|
G2 (mathematics)
In mathematics, G2 is three simple Lie groups (a complex form, a compact real form and a split real form), their Lie algebras \mathfrak_2, as well as some algebraic groups. They are the smallest of the five exceptional simple Lie groups. G2 has rank 2 and dimension 14. It has two fundamental representations, with dimension 7 and 14. The compact form of G2 can be described as the automorphism group of the Octonion, octonion algebra or, equivalently, as the subgroup of SO(7) that preserves any chosen particular vector in its 8-dimensional Real representation, real spinor Group representation, representation (a spin representation). History The Lie algebra \mathfrak_2, being the smallest exceptional simple Lie algebra, was the first of these to be discovered in the attempt to classify simple Lie algebras. On May 23, 1887, Wilhelm Killing wrote a letter to Friedrich Engel (mathematician), Friedrich Engel saying that he had found a 14-dimensional simple Lie algebra, which we now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynkin Diagram
In the Mathematics, mathematical field of Lie theory, a Dynkin diagram, named for Eugene Dynkin, is a type of Graph (discrete mathematics), graph with some edges doubled or tripled (drawn as a double or triple line). Dynkin diagrams arise in the classification of semisimple Lie algebras over algebraically closed fields, in the classification of Weyl groups and other finite reflection groups, and in other contexts. Various properties of the Dynkin diagram (such as whether it contains multiple edges, or its symmetries) correspond to important features of the associated Lie algebra. The term "Dynkin diagram" can be ambiguous. In some cases, Dynkin diagrams are assumed to be directed graph, directed, in which case they correspond to root systems and semi-simple Lie algebras, while in other cases they are assumed to be undirected graph, undirected, in which case they correspond to Weyl groups. In this article, "Dynkin diagram" means ''directed'' Dynkin diagram, and ''undirected'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weyl Group
In mathematics, in particular the theory of Lie algebras, the Weyl group (named after Hermann Weyl) of a root system Φ is a subgroup of the isometry group of that root system. Specifically, it is the subgroup which is generated by reflections through the hyperplanes orthogonal to at least one of the roots, and as such is a finite reflection group. In fact it turns out that ''most'' finite reflection groups are Weyl groups. Abstractly, Weyl groups are finite Coxeter groups, and are important examples of these. The Weyl group of a semisimple Lie group, a semisimple Lie algebra, a semisimple linear algebraic group, etc. is the Weyl group of the root system of that group or algebra. Definition and examples Let \Phi be a root system in a Euclidean space V. For each root \alpha\in\Phi, let s_\alpha denote the reflection about the hyperplane perpendicular to \alpha, which is given explicitly as :s_\alpha(v)=v-2\frac\alpha, where (\cdot,\cdot) is the inner product on V. The Weyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
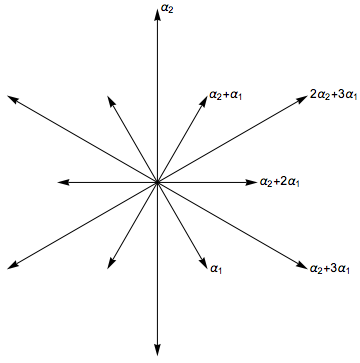
Root System
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vector space, vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups (and some analogues such as algebraic groups) and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied. Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagrams, occurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory (such as singularity theory). Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. Definitions and examples As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, R2, as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Space
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set (mathematics), set whose elements, often called vector (mathematics and physics), ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called scalar (mathematics), ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication must satisfy certain requirements, called ''vector axioms''. Real vector spaces and complex vector spaces are kinds of vector spaces based on different kinds of scalars: real numbers and complex numbers. Scalars can also be, more generally, elements of any field (mathematics), field. Vector spaces generalize Euclidean vectors, which allow modeling of Physical quantity, physical quantities (such as forces and velocity) that have not only a Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, but also a Orientation (geometry), direction. The concept of vector spaces is fundamental for linear algebra, together with the concept of matrix (mathematics), matrices, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Span
In mathematics, the linear span (also called the linear hull or just span) of a set S of elements of a vector space V is the smallest linear subspace of V that contains S. It is the set of all finite linear combinations of the elements of , and the intersection of all linear subspaces that contain S. It is often denoted pp. 29-30, §§ 2.5, 2.8 or \langle S \rangle. For example, in geometry, two linearly independent vectors span a plane. To express that a vector space is a linear span of a subset , one commonly uses one of the following phrases: spans ; is a spanning set of ; is spanned or generated by ; is a generator set or a generating set of . Spans can be generalized to many mathematical structures, in which case, the smallest substructure containing S is generally called the substructure ''generated'' by S. Definition Given a vector space over a field , the span of a set of vectors (not necessarily finite) is defined to be the intersection of all subsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Roots
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups (and some analogues such as algebraic groups) and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied. Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagrams, occurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory (such as singularity theory). Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. Definitions and examples As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, R2, as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors span the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G2Coxeter
G, or g, is the seventh letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''gee'' (pronounced ), plural ''gees''. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the single-storey (sometimes "opentail") and the double-storey (sometimes "looptail") . The former is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children. History The evolution of the Latin alphabet's G can be traced back to the Latin alphabet's predecessor, the Greek alphabet. The voiced velar stop was represented by the third letter of the Greek alphabet, gamma (Γ), which was later adopted by the Etruscan language. Latin then borrowed this "rounded form" of gamma, C, to represent the same sound in words such as ''recei'', which was likely an early dative form of '' rex'', meaning "king", as found in an "early Latin inscription." Over time, how ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuboctahedron
A cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with 8 triangular faces and 6 square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertex (geometry), vertices, with 2 triangles and 2 squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edge (geometry), edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such, it is a quasiregular polyhedron, i.e., an Archimedean solid that is not only vertex-transitive but also edge-transitive. It is Cuboctahedron#Radial equilateral symmetry, radially equilateral. Its dual polyhedron is the rhombic dodecahedron. Construction The cuboctahedron can be constructed in many ways: * Its construction can be started by attaching two regular triangular cupolas base-to-base. This is similar to one of the Johnson solids, triangular orthobicupola. The difference is that the triangular orthobicupola is constructed with one of the cupolas twisted so that similar polygonal faces are adjacent, whereas the cuboctahedron is not. As a result, the cuboctahedron may also called the ''triangular gyro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter Plane
In mathematics, a Coxeter element is an element of an irreducible Coxeter group which is a product of all simple reflections. The product depends on the order in which they are taken, but different orderings produce conjugate elements, which have the same order. This order is known as the Coxeter number. They are named after British-Canadian geometer H.S.M. Coxeter, who introduced the groups in 1934 as abstractions of reflection groups. Definitions Note that this article assumes a finite Coxeter group. For infinite Coxeter groups, there are multiple conjugacy classes of Coxeter elements, and they have infinite order. There are many different ways to define the Coxeter number of an irreducible root system. *The Coxeter number is the order of any Coxeter element;. *The Coxeter number is where is the rank, and is the number of reflections. In the crystallographic case, is half the number of roots; and is the dimension of the corresponding semisimple Lie algebra. *If the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-cube T1
A cube or regular hexahedron is a three-dimensional solid object in geometry, which is bounded by six congruent square faces, a type of polyhedron. It has twelve congruent edges and eight vertices. It is a type of parallelepiped, with pairs of parallel opposite faces, and more specifically a rhombohedron, with congruent edges, and a rectangular cuboid, with right angles between pairs of intersecting faces and pairs of intersecting edges. It is an example of many classes of polyhedra: Platonic solid, regular polyhedron, parallelohedron, zonohedron, and plesiohedron. The dual polyhedron of a cube is the regular octahedron. The cube can be represented in many ways, one of which is the graph known as the cubical graph. It can be constructed by using the Cartesian product of graphs. The cube is the three-dimensional hypercube, a family of polytopes also including the two-dimensional square and four-dimensional tesseract. A cube with unit side length is the canonical unit of volume in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root System
In mathematics, a root system is a configuration of vector space, vectors in a Euclidean space satisfying certain geometrical properties. The concept is fundamental in the theory of Lie groups and Lie algebras, especially the classification and representation theory of semisimple Lie algebras. Since Lie groups (and some analogues such as algebraic groups) and Lie algebras have become important in many parts of mathematics during the twentieth century, the apparently special nature of root systems belies the number of areas in which they are applied. Further, the classification scheme for root systems, by Dynkin diagrams, occurs in parts of mathematics with no overt connection to Lie theory (such as singularity theory). Finally, root systems are important for their own sake, as in spectral graph theory. Definitions and examples As a first example, consider the six vectors in 2-dimensional Euclidean space, R2, as shown in the image at the right; call them roots. These vectors Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |