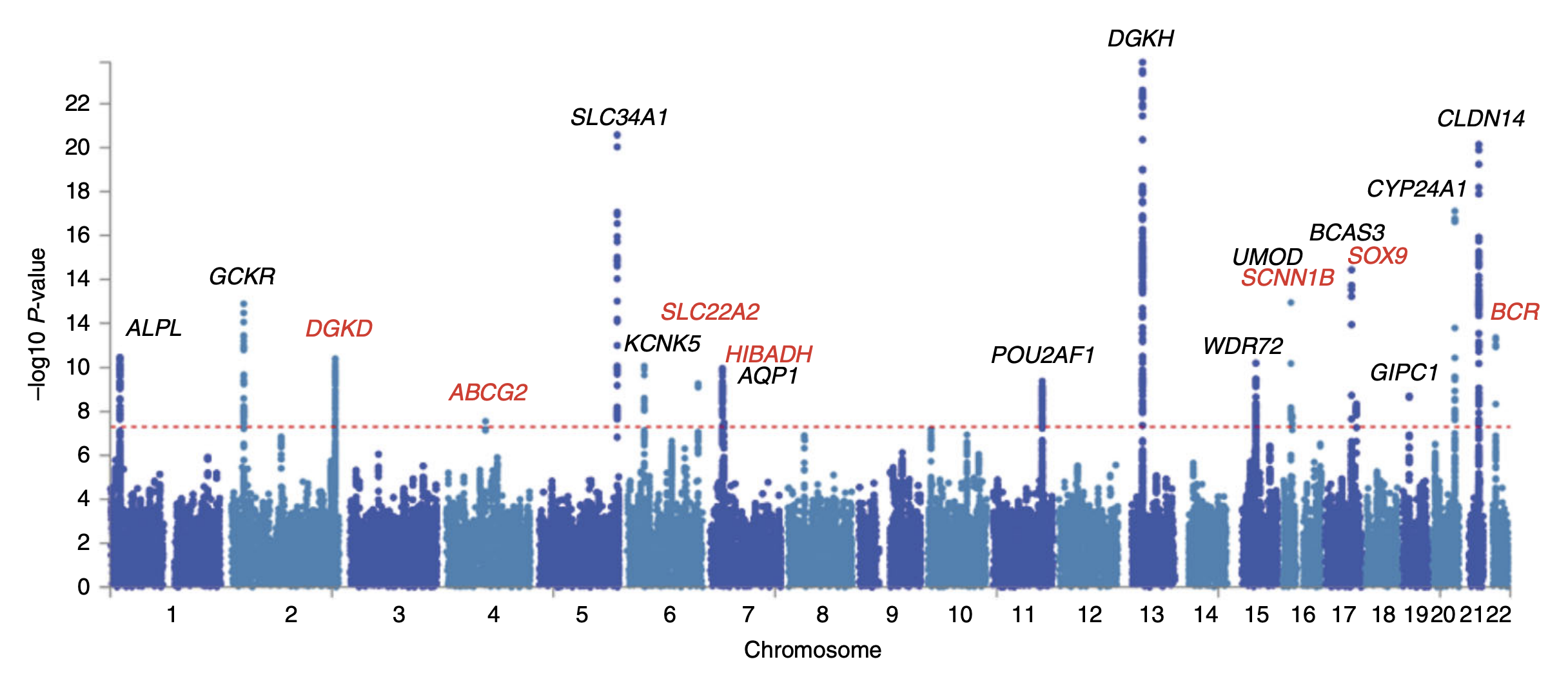
GWAS in allergy is a study of a meta-analysis of genome-wide association study in which allergy is associated with different susceptibility loci . The three allergic phenotypes studied were to cat, dust mites and pollen, for which found patients presenting allergic symptoms. History Allergy is a very common disease and leads to numerous health problems, with allergies and allergic asthma are the two most common diseases in the industrialized world, where half of the population of United States tested positive in a test of awareness for at least one common allergen. It has been shown that this type of disease has risen in prevalence over the past ten years. Furthermore, is estimated that allergy has a hereditary component, suggesting that knowledge of the genetic component is a key to understand the disease. It has been shown that the genes involved in allergy and asthma, are implicated in both immune and inflammatory processes . These genes belong to the family of Toll rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as opposed to Genotype-first approach, genotype-first. Each person gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23andMe
23andMe Holding Co. is an American personal genomics and biotechnology company based in South San Francisco, California. It is best known for providing a direct-to-consumer genetic testing service in which customers provide a saliva testing, saliva sample that is laboratory analysed, using SNP genotyping, single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping, to generate reports relating to the customer's ancestry and genetic predispositions to health-related topics. The company's name is derived from the 23 pairs of chromosomes in a diploid human cell (biology), cell. Founded in 2006, 23andMe soon became the first company to begin offering autosomal DNA testing for ancestry, which all other major companies now use. Its saliva-based direct-to-consumer genetic testing business was named "Invention of the Year" by ''Time (magazine), Time'' in 2008. The company had a previously fraught relationship with the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) due to its genetic health tests; as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
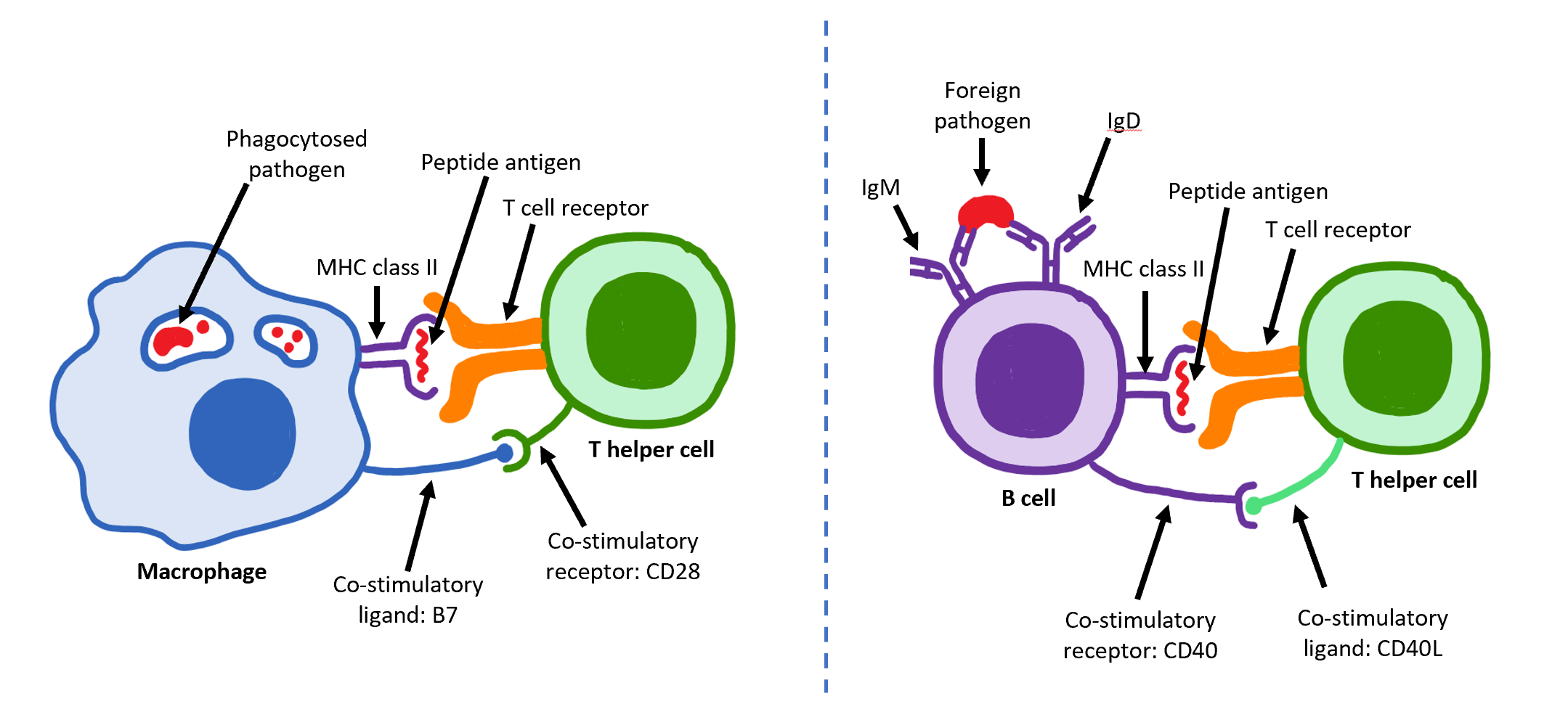
T Helper Cells
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell Immunoglobulin class switching, antibody class switching, breaking Cross-presentation, cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express Receptor (biochemistry), receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spondylitis
Spondylitis is an inflammation of the vertebrae. It is a form of spondylopathy. In many cases, spondylitis involves one or more vertebral joints, as well, which itself is called spondylarthritis. __TOC__ Types Pott disease is a tuberculous disease of the vertebrae marked by stiffness of the vertebral column The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ..., pain on motion, tenderness on pressure, prominence of certain vertebral spines, and occasionally abdominal pain, abscess formation, and paralysis. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a form of arthritis that primarily affects the spine, although other joints can become involved. It causes inflammation of the spinal joints (vertebrae) that can lead to severe, chronic pain and discomfort. In more advanced cases this inflammation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linkage Disequilibrium
Linkage disequilibrium, often abbreviated to LD, is a term in population genetics referring to the association of genes, usually linked genes, in a population. It has become an important tool in medical genetics and other fields In defining LD, it is important first to distinguish the two very different concepts, linkage disequilibrium and linkage (genetic linkage). Linkage disequilibrium refers to the association of genes ''in a population.'' Linkage, on the other hand, tells us whether genes are on the same chromosome ''in an individual''. There is no necessary relationship between the two. Genes that are closely linked may or may not be associated in populations. Looking at parents and offspring, if genes at closely linked loci are together in the parent then they will usually be together in the offspring. But looking at individuals in a population with no known common ancestry, it is much more difficult to see any relationships. To give a concrete, although imaginary, example i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 5
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 5 spans about 182 million base pairs (the building blocks of DNA) and represents almost 6% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 5 is the 5th largest human chromosome, yet has one of the lowest gene densities. This is partially explained by numerous gene-poor regions that display a remarkable degree of non-coding and syntenic conservation with non-mammalian vertebrates, suggesting they are functionally constrained. Because chromosome 5 is responsible for many forms of growth and development (cell divisions) changes may cause cancers. One example would be acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 5. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene predicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
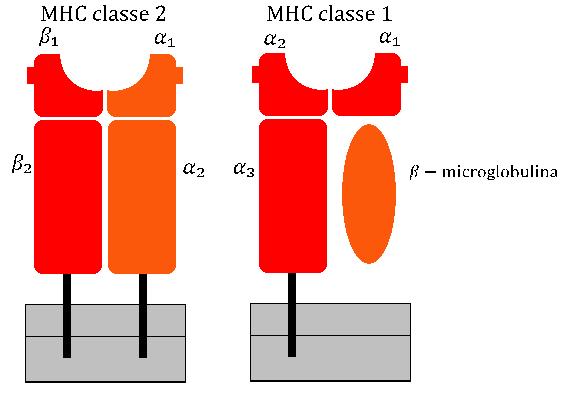
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. Its name comes from its discovery during the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules, which is to bind an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bring the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cell, T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNPs
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two common SNPs in the ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the nuclear genome and the Human mitochondrial genetics, mitochondrial genome. Human genomes include both protein-coding DNA sequences and various types of non-coding DNA, DNA that does not encode proteins. The latter is a diverse category that includes DNA coding for non-translated RNA, such as that for ribosomal RNA, transfer RNA, ribozymes, small nuclear RNAs, and several types of RNA#Regulatory RNA, regulatory RNAs. It also includes Promoter (biology), promoters and their associated Cis-regulatory element, gene-regulatory elements, DNA playing structural and replicatory roles, such as Scaffold/matrix attachment region, scaffolding regions, telomeres, centromeres, and Origin of replication, origins of repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Variation
Genetic variation is the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations among the same species. The multiple sources of genetic variation include mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are the ultimate sources of genetic variation, but other mechanisms, such as genetic drift, contribute to it, as well. Among individuals within a population Genetic variation can be identified at many levels. Identifying genetic variation is possible from observations of phenotypic variation in either quantitative traits (traits that vary continuously and are coded for by many genes, e.g., leg length in dogs) or discrete traits (traits that fall into discrete categories and are coded for by one or a few genes, e.g., white, pink, or red petal color in certain flowers). Genetic variation can also be identified by examining variation at the level of enzymes using the process of protein electrophoresis. Polymorphic genes have more than one allele at each locu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male Conifer cone, cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it Germination, germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and Forensic science, forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid male genetic ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include allergic conjunctivitis, red eyes, an itchy rash, sneeze, sneezing, coughing, a rhinorrhea, runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to FcεRI, a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |