|
François Jules Pictet De La Rive
François-Jules Pictet de la Rive (27 September 180915 March 1872) was a Switzerland, Swiss zoologist and palaeontologist. Biography He was born in Geneva. He graduated B. Sc. at Geneva in 1829, and pursued his studies for a short time at Paris, where under the influence of Georges Cuvier, de Blainville and others, he worked at natural history and comparative anatomy. On his return to Geneva in 1830 he assisted A. P. de Candolle by giving demonstrations in comparative anatomy. Five years later, when de Candolle retired, Pictet was appointed professor of zoology and comparative anatomy. Endnotes: *Obituary by W. S. Dallas, ''Quart. Journ. Geol. Soc.'' (1873), vol. xxix. In 1846 his duties were restricted to certain branches of zoology, including geology and palaeontology, and these he continued to teach until 1859, when he retired to devote his energies to the Natural History Museum of Geneva, museum of natural history and to special palaeontological work. He was rector (academia) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
On The Origin Of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life'')The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''. In the 1872 sixth edition, "On" was omitted, so the full title is ''The origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life.'' This edition is usually known as ''The Origin of Species.'' The 6th is Darwin's final edition; there were minor modifications in the text of certain subsequent issues. See Freeman, R. B. In Van Wyhe, John, ed. ''Darwin Online: On the Origin of Species'', 2002. is a work of scientific literature by Charles Darwin that is considered to be the foundation of evolutionary biology. It was published on 24 November 1859. Darwin's book introduced the scientific theory that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fossil Record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Progressive Creationism
Progressive creationism is the religious belief that God created new forms of life gradually over a period of hundreds of millions of years. As a form of old Earth creationism, it accepts mainstream geological and cosmological estimates for the age of the Earth, some tenets of biology such as microevolution as well as archaeology to make its case. In this view creation occurred in rapid bursts in which all "kinds" of plants and animals appear in stages lasting millions of years. The bursts are followed by periods of stasis or equilibrium to accommodate new arrivals. These bursts represent instances of God creating new types of organisms by divine intervention. As viewed from the archaeological record, progressive creationism holds that "species do not gradually appear by the steady transformation of its ancestors; utappear all at once and "fully formed." The view rejects macroevolution, claiming it is biologically untenable and not supported by the fossil record, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
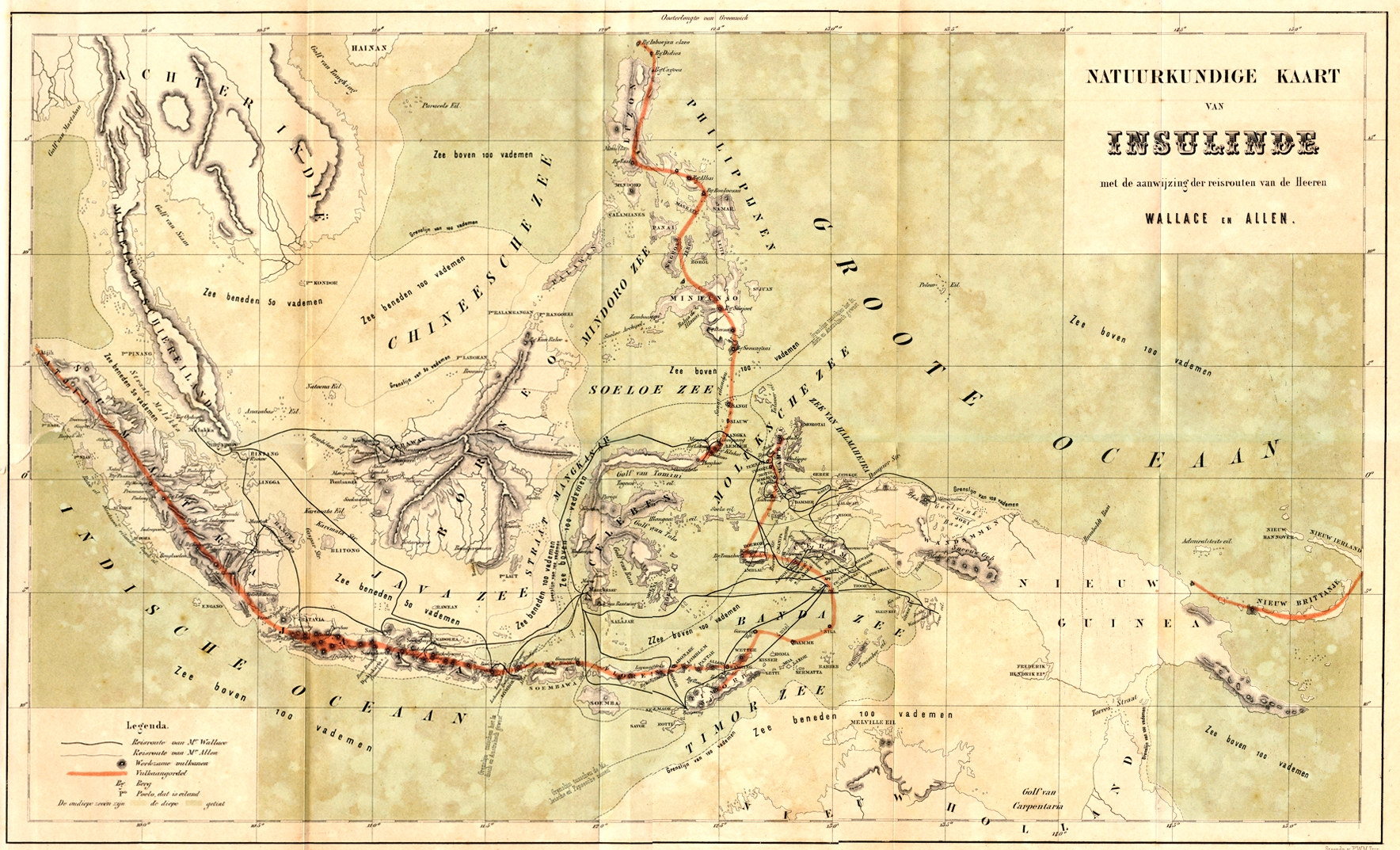
Alfred Russel Wallace
Alfred Russel Wallace (8 January 1823 – 7 November 1913) was an English naturalist, explorer, geographer, anthropologist, biologist and illustrator. He independently conceived the theory of evolution through natural selection; his 1858 paper on the subject was published that year On the Tendency of Species to form Varieties; and on the Perpetuation of Varieties and Species by Natural Means of Selection, alongside extracts from Charles Darwin's earlier writings on the topic. It spurred Darwin to set aside the Natural Selection (manuscript), "big species book" he was drafting and to quickly write an Abstract (summary), abstract of it, which was published in 1859 as ''On the Origin of Species''. Wallace did extensive fieldwork, starting in the Amazon River basin. He then did fieldwork in the Malay Archipelago, where he identified the faunal divide now termed the Wallace Line, which separates the Indonesian archipelago into two distinct parts: a western portion in which the ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Elapotinus Picteti
''Elapotinus'' is a monotypic genus created for the rear-fanged snake species, ''Elapotinus picteti''. The species is endemic to Madagascar. It is also known commonly as Jan's snake in honor of Italian herpetologist Giorgio Jan. There are no subspecies that are recognized as being valid. Description (diagnosis) of genus Maxillary very short, with five teeth gradually increasing in size and followed, after an interspace, by a large grooved fang situated below the eye. Mandibular teeth decreasing in size posteriorly. Head small, not distinct from neck. Eye minute, with round pupil. Nostril between two nasals. No loreal. Body cylindrical; tail short. Dorsal scales smooth, without pits, in 17 rows. Ventrals rounded; subcaudals in two rows. Boulenger GA (1896). ''Catalogue of the Snakes in the British Museum (Natural History), Volume III., Containing the Colubridæ (Opisthoglyphæ and Proteroglyphæ) ...'' London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Philippe De La Harpe
Philippe de La Harpe (1 April 1830, Paudex – 25 February 1882, Lausanne) was a Swiss physician known for research in the fields of geology and paleontology. He studied medicine in Bonn, Berlin, Prague, Vienna and Lyon, then received his doctor-surgeon licence from the University of Bern in 1854. He spent the winter of 1855/56 in England, where he made the acquaintance of several geologists, then settled as a doctor in Lausanne during the spring of 1856. In Lausanne, he worked as a physician for the remainder of his life, being very active in medical research and a member of various professional groups.Dictionnaire historique de la Suisse La Harpe, Philippe For several years, he was curator of the canton's geological and mineral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Auguste Jaccard
Auguste Jaccard (6 July 1833, in Culliairy near Sainte-Croix – 5 January 1895, in Le Locle) was a Swiss geologist and paleontologist. His scientific research, for the most part, was associated with the Jura Mountains. In around 1845, he moved with his father to Le Locle, where the elder Jaccard opened a guilloché workshop that was later managed by his son. As a geologist, Auguste Jaccard was self-taught, having Oswald Heer and Pierre Jean Édouard Desor as important influences to his career. In 1856 he released his first publication, a treatise on fossils found in the basin of Le Locle.Historisches Lexikon der Schweiz biography From 1861 he was a member of the geological survey group of the ''Société helvétique des sciences naturelles'' (Swiss Society of Natural Sciences), tasked with mapping the western part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Perceval De Loriol
Charles Louis Perceval de Loriol (24 July 1828, Geneva – 23 December 1908, Cologny) was a Swiss paleontologist and stratigraphist. He studied natural sciences and paleontology in Geneva as a pupil of François-Jules Pictet. For a period of time, he worked as an estate manager in Geneva and Lorraine, then for nearly forty years was associated with the Natural History Museum of Geneva. He was one of the founders of the ''Schweizerische Paläontologische Gesellschaft'' and editor of the ''Mémoires de la Société suisse paléontologique''. In 1902 he received an honorary doctorate from the University of GenevaLoriol, Perceval de Historischen Lexikon der Schweiz He is remembered for his investigations of fossil |
Alois Humbert
Alois (Latinized ''Aloysius'') is an Old Occitan form of the name Louis. Modern variants include ''Aloïs'' (French), ''Aloys'' (German), ''Alois'' (Czech), ''Alojz'' ( Slovak, Slovenian, Croatian), '' Alojzy'' (Polish), '' Aloísio'' (Portuguese, Spanish, Italian), '' Alajos'' ( Hungarian), and ''Aloyzas'' (Lithuanian). People called Alois/Aloys * Alois Alzheimer (1864–1915), German psychiatrist and neuropathologist * Alois Arnegger (1879–1963), Austrian painter * Alois Berla (1826–1896), Austrian actor and playwright * Alois Biach (1849–1918), Austrian physician and medical writer * Alois Brunner (1912–2001), Austrian Nazi SS concentration camp war criminal * Alois Carigiet (1902–1985), Swiss illustrator * Alois Dryák (1872–1932), Czech architect * Alois Eliáš (1890–1942), Czech general and politician * Alois Estermann, senior officer of the Pontifical Swiss Guard who was murdered in his apartment * Alois Hába, Czech composer * Alois Hitler (1837–1903), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |