|
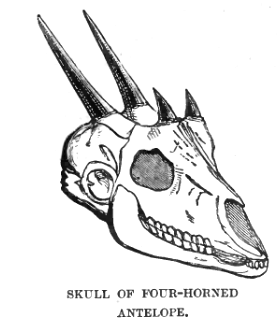
Four-horned Antelope
The four-horned antelope (''Tetracerus quadricornis''), also called ''chousingha'', is a small bovid antelope native to central, South and Western India, along with a smaller population in Nepal. The sole member of the genus ''Tetracerus'', the chousingha was first scientifically described in 1816 by French zoologist Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville. Three regional subspecies are currently recognised. The four-horned antelope has a yellowish-tan, sometimes reddish or goldenrod coat. It is slender with thin legs and a short tail. It stands nearly at the shoulder and weighs about . Its four horns are unique among antelopes and distinguish it from most other bovids. The longer pair of straight, spike-like horns is atop its head between the ears, while the other, shorter pair is on the forehead; its posterior horns are always longer than the anterior horns, which may even present as merely fur-covered "studs". While the posterior horns measure , the anterior ones are usually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary
Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary is located in northeastern Goa, India in Sattari, Ponda and Sanguem. The total area of the park is 7.98 km2, making it the smallest of the wildlife sanctuaries in Goa. It is a popular destination for both tourists and schoolchildren, as it contains the only zoo in Goa. Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary provides sanctuary to leopards who have been injured in human-wildlife conflict, as well as "dancing" bears and cobras who, along with their trainers, need a new life after this treatment of endangered wildlife. Bondla Zoo is known for its successful breeding of gaur. The zoo provides an excellent environment to breed and do research on animals. Geography Bondla Wildlife Sanctuary is located 38 km from Madgaon and 46 km from Panaji. It is located next to Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary and Mollem National Park and Bhagwan Mahaveer Wildlife Sanctuary. The forest is a moist deciduous forest filled with patches of semi-evergreen trees. The best time to visit th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Description
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been previously described or related species. For a species to be considered valid, a species description must follow established guidelines and naming conventions dictated by relevant nomenclature codes. These include the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN) for animals, the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) for plants, and the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) for viruses. A species description often includes photographs or other illustrations of type material and information regarding where this material is deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophy Hunting
Trophy hunting is a form of hunting for field sports, sport in which parts of the hunted wild animals are kept and displayed as trophies. The animal being targeted, known as the "game (hunting), game", is typically a mature male specimen from a popular species of collectable interests, usually of large sizes, holding impressive horn (anatomy), horns, antlers, furs, or manes. Most trophies consist of only select parts of the animal, which are prepared for display by a taxidermy, taxidermist. The parts most commonly kept vary by species but often include the head, Hide (skin), hide, tusks, horns, or antlers. Trophies are often displayed in trophy rooms or game rooms, or in gun rooms along with the hunter's gun collection. Trophy hunting has strong supporters and opponents. The controversy focuses on the morality of hunting for pleasure rather than for practical use, as well as questions about the extent to which big-game hunting benefits Nature conservation, conservation efforts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Expansion
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land ( arable land, pastures, etc.) especially in the 20th and 21st centuries. The agricultural expansion is often explained as a direct consequence of the global increase in food and energy Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ... requirements due to population growth (both which in turn have been attributed to agricultural expansion itself), with an estimated expectation of 10 billion people on Earth by end of this century. It is foreseen that most of the world's non-agrarian ecosystems (terrestrial ecosystem, terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem, aquatic) will be environmental impact, affected adversely, from habitat loss, land degradation, overexploitation, and other problems. The intensified food production, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seasonal Breeder
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and changes in the predation behaviors of other species. Related sexual interest and behaviors are expressed and accepted only during this period. Female seasonal breeders will have one or more estrus cycles only when she is "in season" or fertile and receptive to mating. At other times of the year, they will be anestrus, or have a dearth of their sexual cycle. Unlike reproductive cyclicity, seasonality is described in both males and females. Male seasonal breeders may exhibit changes in testosterone levels, testes weight, and fertility depending on the time of year. Seasonal breeders are distinct from opportunistic breeders, that mate whenever the conditions of their environment become favorable, and continuous breeders that mate year-rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and other consequences that may arise from expression of wikt:deleterious, deleterious dominance (genetics), recessive traits resulting from incestuous sexual relationships and consanguinity. Animals avoid inbreeding only rarely. Inbreeding results in homozygous, homozygosity which can increase the chances of offspring being affected by recessive phenotypic trait, traits. In extreme cases, this usually leads to at least temporarily decreased Fitness (biology), biological fitness of a population (called inbreeding depression), which is its ability to survive and reproduce. An individual who inherits such deleterious traits is colloquially referred to as ''inbred''. The avoidance of expression of such deleterious recessive allel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deciduous Forest
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, after flowering; and to the shedding of ripe fruit. The antonym of deciduous in the botanical sense is evergreen. Generally, the term "deciduous" means "the dropping of a part that is no longer needed or useful" and the "falling away after its purpose is finished". In plants, it is the result of natural processes. "Deciduous" has a similar meaning when referring to animal parts, such as deciduous antlers in deer, deciduous teeth (baby teeth) in some mammals (including humans); or decidua, the uterine lining that sheds off after birth. Botany In botany and horticulture, deciduous plants, including trees, shrubs and herbaceous perennials, are those that lose all of their leaves for part of the year. This process is called abscission. In some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregnancy can have one or more gestations at the same time, for example in a multiple birth. The time interval of a gestation is called the '' gestation period''. In obstetrics, '' gestational age'' refers to the time since the onset of the last menses, which on average is fertilization age plus two weeks. Mammals In mammals, pregnancy begins when a zygote (fertilized ovum) implants in the female's uterus and ends once the fetus leaves the uterus during labor or an abortion (whether induced or spontaneous). Humans In humans, pregnancy can be defined clinically, biochemically or biologically. Clinically, pregnancy starts from first day of the mother's last period. Biochemically, pregnancy starts when a woman's human chorionic gonado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized as an independent person capable of giving consent and taking responsibility, generally implies sexual maturity (certain disorders of sexual development notwithstanding), but depends on other criteria, defined by specific cultural expectations. Most multicellular organisms are unable to sexually reproduce at birth (animals) or germination (e.g. plants): depending on the species, it may be days, weeks, or years until they have developed enough to be able to do so; in addition, certain cues may trigger an organism to become sexually mature. These may be external, such as drought, or fire, that triggers sexual maturation of certain plants, or internal, such as percentage of body fat (certain animals). Internal cues are not to be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnality
Diurnality is a form of plant and ethology, animal behavior characterized by activity during daytime, with a period of sleeping or other inactivity at night. The common adjective used for daytime activity is "diurnal". The timing of activity by an animal depends on a variety of environmental factors such as the temperature, the ability to gather food by sight, the risk of predation, and the time of year. Diurnality is a cycle of activity within a 24-hour period; cyclic activities called circadian rhythms are endogenous cycles not dependent on external cues or environmental factors except for a zeitgeber. Animals active during twilight are crepuscular, those active during the night are nocturnal and animals active at sporadic times during both night and day are cathemerality, cathemeral. Plants that open their flowers during the daytime are described as diurnal, while those that bloom during nighttime are nocturnal. The timing of flower opening is often related to the time at whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. For example, '' Termin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior (anatomy)
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek language, Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes, axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether a vertebrate is a biped or a quadruped, due to the difference in the neuraxis, or if an invertebrate is a non-bilaterian. A non-bilaterian has no anterior or posterior surface for example but can still have a descriptor used such as proximal or distal in relation to a body part that is nearest to, or furthest from its middle. International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standards for subdisciplines of anatomy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |