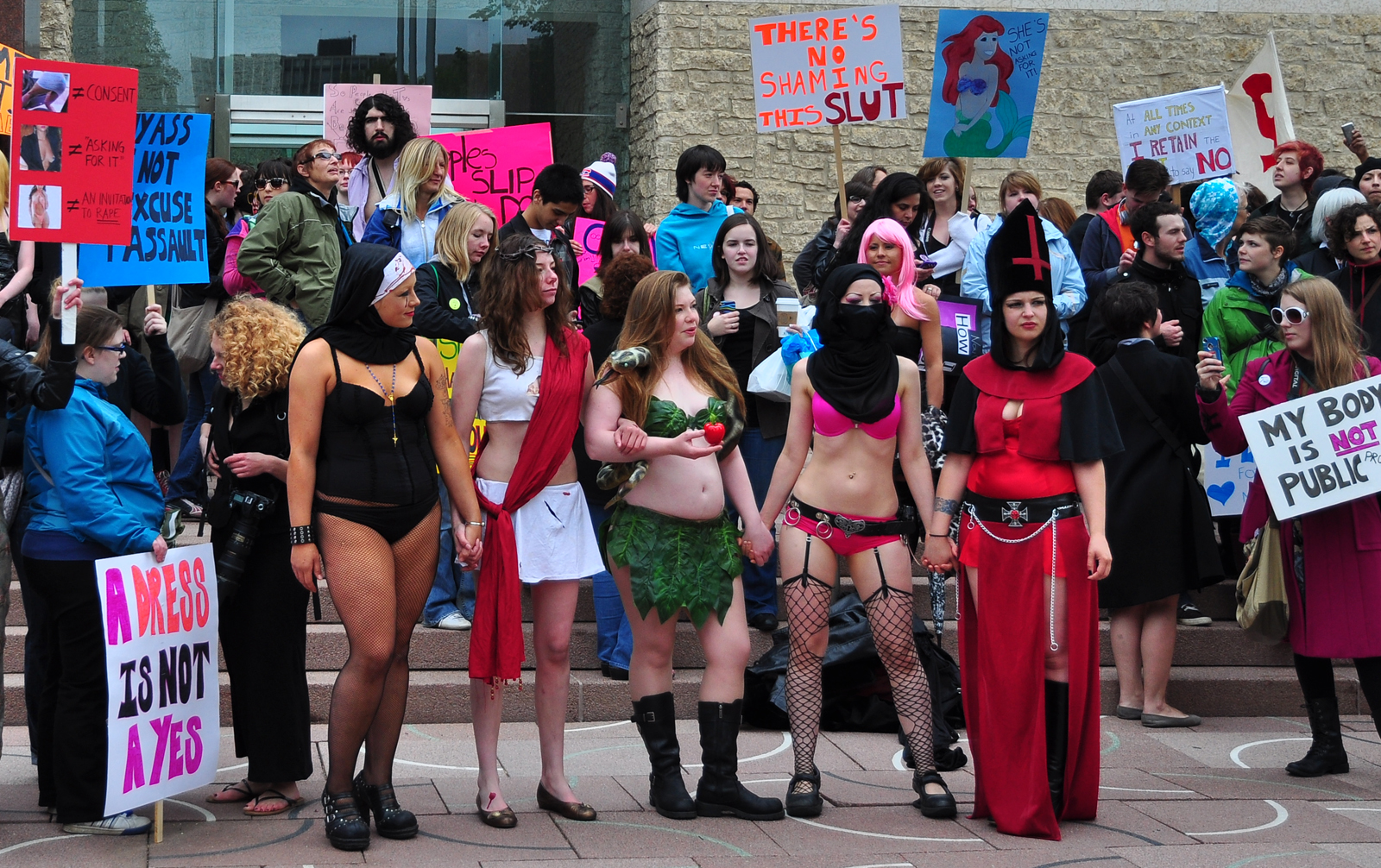|
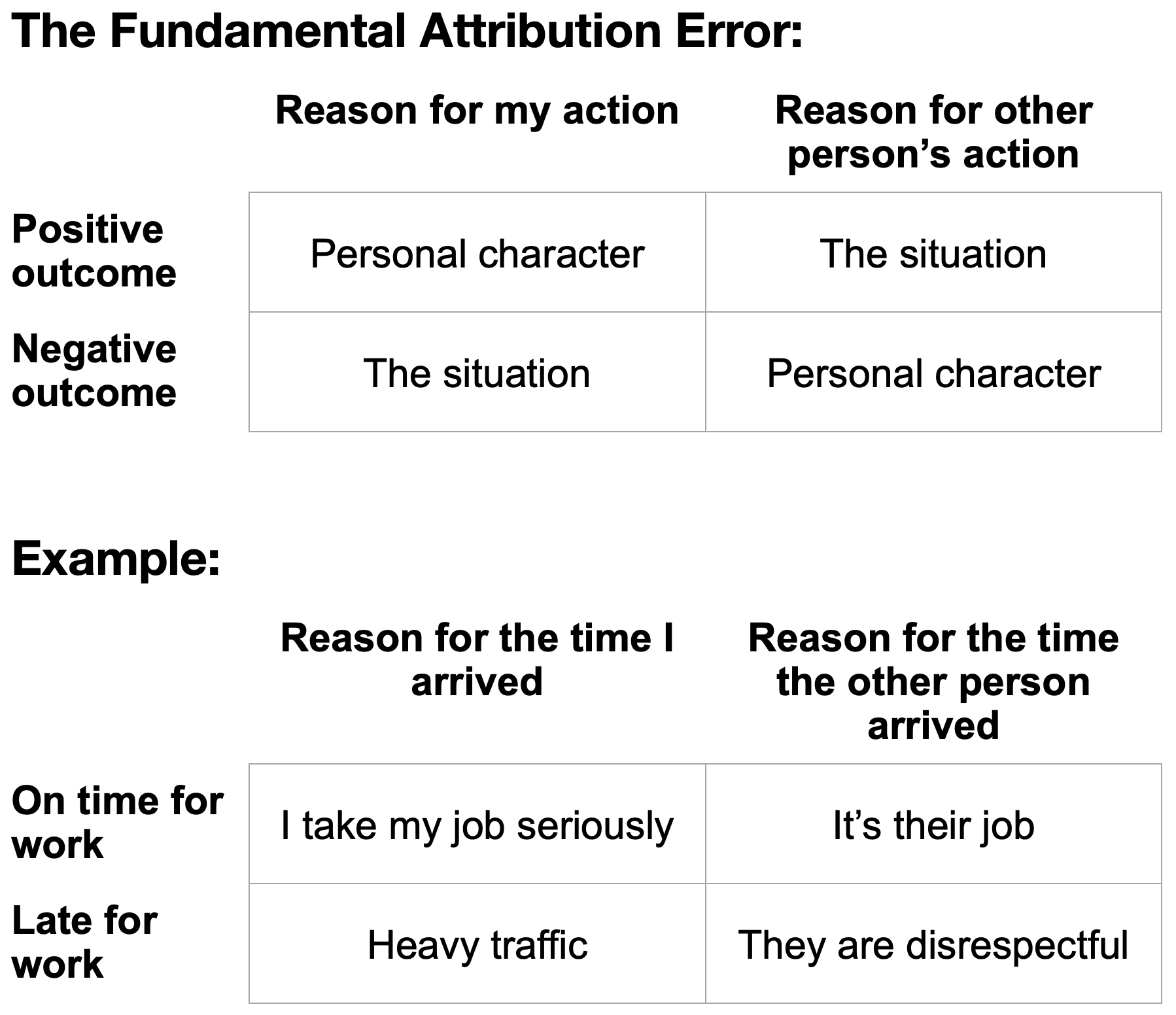
Fundamental Attribution Error
In social psychology, the fundamental attribution error is a cognitive attribution bias in which observers underemphasize situational and environmental factors for the behavior of an actor while overemphasizing dispositional or personality factors. In other words, observers tend to overattribute the behaviors of others to their personality (e.g., ''he is late because he's selfish'') and underattribute them to the situation or context (e.g., ''he is late because he got stuck in traffic''). Although personality traits and predispositions are considered to be observable facts in psychology, the fundamental attribution error is an error because it misinterprets their effects. The group attribution error is identical to the fundamental attribution error, where the bias is shown between members of different groups rather than different individuals. The ultimate attribution error is a derivative of the fundamental attribution error and group attribution error relating to the acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melvin J
Melvin is a masculine given name and surname, likely a variant of Melville and a descendant of the French surname de Maleuin and the later Melwin. It may alternatively be spelled as Melvyn or, in Welsh, Melfyn and the name Melivinia or Melva may be used a feminine form. Of Norman French origin, originally Malleville, which translates to "bad town," it likely made its way into usage in Scotland as a result of the Norman conquest of England. It came into use as a given name as early as the 19th century, in English-speaking populations. As a name Given name Academics * Melvin Calvin (1911–1997), American chemist who discovered the Calvin cycle * Melvin Day (1923–2016), New Zealand artist and art historian * Melvin Hochster (born 1943), American mathematician * Melvin Konner (born 1946), Professor of Anthropology * Melvin Schwartz (1932–2006), American physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1988 * Melvin Alvah Traylor, Jr. (1915–2008), American ornithologist B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Rate Fallacy
The base rate fallacy, also called base rate neglect or base rate bias, is a type of fallacy in which people tend to ignore the base rate (e.g., general prevalence) in favor of the individuating information (i.e., information pertaining only to a specific case). For example, if someone hears that a friend is very shy and quiet, they might think the friend is more likely to be a librarian than a salesperson. However, there are far more salespeople than librarians overall—hence making it more likely that their friend is actually a salesperson, even if a greater proportion of librarians fit the description of being shy and quiet. Base rate neglect is a specific form of the more general extension neglect. It is also called the prosecutor's fallacy or defense attorney's fallacy when applied to the results of statistical tests (such as DNA tests) in the context of law proceedings. These terms were introduced by William C. Thompson and Edward Schumann in 1987, although it has been arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attribution (psychology)
Attribution is a term used in psychology which deals with how individuals perceive the causes of everyday experience, as being either external or internal. Models to explain this process are called Attribution theory. Psychological research into attribution began with the work of Fritz Heider in the early 20th century, and the theory was further advanced by Harold Kelley and Bernard Weiner. Heider first introduced the concept of perceived 'locus of causality' to define the perception of one's environment. For instance, an experience may be perceived as being caused by factors outside the person's control (external) or it may be perceived as the person's own doing (internal). These initial perceptions are called attributions. Psychologists use these attributions to better understand an individual's motivation and competence. The theory is of particular interest to employers who use it to increase worker motivation, goal orientation, and productivity. Psychologists have identifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency (philosophy)
Agency is the capacity of an actor to act in a given environment. It is independent of the moral dimension, which is called moral agency. In sociology, an agent is an individual engaging with the social structure. Notably, though, the primacy of social structure vs. individual capacity with regard to persons' actions is debated within sociology. This debate concerns, at least partly, the level of reflexivity an agent may possess. Agency may either be classified as unconscious, involuntary behavior, or purposeful, goal directed activity (intentional action). An agent typically has some sort of immediate awareness of their physical activity and the goals that the activity is aimed at realizing. In 'goal directed action' an agent implements a kind of direct control or guidance over their own behavior. Human agency Agency is contrasted to objects reacting to natural forces involving only unthinking deterministic processes. In this respect, agency is subtly distinct from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-determination Theory
Self-determination theory (SDT) is a macro theory of human motivation and personality regarding individuals' innate tendencies toward growth and innate psychological needs. It pertains to the motivation behind individuals' choices in the absence of external influences and distractions. SDT focuses on the degree to which human behavior is self-motivated and self-determined. In the 1970s, research on SDT evolved from studies comparing intrinsic motivation, intrinsic and intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motives and a growing understanding of the dominant role that intrinsic motivation plays in individual behavior.e.g. Lepper, M. K., Greene, D., & Nisbett, R. (1973). ''Undermining children's intrinsic interest with extrinsic reward: A test of the "overjustification" hypothesis''. ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology'', ''28'', 129–137. It was not until the mid-1980s, when Edward L. Deci and Richard Ryan (professor), Richard Ryan wrote a book entitled ''Intrinsic Motiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collectivism And Individualism
In sociology, a social organization is a pattern of relationships between and among individuals and groups. Characteristics of social organization can include qualities such as sexual composition, spatiotemporal cohesion, leadership, structure, division of labor, communication systems, and so on. Because of these characteristics of social organization, people can monitor their everyday work and involvement in other activities that are controlled forms of human interaction. These interactions include: affiliation, collective resources, substitutability of individuals and recorded control. These interactions come together to constitute common features in basic social units such as family, enterprises, clubs, states, etc. These are social organizations. Common examples of modern social organizations are government agencies, NGOs, and corporations. Elements Social organizations happen in everyday life. Many people belong to various social structures—institutional and info ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individualistic
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote realizing one's goals and desires, valuing independence and self-reliance, and advocating that the interests of the individual should gain precedence over the state or a social group, while opposing external interference upon one's own interests by society or institutions such as the government. Individualism makes the individual its focus, and so starts "with the fundamental premise that the human individual is of primary importance in the struggle for liberation". L. Susan Brown. '' The Politics of Individualism: Liberalism, Liberal Feminism, and Anarchism''. Black Rose Books Ltd. 1993 Individualism represents one kind of sociocultural perspective and is often defined in contrast to other perspectives, such as communitarianism, collectivism and corporatism. Individualism is also associated with artistic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Load
In cognitive psychology, cognitive load is the effort being used in the working memory. According to work conducted in the field of instructional design and pedagogy, broadly, there are three types of cognitive load: * ''Intrinsic'' cognitive load is the effort associated with a specific topic. * ''Germane cognitive load refers to the work put into creating a permanent store of knowledge (a schema).'' * ''Extraneous'' cognitive load refers to the way information or tasks are presented to a learner. However, over the years, the additivity of these types of cognitive load has been investigated and questioned. Now it is believed that they circularly influence each other. Cognitive load theory was developed in the late 1980s out of a study of problem solving by John Sweller. Sweller argued that instructional design can be used to reduce cognitive load in learners. Much later, other researchers developed a way to measure perceived mental effort which is indicative of cognitive load. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automaticity
In the field of psychology, automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tasks carried out by ' muscle memory' often involve some degree of automaticity. Examples of automaticity are common activities such as walking, speaking, bicycle-riding, assembly-line work, and driving a car (the last of these sometimes being termed " highway hypnosis"). After an activity is sufficiently practiced, it is possible to focus the mind on other activities or thoughts while undertaking an automatized activity (for example, holding a conversation or planning a speech while driving a car). Characteristics John Bargh (1994), based on over a decade of research, suggested that four characteristics usually accompany automatic behavior: ;Awareness :A person may be unaware of the mental process that is oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salience (language)
Salience is the state or condition of being prominent. The Oxford English Dictionary defines salience as "most noticeable or important." The concept is discussed in communication, semiotics, linguistics, sociology, psychology, and political science. It has been studied with respect to interpersonal communication, persuasion, politics, and its influence on mass media. Semiotics In semiotics (the study of signs or symbolism), ''salience'' refers to the relative importance or prominence of a part of a sign. The salience of a particular sign when considered in the context of others helps an individual to quickly rank large amounts of information by importance and thus give attention to that which is the most important. This process keeps an individual from being overwhelmed with information overload. Discussion Meaning can be described as the "system of mental representations of an object or phenomenon, its properties and associations with other objects and/or phenomena. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blame The Victim
Victim blaming occurs when the victim of a crime or any wrongful act is held entirely or partially at fault for the harm that befell them. There is historical and current prejudice against the victims of domestic violence and sex crimes, such as the greater tendency to blame victims of rape than victims of robbery if victims and perpetrators knew each other prior to the commission of the crime. The Gay Panic Defense has been characterized as a form of victim blaming. Coining of the phrase Psychologist William Ryan coined the phrase "blaming the victim" in his 1971 book of that title. In the book, Ryan described victim blaming as an ideology used to justify racism and social injustice against black people in the United States. Ryan wrote the book to refute Daniel Patrick Moynihan's 1965 work ''The Negro Family: The Case for National Action'' (usually simply referred to as the Moynihan Report). Moynihan had concluded that three centuries of oppression of black people, and in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |