|
Foundation Model
A foundation model, also known as large AI model, is a machine learning or deep learning model that is trained on broad data such that it can be applied across a wide range of use cases.Competition and Markets Authority (2023). ''AI Foundation Models: Initial Report''. Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/65081d3aa41cc300145612c0/Full_report_.pdf Foundation models have transformed artificial intelligence (AI), powering prominent generative AI applications like ChatGPT. The Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence's (HAI) Center for Research on Foundation Models (CRFM) created and popularized the term. Foundation models are general-purpose technologies that can support a diverse range of use cases. Building foundation models is often highly resource-intensive, with the most expensive models costing hundreds of millions of dollars to pay for the underlying data and compute required. In contrast, adapting an existing foundation model for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Eshoo
Anna A. Eshoo ( ; née Georges; born December 13, 1942) is an American politician serving as the U.S. representative from . She is a member of the Democratic Party. The district, numbered as the 14th district from 1993 to 2013, is based in Silicon Valley, including the cities of Redwood City, Sunnyvale, Mountain View, and Palo Alto, as well as part of San Jose. Eshoo is the only Assyrian American in Congress and the only Armenian American woman in Congress. Early life and education Anna Eshoo was born in New Britain, Connecticut, of Assyrian and Armenian heritage. Her mother fled from Armenia to Iraq, and subsequently to the United States. Her father, Fred Georges, a jeweler and watchmaker, was a Chaldean Christian. Eshoo graduated from New Britain High School in 1960, and later moved to California. She received an associate of arts degree from Cañada College in 1975. Early political career Eshoo was Chair of the San Mateo Democratic Party from 1978 to 1982. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPT-1
Generative Pre-trained Transformer 1 (GPT-1) was the first of OpenAI's large language models following Google's invention of the transformer (machine learning model), transformer architecture in 2017. In June 2018, OpenAI released a paper entitled "Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training", in which they introduced that initial model along with the general concept of a generative pre-trained transformer. Up to that point, the best-performing neural NLP models primarily employed supervised learning from large amounts of manually labeled data. This reliance on supervised learning limited their use of datasets that were not well-annotated, in addition to making it prohibitively expensive and time-consuming to train extremely large models; many languages (such as Swahili language, Swahili or Haitian Creole) are difficult to translate and interpret using such models due to a lack of available text for corpus-building. In contrast, a GPT's "semi-supervised" approac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELMo
Elmo is a red Muppet monster character on the long-running PBS/ HBO children's television show ''Sesame Street''. A furry red monster who has a falsetto voice and illeism, he hosts the last full five-minute segment (fifteen minutes prior to 2017) on ''Sesame Street'', " Elmo's World", which is aimed at toddlers. He was most often puppeteered by Kevin Clash, but since his resignation in late 2012, he has been puppeteered by Ryan Dillon. History Elmo is self-described as three-and-a-half years old and his birthday is on February 3. Elmo characteristically avoids pronouns in reference to himself, instead referring to himself in the third person (e.g. saying "Elmo wants this" instead of "I want this"). ''Sesame Street'' staff writer Nancy Sans once described Elmo's origins: "There was this extra red puppet lying around and the cast would pick him up sometimes and try to create a personality, but nothing seemed to materialize." The character of Elmo was originally conceiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TensorFlow
TensorFlow is a free and open-source software library for machine learning and artificial intelligence. It can be used across a range of tasks but has a particular focus on training and inference of deep neural networks. "It is machine learning software being used for various kinds of perceptual and language understanding tasks" – Jeffrey Dean, minute 0:47 / 2:17 from YouTube clip TensorFlow was developed by the Google Brain team for internal Google use in research and production. The initial version was released under the Apache License 2.0 in 2015. Google released the updated version of TensorFlow, named TensorFlow 2.0, in September 2019. TensorFlow can be used in a wide variety of programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, C++, and Java. This flexibility lends itself to a range of applications in many different sectors. History DistBelief Starting in 2011, Google Brain built DistBelief as a proprietary machine learning system based on deep learning neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PyTorch
PyTorch is a machine learning framework based on the Torch library, used for applications such as computer vision and natural language processing, originally developed by Meta AI and now part of the Linux Foundation umbrella. It is free and open-source software released under the modified BSD license. Although the Python interface is more polished and the primary focus of development, PyTorch also has a C++ interface. A number of pieces of deep learning software are built on top of PyTorch, including Tesla Autopilot, Uber's Pyro, Hugging Face's Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, and Catalyst. PyTorch provides two high-level features: * Tensor computing (like NumPy) with strong acceleration via graphics processing units (GPU) * Deep neural networks built on a tape-based automatic differentiation system History Meta (formerly known as Facebook) operates both ''PyTorch'' and ''Convolutional Architecture for Fast Feature Embedding'' ( Caffe2), but models defined by the two f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AlexNet
AlexNet is the name of a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture, designed by Alex Krizhevsky in collaboration with Ilya Sutskever and Geoffrey Hinton, who was Krizhevsky's Ph.D. advisor. AlexNet competed in the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge on September 30, 2012. The network achieved a top-5 error of 15.3%, more than 10.8 percentage points lower than that of the runner up. The original paper's primary result was that the depth of the model was essential for its high performance, which was computationally expensive, but made feasible due to the utilization of graphics processing units (GPUs) during training. Historic context AlexNet was not the first fast GPU-implementation of a CNN to win an image recognition contest. A CNN on GPU by K. Chellapilla et al. (2006) was 4 times faster than an equivalent implementation on CPU. A deep CNN oDan Cireșanet al. (2011) at IDSIA was already 60 times faster and outperformed predecessors in August 2011. Betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expert System
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert. Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if–then rules rather than through conventional procedural code. The first expert systems were created in the 1970s and then proliferated in the 1980s. Expert systems were among the first truly successful forms of artificial intelligence (AI) software. An expert system is divided into two subsystems: the inference engine and the knowledge base. The knowledge base represents facts and rules. The inference engine applies the rules to the known facts to deduce new facts. Inference engines can also include explanation and debugging abilities. History Early development Soon after the dawn of modern computers in the late 1940s and early 1950s, researchers started realizing the immense potential these machines had for modern society. One ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
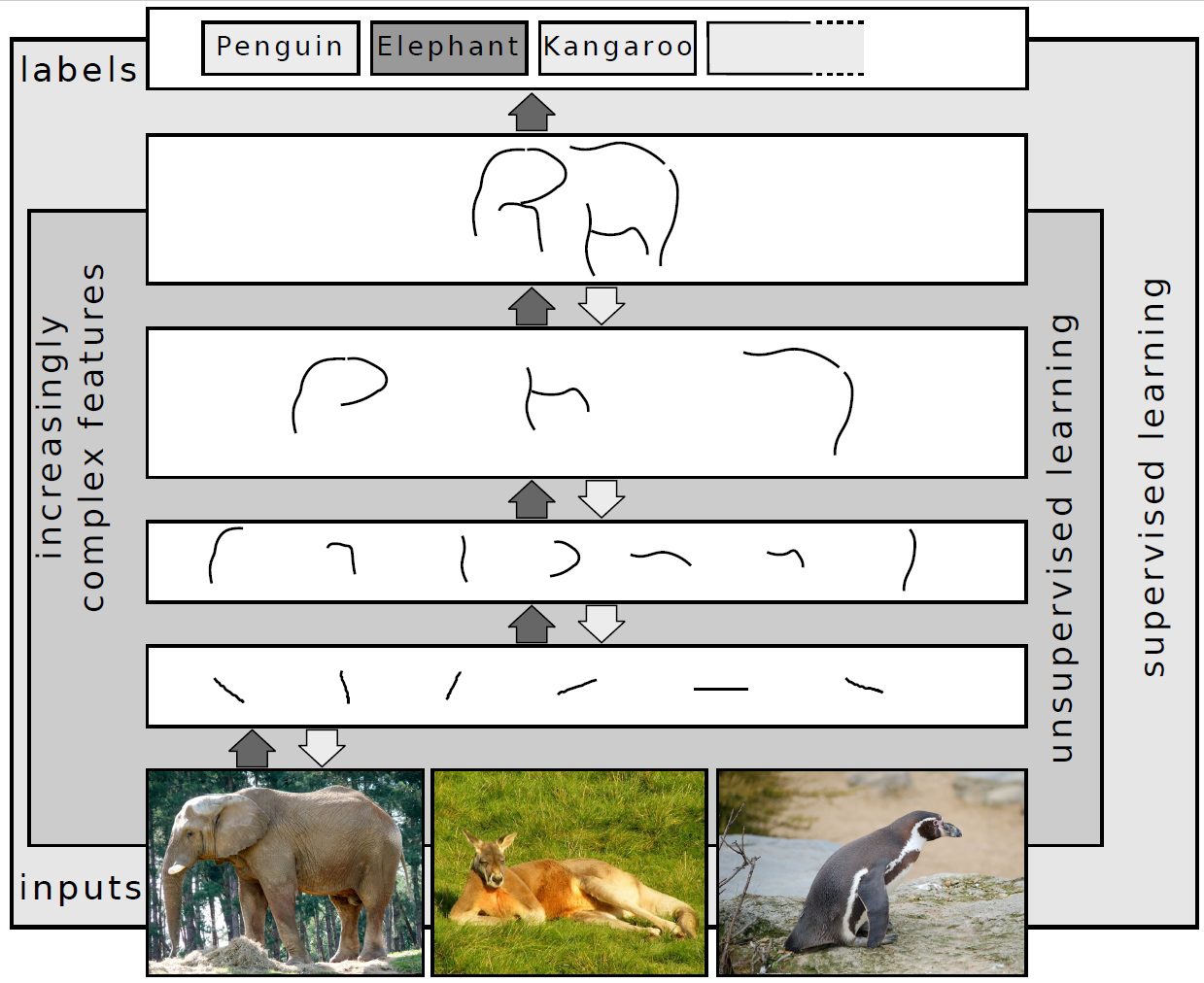
Self-supervised Learning
Self-supervised learning (SSL) refers to a machine learning paradigm, and corresponding methods, for processing unlabelled data to obtain useful representations that can help with downstream learning tasks. The most salient thing about SSL methods is that they do not need human-annotated labels, which means they are designed to take in datasets consisting entirely of unlabelled data samples. Then the typical SSL pipeline consists of learning supervisory signals (labels generated automatically) in a first stage, which are then used for some supervised learning task in the second and later stages. For this reason, SSL can be described as an intermediate form of unsupervised and supervised learning. The typical SSL method is based on an artificial neural network or other model such as a decision list. The model learns in two steps. First, the task is solved based on an auxiliary or pretext classification task using pseudo-labels which help to initialize the model parameters. Second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Learning
Transfer learning (TL) is a research problem in machine learning (ML) that focuses on storing knowledge gained while solving one problem and applying it to a different but related problem. For example, knowledge gained while learning to recognize cars could apply when trying to recognize trucks. This area of research bears some relation to the long history of psychological literature on transfer of learning, although practical ties between the two fields are limited. From the practical standpoint, reusing or transferring information from previously learned tasks for the learning of new tasks has the potential to significantly improve the sample efficiency of a reinforcement learning agent. History In 1976, Stevo Bozinovski and Ante Fulgosi published a paper explicitly addressing transfer learning in neural networks training. The paper gives a mathematical and geometrical model of transfer learning. In 1981, a report was given on the application of transfer learning in training ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Neural Networks
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Deep-learning architectures such as deep neural networks, deep belief networks, deep reinforcement learning, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks and Transformers have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, climate science, material inspection and board game programs, where they have produced results comparable to and in some cases surpassing human expert performance. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) were inspired by information processing and distributed communication nodes in biological systems. ANNs have various differences from biological brains. Specifically, artificial neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)