|
GCube System
gCube is an open source software system specifically designed and developed to enact the building and operation of a Data Infrastructure providing their users with a rich array of services suitable for supporting the co-creation of Virtual Research Environments and promoting the implementation of open science workflows and practices. It is at the heart of the D4Science Data Infrastructure. It is primarily organised in a number of web service called to offer functionality supporting the phases of knowledge production and sharing. In addition, it consists of a set of software libraries supporting service development, service-to-service integration, and service capabilities extension, and a set of portlets dedicated to realise user interface constituents facilitating the exploitation of one or more services. It is designed and conceived to enact system of systems. In fact, its gCube services rely on standards and mediators to interact with other services as well as are made avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D4Science
D4Science is a Data Infrastructure offering services by community-driven virtual research environments. In particular, it supports communities of practice willing to implement open science practices, thus it is an Open Science Infrastructure. The infrastructure follows the system of systems approach, where the constituent systems (Service providers) offer “resources” (namely services and by them data, computing, storage) assembled together to implement the overall set of D4Science services. In particular, D4Science aggregates “domain agnostic” service providers as well as community-specific ones to build a unifying space where the aggregated resources can be exploited via Virtual research Environments and their services. It is spread across several sites, the primary one is hosted by the Istituto di Scienza e Tecnologie dell'Informazione of National Research Council (Italy). At the earth of this infrastructure there is an Open Source Software named gCube system. Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
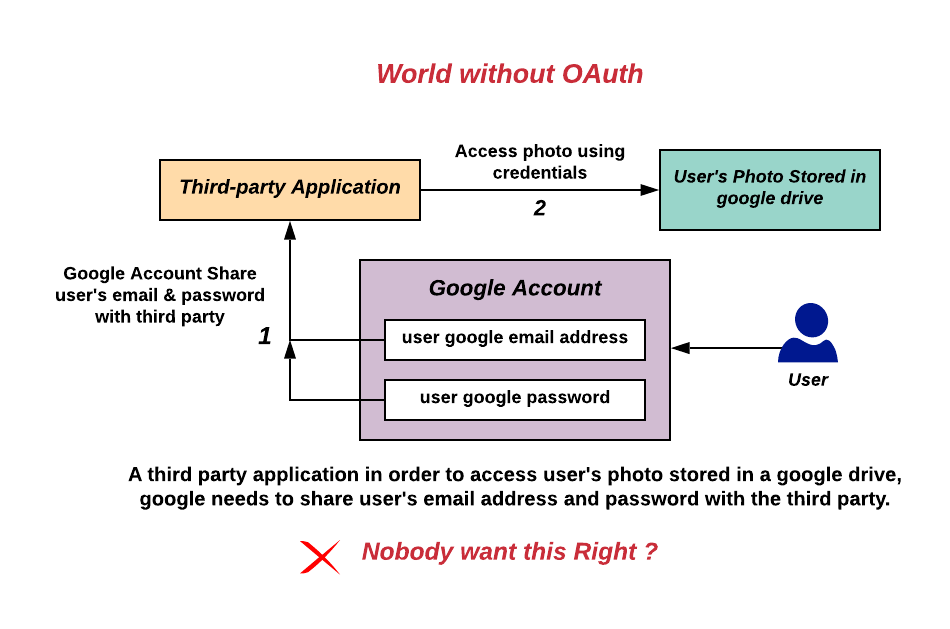
OAuth
OAuth (short for open authorization) is an open standard for access delegation, commonly used as a way for internet users to grant websites or applications access to their information on other websites but without giving them the passwords. This mechanism is used by companies such as Amazon, Google, Meta Platforms, Microsoft, and Twitter to permit users to share information about their accounts with third-party applications or websites. Generally, the OAuth protocol provides a way for resource owners to provide a client application with secure delegated access to server resources. It specifies a process for resource owners to authorize third-party access to their server resources without providing credentials. Designed specifically to work with Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), OAuth essentially allows access tokens to be issued to third-party clients by an authorization server, with the approval of the resource owner. The third party then uses the access token to access th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is "a paradigm for enabling network access to a scalable and elastic pool of shareable physical or virtual resources with self-service provisioning and administration on-demand," according to International Organization for Standardization, ISO. Essential characteristics In 2011, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) identified five "essential characteristics" for cloud systems. Below are the exact definitions according to NIST: * On-demand self-service: "A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider." * Broad network access: "Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations)." * Pooling (resource management), Resource pooling: " The provider' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-Science
E-Science or eScience is computationally intensive science that is carried out in highly distributed network environments, or science that uses immense data sets that require grid computing; the term sometimes includes technologies that enable distributed collaboration, such as the Access Grid. The term was created by John Taylor, the Director General of the United Kingdom's Office of Science and Technology in 1999 and was used to describe a large funding initiative starting in November 2000. E-science has been more broadly interpreted since then, as "the application of computer technology to the undertaking of modern scientific investigation, including the preparation, experimentation, data collection, results dissemination, and long-term storage and accessibility of all materials generated through the scientific process. These may include data modeling and analysis, electronic/digitized laboratory notebooks, raw and fitted data sets, manuscript production and draft versions, pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLite
gLite (pronounced "gee-lite") is a middleware computer software project for grid computing used by the CERN LHC experiments and other scientific domains. It was implemented by collaborative efforts of more than 80 people in 12 different academic and industrial research centers in Europe. gLite provides a framework for building applications tapping into distributed computing and storage resources across the Internet. The gLite services were adopted by more than 250 computing centres, and used by more than 15000 researchers in Europe and around the world. History After prototyping phases in 2004 and 2005, convergence with the LHC Computing Grid (LCG-2) distribution was reached in May 2006, when gLite 3.0 was released, and became the official middle-ware of the Enabling Grids for E-sciencE (EGEE) project which ended in 2010. Development of the gLite middle-ware was then taken over by the European Middleware Initiative, and is now maintained as part of the EMI software stack. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jenkins (software)
Jenkins is an open source automation server. It helps automate the parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying, facilitating continuous integration, and continuous delivery. It is a server-based system that runs in servlet containers such as Apache Tomcat, or by default as a stand-alone web-application in co-bundled Eclipse Jetty. It supports version control tools, including AccuRev, CVS, Subversion, Git, Mercurial, Perforce, ClearCase, and RTC, and can execute Apache Ant, Apache Maven, and sbt based projects as well as arbitrary shell scripts and Windows batch commands. History The Jenkins project was originally named '' Hudson'', and was renamed in 2011 after a dispute with Oracle, which had forked the project and claimed rights to the project name. The Oracle fork, ''Hudson'', continued to be developed for a time before being donated to the Eclipse Foundation. Oracle's Hudson is no longer maintained and was announced as obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery. Principles According to Neal Ford, continuous delivery adopts "Bring the pain forward," tackling tough tasks early, fostering automation and swift issue detection. Continuous delivery treats the commonplace notion of a ''deployment pipeline'' as a lean Poka-Yoke: a set of validations through which a piece of software must pass on its way to release. Code is compiled if necessary and then packaged by a build server every time a change is committed to a source control repository, then teste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
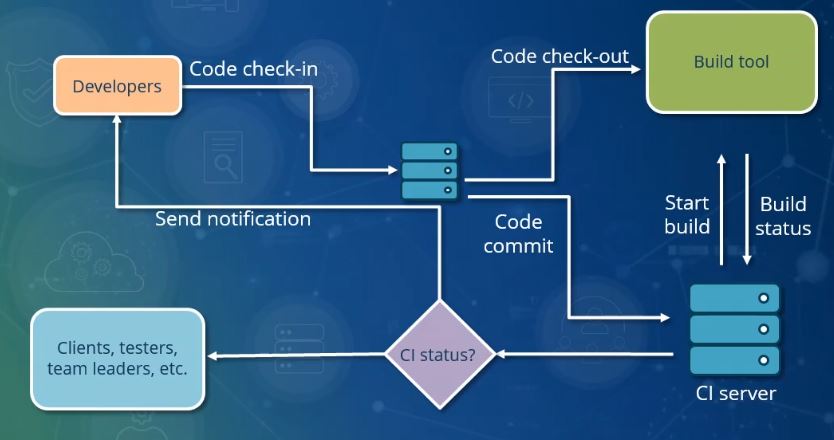
Continuous Integration
Continuous integration (CI) is the practice of integrating source code changes frequently and ensuring that the integrated codebase is in a workable state. Typically, developers Merge (version control), merge changes to an Branching (revision control), integration branch, and an automated system Software build, builds and software testing, tests the software system. Often, the automated process runs on each Commit (version control), commit or runs on a schedule such as once a day. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in Booch method, 1991, although he did not advocate integrating multiple times a day, but later, CI came to include that aspect. History The earliest known work (1989) on continuous integration was the Infuse environment developed by G. E. Kaiser, D. E. Perry, and W. M. Schell. In 1994, Grady Booch used the phrase continuous integration in ''Object-Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications'' (2nd edition) to explain how, when developing using micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Catalog Vocabulary
Data Catalog Vocabulary (DCAT) is an RDF vocabulary designed to facilitate interoperability between data catalogs published on the Web. By using DCAT to describe datasets in catalogs, publishers increase discoverability and enable applications to consume metadata from multiple catalogs. It enables decentralized publishing of catalogs and facilitates federated dataset search across catalogs. Aggregated DCAT metadata can serve as a manifest file to facilitate digital preservation. The original DCAT vocabulary was developed at DERI, as an idea from Vassilios Peristeras and his master student Fadi Maali together also with Richard Cyganiak. The vocabulary was further developed by W3C's eGov Interest Group, then brought onto the Recommendation Track by W3C's "Government Linked Data" Working Group. DCAT is the foundation for open dataset descriptions in the European Union public sector and was adapted by the ISA programme of the European Commission. A2022 report reviews DCATAP complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalogue Service For The Web
Catalogue Service for the Web (CSW), sometimes seen as Catalogue Service - Web, is a standard for exposing a catalogue of geospatial records in XML on the Internet (over HTTP). The catalogue is made up of records that describe geospatial data (e.g. KML), geospatial services (e.g. WMS), and related resources. CSW is one part (or "profile") of the OGC Catalogue Service, which defines common interfaces to discover, browse, and query metadata about data, services, and other potential resources. Version 2.0 of the specification was released in May 2004. The most recent release is 2.0.2, which was published in 2007. The records are in XML according to the standard. Typically the records include Dublin Core, ISO 19139 or FGDC metadata, encoded in UTF-8 characters. Each record must contain certain core fields including: Title, Format, Type (e.g. Dataset, DatasetCollection or Service), BoundingBox (a rectangle of interest, expressed in latitude and longitude), Coordinate Reference Syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OAI-PMH
The Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) is a protocol developed for harvesting metadata descriptions of records in an archive so that services can be built using metadata from many archives. An implementation of OAI-PMH must support representing metadata in Dublin Core, but may also support additional representations. The protocol is usually just referred to as the OAI Protocol. OAI-PMH uses XML over HTTP. Version 2.0 of the protocol was released in 2002; the document was last updated in 2015. It has a Creative Commons license BY-SA. History In the late 1990s, Herbert Van de Sompel (Ghent University) was working with researchers and librarians at Los Alamos National Laboratory (US) and called a meeting to address difficulties related to interoperability issues of e-print servers and digital repositories. The meeting was held in Santa Fe, New Mexico, in October 1999. A key development from the meeting was the definition of an interface that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Catalog Vocabulary
Data Catalog Vocabulary (DCAT) is an RDF vocabulary designed to facilitate interoperability between data catalogs published on the Web. By using DCAT to describe datasets in catalogs, publishers increase discoverability and enable applications to consume metadata from multiple catalogs. It enables decentralized publishing of catalogs and facilitates federated dataset search across catalogs. Aggregated DCAT metadata can serve as a manifest file to facilitate digital preservation. The original DCAT vocabulary was developed at DERI, as an idea from Vassilios Peristeras and his master student Fadi Maali together also with Richard Cyganiak. The vocabulary was further developed by W3C's eGov Interest Group, then brought onto the Recommendation Track by W3C's "Government Linked Data" Working Group. DCAT is the foundation for open dataset descriptions in the European Union public sector and was adapted by the ISA programme of the European Commission. A2022 report reviews DCATAP complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |