|
Friedrich-Carl Von Steinkeller
__NOTOC__ Friedrich-Carl von Steinkeller (28 March 1896 – 19 October 1981) was a general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. Steinkeller surrendered to the Red Army forces in the course of the Soviet Mogilev Offensive in June 1944; he was released in 1955. Awards * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 31 March 1943 as ''Oberstleutnant () (English: Lieutenant Colonel) is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to lieutenant colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, ...'' and commander Panzergrenadier-Regiment 7Fellgiebel 2000, p. 333. References Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Steinkeller, Friedrich-Carl von 1896 births 1981 deaths People from Wałcz Military personnel from West Prussia Major generals of the German Army (Wehrmacht) Recipients of the Gold German Cross R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wałcz
Wałcz (pronounced ; ) is a county town in Wałcz County of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Granted city rights in 1303, Wałcz has become the administrative, industrial and cultural center of the Wałcz Lake District with the city itself situated on the banks of the Raduń and Zamkowe lakes. Wałcz is located in the southestern portion of West Pomeranian Voivodeship. The closest cities are Szczecin , Bydgoszcz , Piła , Poznań , Gorzów Wielkopolski and Koszalin . Historically, the town belonged to the province of Greater Poland and was a royal city of Poland until the Partitions of Poland. Afterwards, from 1772 to 1945 it was part of Prussia and, from 1871 to 1945, it was also part of Germany, before being reintegrated with Poland. It is the location of one of the oldest high schools in Poland, founded over 350 years ago, and a garrison of the Polish Army. Geography According to a report from 2002, Wałcz has an area of of which 41% is used for agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
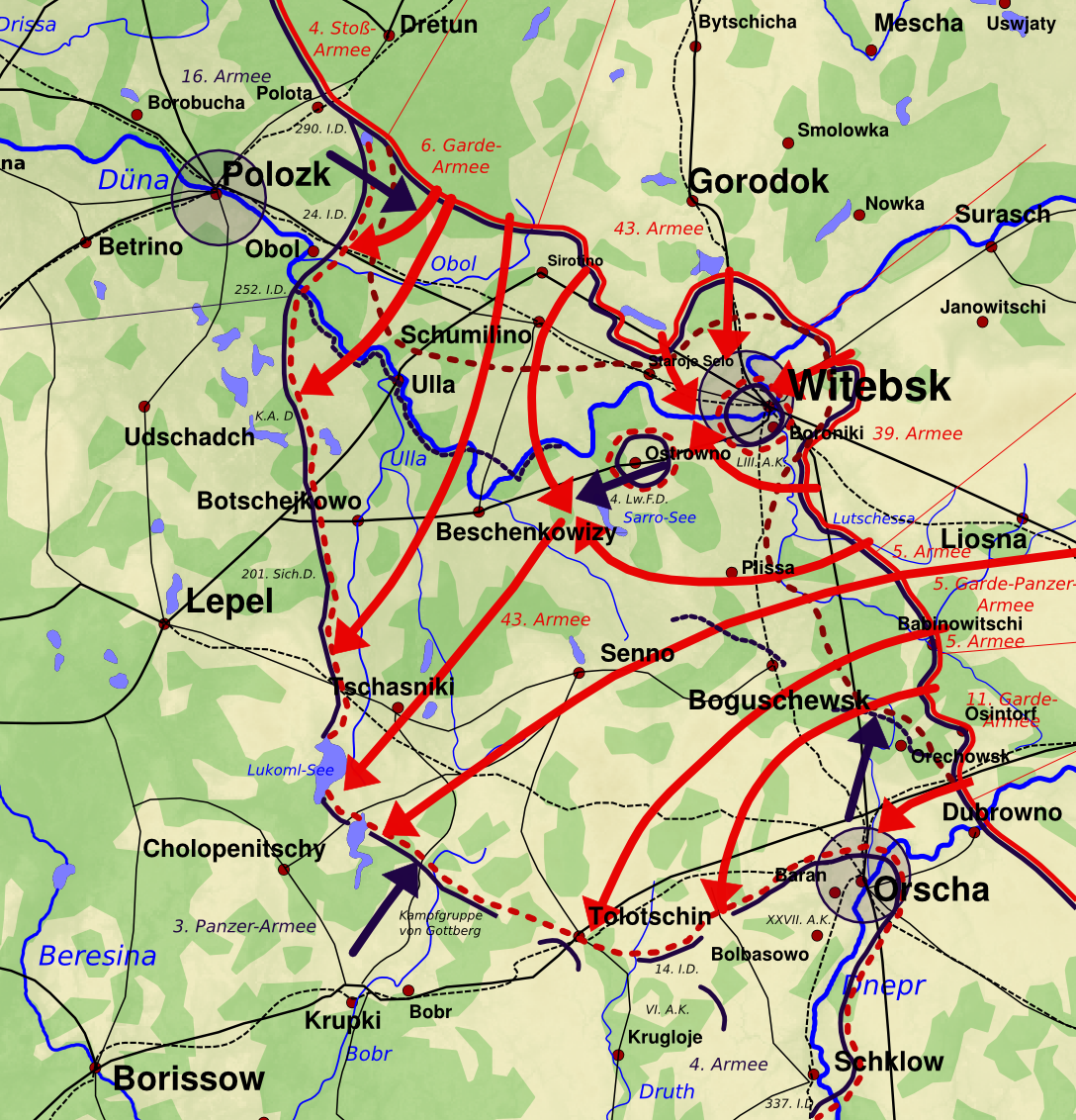
Operation Bagration
Operation Bagration () was the codename for the 1944 Soviet Byelorussian strategic offensive operation (), a military campaign fought between 22 June and 19 August 1944 in Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Soviet Byelorussia in the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front of World War II, just over two weeks after the start of Operation Overlord in the west. It was during this operation that Nazi Germany was forced to fight simultaneously on two major fronts for the first time since the war began. The Soviet Union destroyed 28 of the divisions of Army Group Centre and completely shattered the German front line. The overall engagement is the largest defeat in German military history, with around 450,000 German casualties, while setting the stage for the subsequent isolation of 300,000 German soldiers in the Courland Pocket. On 22 June 1944, the Red Army attacked Army Group Centre in Byelorussia, with the objective of encircling and destroying its main component armies. By ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Wałcz
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Deaths
Events January * January 1 ** Greece enters the European Economic Community, predecessor of the European Union. ** Palau becomes a self-governing territory. * January 6 – A funeral service is held in West Germany for Nazi Grand Admiral Karl Doenitz following his death on December 24. * January 10 – Salvadoran Civil War: The FMLN launches its first major offensive, gaining control of most of Morazán and Chalatenango departments. * January 15 – Pope John Paul II receives a delegation led by Polish Solidarity leader Lech Wałęsa at the Vatican. * January 20 – Iran releases the 52 Americans held for 444 days, minutes after Ronald Reagan is sworn in as the 40th President of the United States, ending the Iran hostage crisis. * January 21 – The first DeLorean automobile, a stainless steel sports car with gull-wing doors, rolls off the production line in Dunmurry, Northern Ireland. * January 24 – An earthquake of magnitude in Sichuan, China, kills 150 people. J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1896 Births
Events January * January 2 – The Jameson Raid comes to an end as Jameson surrenders to the Boers. * January 4 – Utah is admitted as the 45th U.S. state. * January 5 – An Austrian newspaper reports Wilhelm Röntgen's discovery, last November, of a type of electromagnetic radiation, later known as X-rays. * January 6 – Cecil Rhodes is forced to resign as Prime Minister of the Cape Colony, Cape of Good Hope for his involvement in the Jameson Raid. * January 7 – American culinary expert Fannie Farmer publishes her first cookbook. * January 12 – H. L. Smith takes the first X-ray photograph. * January 16 – Devonport High School for Boys is founded in Plymouth (England). * January 17 – Anglo-Ashanti wars#Fourth Anglo-Ashanti War (1895–1896), Fourth Anglo-Ashanti War: British British Army, redcoats enter the Ashanti people, Ashanti capital, Kumasi, and Asantehene Agyeman Prempeh I is deposed. * January 28 – Walter Arnold, of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Günther Pape
__NOTOC__ Günther Pape (14 July 1907 – 21 January 1986) was a German general during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves of Nazi Germany. Following World War II, Pape served in the Bundeswehr of West Germany. The force underwent a series of internal discussion and controversies which led to the "''Generalkrise''" (Crisis of the generals) in August 1966. Among other issues, the discussion was centered about the inner leadership of the Bundeswehr and the hierarchy of command between the Federal Ministry of Defence and the armed forces. The Inspector of the Luftwaffe General Werner Panitzki and Minister of Defence Kai-Uwe von Hassel resigned on 12 August 1966. Inspector General of the Bundeswehr General Heinrich Trettner resigned the next day followed shortly by Pape, who resigned out of loyalty to his commanding officers. Awards * Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (20 September 1939) & 1st Class (21 May 1940)Thomas 1998, p. 142. * Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Henze
Albert Henze (7 August 1894 – 31 March 1979) was a general who commanded several divisions in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves. Henze surrendered to the Soviet forces in the Courland Pocket and was held as a war criminal in the Soviet Union until 1955. Awards and decorations * Iron Cross (1914) 2nd Class (27 July 1916) & 1st Class (27 January 1918)Thomas 1997, p. 269. * Clasp to the Iron Cross (1939) 2nd Class (2 October 1939) & 1st Class (12 July 1940) * Honour Roll Clasp of the Army (18 August 1943) * German Cross in Gold on 2 March 1943 as ''Oberst'' in Panzergrenadier-Regiment 110 * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves ** Knight's Cross on 15 January 1944 as ''Oberst'' and commander of Panzergrenadier-Regiment 110 ** 709th Oak Leaves on 21 January 1945 as ''Generalmajor is the Germanic languages, Germanic variant of major general, used in a number of Central Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberstleutnant
() (English: Lieutenant Colonel) is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to lieutenant colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, Finland and Norway. The Swedish rank is a direct translation, as is the Finnish rank . Austria Austria's armed forces, the ''Bundesheer'', uses the rank Oberstleutnant as its sixth-highest officer rank. Like in Germany and Switzerland, Oberstleutnants are above Majors and below Obersts. The term also finds usage with the Austrian Bundespolizei (federal police force) and Justizwache (prison guards corps). These two organizations are civilian in nature, but their ranks are nonetheless structured in a military fashion. Belgium File:Army-BEL-OF-04.svg, Denmark The Danish rank of is based around the German term. Ranked OF-4 within NATO and having the paygrade of M401, it is used in the Royal Danish Army and the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Cross
The War Order of the German Cross (), normally abbreviated to the German Cross or ''Deutsches Kreuz'', was instituted by Adolf Hitler on 28 September 1941. It was awarded in two divisions: in gold for repeated acts of bravery or military leadership; and in silver for distinguished non-combat war service. The German Cross in Gold ranked higher than the Iron Cross First Class but below the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross, while the German Cross in Silver ranked higher than the War Merit Cross First Class with Swords but below the Knight's Cross of the War Merit Cross with Swords. Eligibility The German Cross was issued in two versions: gold and silver (the color of the laurel wreath around the swastika). The gold version was awarded to military personnel for repeated acts of bravery in combat, or of military leadership, with 6–8 acts as a rule of thumb. The silver version was awarded for multiple distinguished services in the war effort and was considered a continuation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Cross
The Iron Cross (, , abbreviated EK) was a military decoration in the Kingdom of Prussia, the German Empire (1871–1918), and Nazi Germany (1933–1945). The design, a black cross pattée with a white or silver outline, was derived from the insignia of the medieval Teutonic Order and borne by its knights from the 13th century. As well as being a military medal, it has also been used as an emblem by the Prussian Army, the Imperial German Army, and the of the Weimar Republic, while the ''Balkenkreuz'' (bar cross) variant was used by the ''Wehrmacht''. The Iron Cross is now the emblem of the , the modern German armed forces. King Frederick William III of Prussia established the Iron Cross award on 17 March 1813 during the Napoleonic Wars (EK 1813). The award was backdated to the birthday (10 March) of his late wife, Louise of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, Queen Louise, who was the first person to receive it (posthumously). The Iron Cross was also awarded during the Franco-Prussian War ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |