|
Fungal Folliculitis
Majocchi's granuloma is a skin condition characterized by deep, pustular plaques, and is a form of tinea corporis. It is a localized form of fungal folliculitis. Lesions often have a pink and scaly central component with pustules or folliculocentric papules at the periphery. The name comes from Domenico Majocchi, who discovered the disorder in 1883. Majocchi was a professor of dermatology at the University of Parma and later the University of Bologna. This disease is most commonly caused by filamentous fungi in the genus ''Trichophyton''. Symptoms and signs Majocchi's granuloma often presents as pink scaly patches with pustules at the periphery. It is most common on skin exposed to mechanical abuse—wear and tear—such as the upper and lower extremities. Patients experience papules, pustules, or even plaques and nodules at the infection site. The white to red papules and pustules often have a perifollicular location. Hair shafts can be easily removed from the pustules and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Corporis
Tinea corporis is a fungal infection of the body, similar to other forms of tinea. Specifically, it is a type of dermatophytosis (or ringworm) that appears on the arms and legs, especially on glabrous skin; however, it may occur on any superficial part of the body. Signs and symptoms It may have a variety of appearances; most easily identifiable are the enlarging raised red rings with a central area of clearing (ringworm). The same appearances of ringworm may also occur on the scalp (tinea capitis), beard area ( tinea barbae) or the groin ( tinea cruris, known as jock itch or dhobi itch). Other classic features of tinea corporis include: * Itching occurs on infected area. * The edge of the rash appears elevated and is scaly to touch. * Sometimes the skin surrounding the rash may be dry and flaky. * Almost invariably, there will be hair loss in areas of the infection. Causes Tinea corporis is caused by a tiny fungus known as dermatophyte. These tiny organisms normally live on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Medications
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally. Routes of administration Ocular Indicated when the fungal infection is located in the eye. There is currently only one ocular antifungal available: natamycin. However, various other antifungal agents could be compounded in this formulation. Intrathecal Used occasionally when there's an infection of the central nervous system and other systemic options cannot reach the concentration required in that region for therapeutic benefit. Example(s): amphotericin B. Vaginal This may be used to treat some fungal infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompetent
In immunology, immunocompetence is the ability of the body to produce a normal immune response following exposure to an antigen. Immunocompetence is the opposite of immunodeficiency (also known as ''immuno-incompetence'' or being ''immuno-compromised''). In reference to lymphocytes, immunocompetence means that a B cell or T cell is mature and can recognize antigens and allow a person to mount an immune response. In order for lymphocytes such as T cells to become immunocompetent, which refers to the ability of lymphocyte cell receptors to recognize MHC molecules, they must undergo positive selection. Adaptive immunocompetence is regulated by growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and vasopressin (VP) – hormones secreted by the pituitary gland.Berczi, I., Quintanar-Stephano, A., & Kovacs, K. (2009). Neuroimmune regulation in immunocompetence, acute illness, and healing. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1153(1), 220–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03975 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycology
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungus, fungi, including their Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, genetics, biochemistry, biochemical properties, and ethnomycology, use by humans. Fungi can be a source of tinder, Edible mushroom, food, traditional medicine, as well as entheogens, poison, and fungal infection, infection. Yeasts are among the most heavily utilized members of the fungus kingdom, particularly in food manufacturing. Mycology branches into the field of phytopathology, the study of plant diseases. The two disciplines are closely related, because the vast majority of plant pathogens are fungi. A biologist specializing in mycology is called a mycologist. Overview The word ''mycology'' comes from the Greek language, Ancient Greek: wikt:μύκης, μύκης (''mukēs''), meaning "fungus" and the suffix (''-logia''), meaning "study." Pioneer mycologists included Elias Magnus Fries, Christiaan Hendrik Persoon, Heinrich Anton de Bary, Elizabeth E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathological
Pathology is the study of disease. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be " pathophysiologies"). The suffix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment (as in cardiomyopathy) and psychological conditions (such as ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
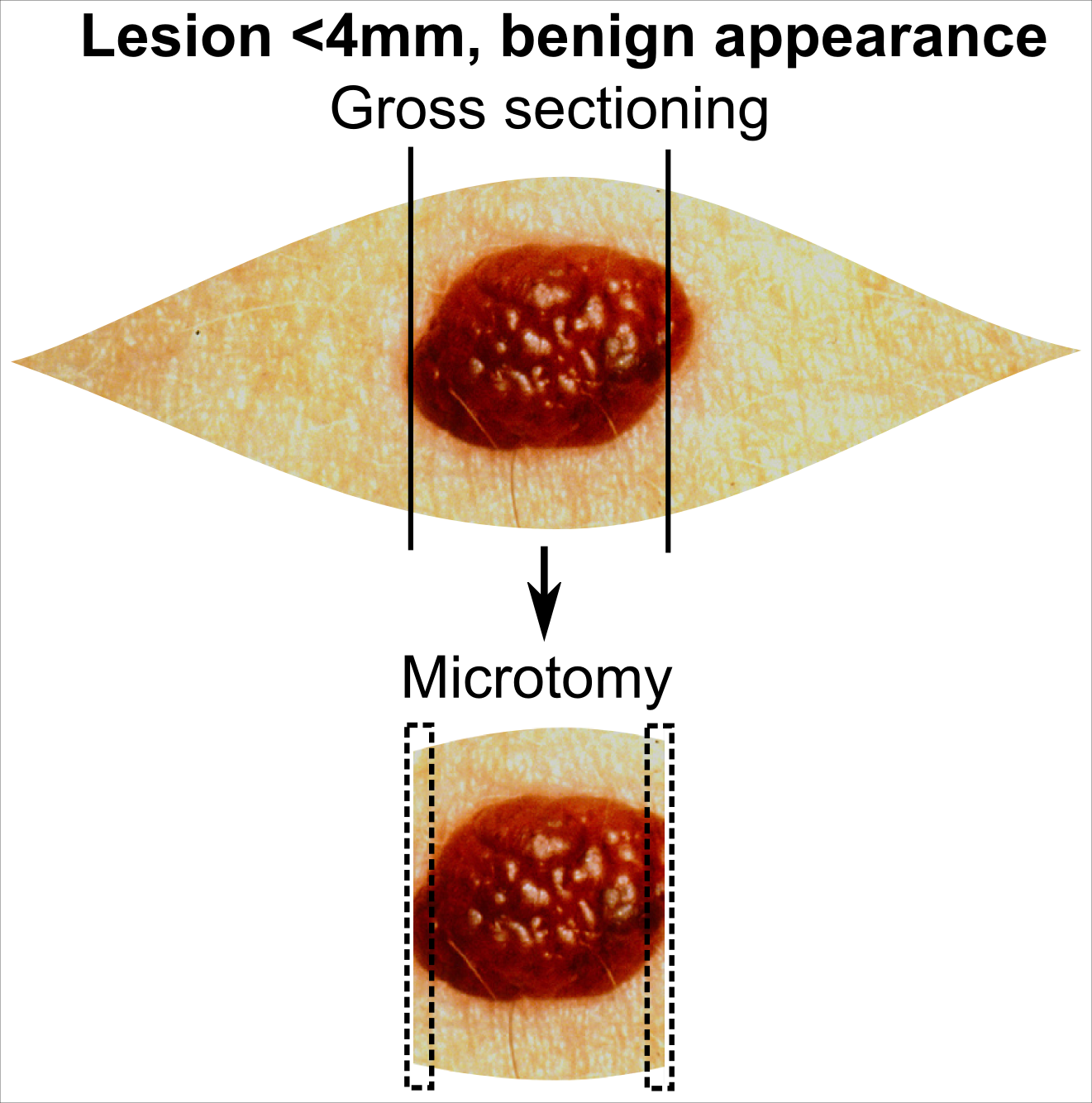
Skin Biopsy
Skin biopsy is a biopsy technique in which a skin lesion is removed to be sent to a pathologist to render a microscopic diagnosis. It is usually done under local anesthetic in a physician's office, and results are often available in 4 to 10 days. It is commonly performed by dermatologists. Skin biopsies are also done by family physicians, internists, surgeons, and other specialties. However, performed incorrectly, and without appropriate clinical information, a pathologist's interpretation of a skin biopsy can be severely limited, and therefore doctors and patients may forgo traditional biopsy techniques and instead choose Mohs surgery. There are four main types of skin biopsies: shave biopsy, punch biopsy, excisional biopsy, and incisional biopsy. The choice of the different skin biopsies is dependent on the suspected diagnosis of the skin lesion. Like most biopsies, patient consent and anesthesia (usually lidocaine injected into the skin) are prerequisites. Types Shave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other conditions. In general, deliberately induced immunosuppression is performed to prevent the body from rejecting an organ transplant. Additionally, it is used for treating graft-versus-host disease after a bone marrow transplant, or for the treatment of auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, or Crohn's disease. This is typically done using medications, but may involve surgery (splenectomy), plasmapheresis, or radiation. A person who is undergoing immunosuppression, or whose immune system is weak for some other reasons (such as chemotherapy or HIV), is said to be ''immunocompromised''. Deliberately induced Administration of immunosuppressive medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcutaneous Tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's Dermatome (anatomy), dermatome region. It consists primarily of loose connective tissue and contains larger blood vessels and nerves than those found in the dermis. It is a major site of fat storage in the body. In arthropods, a hypodermis can refer to an epidermal layer of cells that secretes the chitinous cuticle. The term also refers to a layer of cells lying immediately below the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of plants. Structure * Fibrous bands anchoring the skin to the deep fascia * Collagen and elastin fibers attaching it to the dermis * Fat is absent from the eyelids, clitoris, penis, much of Pinna (anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papule
A papule is a small, well-defined bump in the skin lesion, skin. It may have a rounded, pointed or flat top, and may have a umbilication, dip. It can appear with a Peduncle (anatomy), stalk, be thread-like or look warty. It can be soft or firm and its surface may be rough or smooth. Some have Crust (dermatology), crusts or Scale (dermatology), scales. A papule can be flesh colored, yellow, white, brown, red, blue or purplish. There may be just one or many, and they may occur irregularly in different parts of the body or appear in clusters. It does not contain fluid but may progress to a pustule or vesicle (dermatology), vesicle. A papule is smaller than a Nodule (medicine), nodule; it can be as tiny as a pinhead and is typically less than 1 cm in width, according to some sources, and 0.5 cm according to others. When merged together, it appears as a plaque. A papule's colour might indicate its cause, such as white in Milium (dermatology), milia, red in eczema, yellowish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompetence
In immunology, immunocompetence is the ability of the body to produce a normal immune response following exposure to an antigen. Immunocompetence is the opposite of immunodeficiency (also known as ''immuno-incompetence'' or being ''immuno-compromised''). In reference to lymphocytes, immunocompetence means that a B cell or T cell is mature and can recognize antigens and allow a person to mount an immune response. In order for lymphocytes such as T cells to become immunocompetent, which refers to the ability of lymphocyte cell receptors to recognize MHC molecules, they must undergo positive selection. Adaptive immunocompetence is regulated by growth hormone (GH), prolactin Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ... (PRL), and vasopressin (VP) – hormones secreted by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |