|
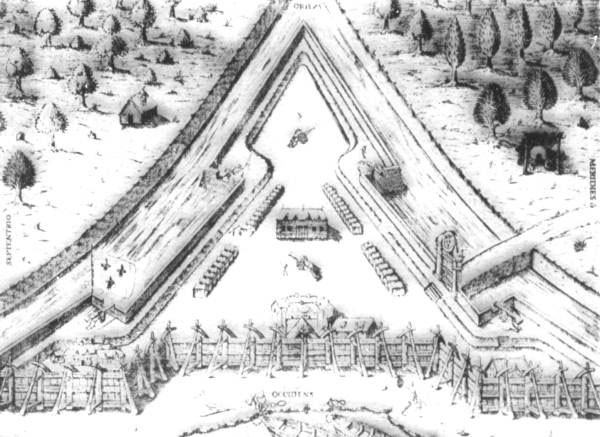
Fort Caroline
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June 1564, following King Charles IX's enlisting of Jean Ribault and his Huguenot settlers to stake a claim in French Florida ahead of Spain. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine on 8 September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on 20 September. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.Morris, p. 470 The exact site of the former fort is unknown. In 1953 the National Park Service established the Fort Caroline National Memorial along the southern bank of the St. John's River near the point that commemorates Laudonnière's first landing. This is generally accepted by scholars as being in the vicinity of the original fort, though prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arlington (Jacksonville)
Arlington is a large region of Jacksonville, Florida, and is generally understood as a counterpart to the city's other large regions, the Urban Core, Northside, Southside, Westside, and the Beaches. It borders the Southside area at its southern end, and has several bridge connections to nearby beaches, the Northside and Downtown. The expansive neighborhood was incorporated into the city in 1968 as a result the Jacksonville Consolidation, a city-county consolidation of the governments of the City of Jacksonville and Duval County. Arlington is known for its mid-century modern architecture, and contains several architecturally significant homes designed by local architects Robert C. Broward, Taylor Hardwick, and William Morgan. History Arlington was one of the first areas in the United States visited by Europeans; it was the site of the French Fort Caroline in 1564–1565, now represented by the Fort Caroline National Memorial. After the destruction of Fort Caroline, the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlesfort
The Charlesfort-Santa Elena Site is an important early colonial archaeological site on Parris Island, South Carolina, United States. It contains the archaeological remains of a French settlement called Charlesfort, settled in 1562 and abandoned the following year, and the later 16th-century Spanish settlement known as Santa Elena. The Spanish remains include a fort built directly on top of the abandoned Charlesfort remains. The fort and other nearby structures have been called, at various times, Fort San Marcos or Fort San Felipe, and have the designated archaeological site identifiers 38BU51 and 38BU162. Because of their remarkable state of preservation, and their importance in understanding early French and Spanish colonial practices, the site was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2001. The site is accessible through the United States Marine Corps Recruit Depot in Port Royal, South Carolina. Charlesfort (1562–1563, 1577-1578) Charlesfort was established wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominique De Gourgues
Dominique (or Domingue) de Gourgues (1530–1593) was a French nobleman and soldier. He is best known for leading a privateer attack against Spanish Florida in 1568, in retaliation for the no quarter given after the capture of Fort Caroline and the subsequent Massacre at Matanzas Inlet. He was a captain in King Charles IX's army. Youth De Gourgue's early life is not well known. He came from the old and powerful family of Gourgue, one of the most important families of the French city of Bordeaux. He served in the Italian wars under Maréchal de Strozzi, was captured by Spaniards in 1557, and then by the Turks, and served several years in the galleys. After his return to France, he made a voyage to Brazil and the West Indies, and then entered the service of Duke de Guise, and was employed against the Huguenots.Appletons' Situation in the colonies Philip II of Spain was a Roman Catholic king who hated Protestants, including the French Huguenots, and considered them heretics. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Matanzas National Monument
Fort Matanzas National Monument () is the site where the Spanish built a fort. It was designated a United States national monument on October 15, 1924. The monument consists of a 1740 Spanish fort called Fort Matanzas, and about 100 acres (0.4 km2) of salt marsh and barrier islands along the Matanzas River on the northern Atlantic coast of Florida. It is operated by the National Park Service in conjunction with the Castillo de San Marcos National Monument in the city of St. Augustine. History Fort Matanzas was built by the Spanish in 1742 to guard Matanzas Inlet, the southern mouth of the Matanzas River, which could be used as a rear entrance to the city of St. Augustine. Such an approach avoided St. Augustine's primary defense system, centered at Castillo de San Marcos. In 1740, Gov. James Oglethorpe of Georgia used the inlet to blockade St. Augustine and launch a thirty-nine-day siege. St. Augustine endured the siege, but the episode convinced the Spanish that pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matanzas Inlet
Matanzas Inlet is a channel in Florida between two barrier islands and the mainland, connecting the Atlantic Ocean and the south end of the Matanzas River. It is south of St. Augustine, in the southern part of St. Johns County. The inlet is not stabilized by jetties, and thus is subject to shifting. It is the last remaining natural or undredged inlet on the Atlantic coast of Florida. Historic maps made by Spanish military engineers in the 18th century show that the inlet today has moved many hundreds of yards south of its location during the time of the Spanish Empire. In 1740, a British invasion force from Fort Frederica, Georgia blockaded this inlet, the southernmost access for boat travel between St. Augustine and Havana, Cuba. Shortly thereafter, in 1742, a coquina stone tower square by high, now called Fort Matanzas, was built by the Spanish authorities in Florida to safeguard this strategic inlet. Origin of name René Goulaine de Laudonnière founded Fort Caroline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in many Western Christian liturgical calendars on 29 September, and on 8 November in the Eastern Christian traditions. Michaelmas has been one of the four quarter days of the English and Irish financial, judicial, and academic year. In the Christian angelology of some traditions, the Archangel Michael is considered as the greatest of all the angels; being particularly honored for defeating the devil in the war in heaven. History The name Michaelmas comes from a shortening of "Michael's Mass", in the same style as Christmas (Christ's Mass) and Candlemas (Candle Mass, the Mass where traditionally the candles to be used throughout the year would be blessed). During the Middle Ages, Michaelmas was celebrated as a Holy Day of Obligation, but this tradition was abolished in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Founding Of Fort Caroline Mg 0318
{{disambiguation ...
Founding may refer to: * The formation of a corporation, government, or other organization * The laying of a building's foundation * The casting of materials in a mold See also * Foundation (other) * Incorporation (other) Incorporation may refer to: * Incorporation (business), the creation of a business or corporation * Incorporation of a place, the creation of municipal corporation such as a city or county * Incorporation (academic), awarding a degree based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Assault On French Florida
The Spanish assault on French Florida began as part of imperial Spain's geopolitical strategy of developing colonies in the New World to protect its claimed territories against incursions by other European powers. From the early 16th century, the French had historic claims to some of the lands in the New World that the Spanish called ''La Florida''. The French crown and the Huguenots led by Admiral Gaspard de Coligny believed that planting French settlers in Florida would help defuse religious conflicts in France and strengthen its own claim to a part of North America. The Crown wanted to discover and exploit valuable commodities, especially silver and gold, as the Spanish had done with the mines of Mexico and Central and South America. The political and religious enmities that existed between the Catholics and Huguenots of France resulted in the attempt by Jean Ribault in February 1562 to settle a colony at Charlesfort on Port Royal Sound, and the subsequent arrival of René Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hawkins (naval Commander)
Admiral Sir John Hawkins (also spelled Hawkyns) (1532 – 12 November 1595) was an English naval commander, naval administrator, privateer and slave trader. Hawkins pioneered, and was an early promoter of, English involvement in the Atlantic slave trade. He is considered to be the first English merchant to profit from the Triangle Trade, selling enslaved people from Africa to the Spanish colonies in the West Indies in the late 16th century. In 1588, Hawkins served as a Vice-Admiral and fought in the victory over the Spanish Armada, for which he was knighted for gallantry. As Treasurer of the Navy, Hawkins became the chief architect of the Elizabethan Navy. He redesigned the navy so the ships were faster, more manoeuvrable and had more firepower. Hawkins' son, Richard Hawkins, was captured by the Spanish. In response, along with his cousin Sir Francis Drake, he raised a fleet of ships to attack the Spanish in the West Indies. However, he died at sea during the expedition. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Caroline, Florida
Fort Caroline was an attempted French colonial settlement in Florida, located on the banks of the St. Johns River in present-day Duval County. It was established under the leadership of René Goulaine de Laudonnière on 22 June 1564, following King Charles IX's enlisting of Jean Ribault and his Huguenot settlers to stake a claim in French Florida ahead of Spain. The French colony came into conflict with the Spanish, who established St. Augustine on 8 September 1565, and Fort Caroline was sacked by Spanish troops under Pedro Menéndez de Avilés on 20 September. The Spanish continued to occupy the site as San Mateo until 1569.Morris, p. 470 The exact site of the former fort is unknown. In 1953 the National Park Service established the Fort Caroline National Memorial along the southern bank of the St. John's River near the point that commemorates Laudonnière's first landing. This is generally accepted by scholars as being in the vicinity of the original fort, though probably n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potano
The Potano (also Potanou or Potavou, Timucua: ''Potano'' "That is happening now") tribe lived in north-central Florida at the time of first European contact. Their territory included what is now Alachua County, the northern half of Marion County and the western part of Putnam County. This territory corresponds to that of the Alachua culture, which lasted from about 700 until 1700. The Potano were among the many tribes of the Timucua people, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language. Early European contact The Pánfilo de Narváez expedition passed to the west of Potano territory in 1528. While not engaging with the Potano, the Spanish incursion spread new infectious diseases and incited warfare by competing tribes in the area. In 1539 Hernando de Soto led an army through Potano territory. There were 700 or more people in de Soto's army. They forced villagers to give up stored food to them. By the time de Soto's army reached Potano territory, he was intent on spend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agua Dulce People
The Agua Dulce or Agua Fresca (Freshwater) were a Timucua people of northeastern Florida. They lived in the St. Johns River watershed north of Lake George (Florida), Lake George, and spoke a dialect of the Timucua language also known as Agua Dulce. In the 1560s, Agua Dulce villages were organized into the chiefdom of Utina, one of the region's most powerful and prominent forces in the early days of European colonization of the Americas, European colonization in Florida. Utina had dealings with the French colony of Fort Caroline, and later allied with the Spanish of St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine, who established several Spanish missions in Florida, missions in its territory. However, the chiefdom declined significantly in the last decades of the 16th century, and the confederacy fragmented into at least three chiefdoms. The main body of the tribe withdrew south along the St. Johns River, and were known as the Agua Dulce to the Spanish. This chiefdom was largely abandoned b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |