|
First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Verdun
The Battle of Verdun ( ; ) was fought from 21 February to 18 December 1916 on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front in French Third Republic, France. The battle was the longest of the First World War and took place on the hills north of Verdun. The German 5th Army (German Empire), 5th Army attacked the defences of the Fortified Region of Verdun (RFV, ) and those of the French Second Army (France), Second Army on the right (east) bank of the Meuse. Using the experience of the Second Battle of Champagne in 1915, the Germans planned to capture the Meuse Heights, an excellent defensive position, with good observation for artillery-fire on Verdun. The Germans hoped that the French would commit their strategic reserve to recapture the position and suffer catastrophic losses at little cost to the German infantry. Poor weather delayed the beginning of the attack until 21 February but the Germans captured Fort Douaumont in the first three days. The advance then slowed for seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Estonia (1920–1939)
The history of Estonia from 1918 to 1940 spanned the interwar period from the end of the Estonian War of Independence until the outbreak of World War II. It covers the years of parliamentary democracy, the Great Depression and the period of corporatist authoritarian rule. Parliamentary democracy Estonia won the Estonian War of Independence against both Soviet Russia and the German Freikorps and '' Baltische Landeswehr'' volunteers. Independence was secured with the Tartu Peace Treaty, signed on 2 February 1920. The first Estonian constitution was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 15 April 1920. Established as a parliamentary democracy, legislative power was held by a 100-seat parliament or Riigikogu. Executive power was held by a government headed by a State Elder, separate from the office of Prime Minister, and both answerable to the parliament. The Republic of Estonia was recognised (''de jure'') by Finland on 7 July 1920, Poland on 31 December 1920, Argent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
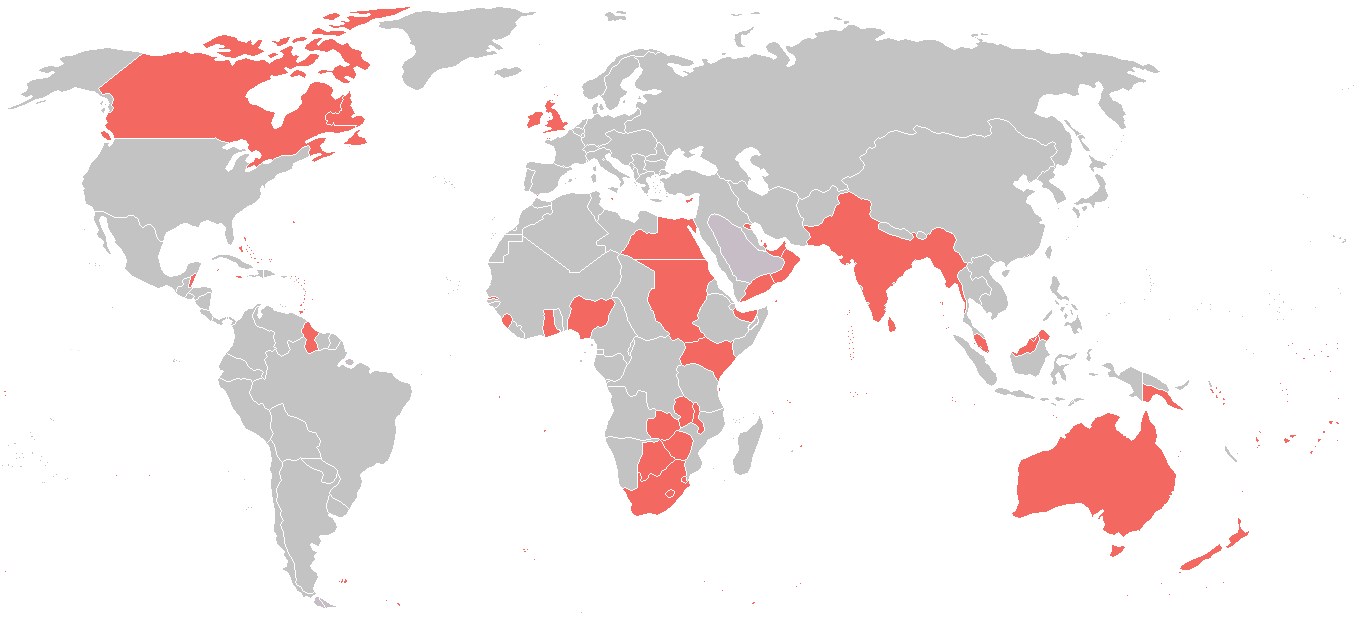
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Warfare In The Mediterranean During World War I
Naval warfare in the Mediterranean during World War I took place between the naval forces of the Entente and the Central Powers in the Mediterranean Sea between 1914 and 1918. Austro-Hungarian Imperial and Royal Navy Austria-Hungary was a medium-sized naval power in 1914. It had a coastline from between Venice and Trieste (in present-day Italy) to below Cattaro in Montenegro. The Austro-Hungarian Navy had nine pre-dreadnought and four brand new dreadnought s, armoured cruisers, protected cruisers, light cruisers, destroyers, large numbers of fast torpedo-boats and a number of submarines. In addition, the Germans managed to send some further U-boats to the Mediterranean which operated from Austrian naval bases, initially under the Austrian navy flag, later under the German navy flag. Italian ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) The Kingdom of Italy during World War I had six dreadnought battleships ( as a prototype, , and of the , and of the ). Only four saw service in WWI and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic U-boat Campaign Of World War I
The Atlantic U-boat campaign of World War I (sometimes called the "First Battle of the Atlantic", in reference to the World War II campaign Battle of the Atlantic, of that name) was the prolonged naval conflict between German submarines and the Allies of World War I, Allied navies in Atlantic waters the North Sea, the seas around the British Isles, and the coast of France. Initially the U-boat campaign was directed against the warships of the British Grand Fleet. Later U-boat fleet action was extended to include action against the trade routes of the Allied powers. This campaign was highly destructive, and resulted in the loss of nearly half of Britain's initial merchant marine fleet during the course of the war. To counter the German submarines, the Allies moved shipping into convoys guarded by destroyers, blockades such as the Dover Barrage and minefields such as the North Sea Mine Barrage were laid, and aircraft patrols monitored the U-boat bases. Increased ship construction m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian And Pacific Theatre Of World War I
During World War I, conflict on the Asian continent and the Pacific islands, islands of the Pacific included naval battles, the Allies of World War I, Allied conquest of German colonial empire, German colonial possessions in the Pacific Ocean and Beiyang government, China, the anti-Russian Central Asian revolt of 1916 in Russian Turkestan and the Ottoman-supported Kelantan rebellion in British Malaya. The most significant military action was the careful and well-executed Siege of Qingdao in China, but smaller actions were also fought at Battle of Bita Paka, Bita Paka and Siege of Toma, Toma in German New Guinea. All other German Empire, German and Austro-Hungarian possessions in Asia and the Pacific fell without bloodshed. Naval warfare was common; all of the colonial powers had naval squadrons stationed in the Indian Ocean, Indian or Pacific oceans. These fleets operated by supporting the invasions of German-held territories and by destroying the East Asia Squadron of the Impe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Theatre Of World War I
The African theatre of the First World War comprises campaigns in North Africa instigated by the German and Ottoman empires, local rebellions against European colonial rule and Allies of World War I, Allied campaigns against the German Empire, German colonies of Kamerun, Togoland, German South West Africa, and German East Africa. The campaigns were fought by German , local resistance movements and forces of the British Empire, French Third Republic, France, Kingdom of Italy, Italy, Belgium, and First Portuguese Republic, Portugal. Background Strategic context German colonies in Africa had been acquired in the 1880s and were not well defended. They were enclosed by territories controlled by British Empire, Britain, French colonial empire, France, Belgian colonial empire, Belgium and Portuguese Empire, Portugal. Colonial military forces in Africa were relatively small, poorly equipped and had been created to maintain internal order, rather than conduct military operations against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Theatre Of World War I
The European theatre was the main theatre of operations during World War I and was where the war began and ended. During the four years of conflict, battle was joined by armies of unprecedented size, which were equipped with new mechanized technologies. The conflict left tens of millions dead or wounded. The European theatre is divided into four main theatres of operations: the Western Front, the Eastern Front, the Italian Front, and the Balkans Front. Not all of Europe was involved in the war, nor did fighting take place throughout all of the major combatants’ territory. The United Kingdom was nearly untouched by the war. Most of France was unaffected, as was most of Germany and Italy. Some large countries in Europe remained neutral for the entire war such as Sweden and Spain – the Great War passed them by without much impact. On the other hand, some countries were conquered (Serbia, Belgium, Romania). Other countries like Russia and the Ottoman Empire saw armies marchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
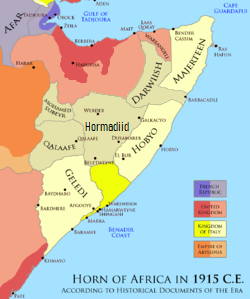
Mutawakkilite Kingdom Of Yemen
The Kingdom of Yemen (), officially the Mutawakkilite Kingdom of Yemen () and also known simply as Yemen or, retrospectively, as North Yemen, was a state that existed between 1918 and 1970 in the northwestern part of the modern country of Yemen. Located in the Middle East, the Kingdom of Yemen had an area of 195,000 km2. The country was bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Aden Protectorate to the south, and the Red Sea to the west. Its capital was Sanaa from 1918 to 1948, then Taiz from 1948 to 1962. Yemen was admitted to the United Nations on 30 September 1947. A republican coup was launched against the government in 1962, leading to the North Yemen Civil War. The royalist government only controlled the northern portions of the country from 1962 to 1970, until a peace deal in 1970 saw it largely dissolved. Three days after the Ottoman Empire's decision to withdraw from Yemen following the 1918 Armistice of Mudros, Imam Yahya, the religious leader of the region, ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hejaz
The Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz (, ''Al-Mamlakah al-Ḥijāziyyah Al-Hāshimiyyah'') was a state in the Hejaz region of Western Asia that included the western portion of the Arabian Peninsula that was ruled by the Hashemite dynasty. It was self-proclaimed as a kingdom in June 1916 during the First World War, to be independent from the Ottoman Empire, on the basis of an alliance with the British Empire to drive the Ottoman Army from the Arabian Peninsula during the Arab Revolt. The British government had promised Hussein bin Ali, King of Hejaz, a single independent Arab state that would include, in addition to the Hejaz region, modern-day Jordan, Iraq, and most of Syria, with the fate of the Palestine region (today's Israel and Palestine) being mentioned in more ambiguous terms. However, at the end of the First World War, the Treaty of Versailles turned Syria into a French League of Nations mandate and Iraq, Mandate Palestine and Transjordan into British mandates. Hashemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include İzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Czechoslovak Republic
The First Czechoslovak Republic, often colloquially referred to as the First Republic, was the first Czechoslovakia, Czechoslovak state that existed from 1918 to 1938, a union of ethnic Czechs and Slovaks. The country was commonly called Czechoslovakia a compound of ''Czech'' and ''Slovak''; which gradually became the most widely used name for its successor states. It was composed of former territories of Austria-Hungary, inheriting different systems of administration from the formerly Cisleithania, Austrian (Bohemia, Moravia, a small part of Silesia) and Kingdom of Hungary, Hungarian territories (mostly Upper Hungary and Carpathian Ruthenia). After 1933, Czechoslovakia remained the only ''de facto'' functioning democracy in Central Europe, organized as a parliamentary republic. Under pressure from Germans in Czechoslovakia, its Sudeten German minority, supported by neighbouring Nazi Germany, Czechoslovakia was forced to cede its Sudetenland region to Germany on 1 October 1938 as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |