|
Foreign Policy Of The Hugo Chávez Administration
The foreign policy of the Hugo Chávez administration concerns the policy initiatives made by Venezuela under its former President of Venezuela, President, Hugo Chávez, towards other states. Chávez's foreign policy may be roughly divided into that concerned with United States-Venezuela relations and that concerned with Venezuela's relations with other states, particularly those in Latin America and developing countries on other continents. In many respects the policies of the Chávez government were substantially different from the previous administrations that governed Venezuela. Policy Latin American integration Hugo Chávez refocused Venezuelan foreign policy on Latin American economic and social integration by enacting bilateral trade and reciprocal aid agreements, including through "oil diplomacy". Chávez stated that Venezuela has "a strong oil card to play on the geopolitical stage ... It is a card that we are going to play with toughness against the toughest countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venezuela
Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. It comprises an area of , and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas. The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of States of Venezuela, 23 states, the Venezuelan Capital District, Capital District and Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. The territory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neocolonialism
Neocolonialism is the control by a state (usually, a former colonial power) over another nominally independent state (usually, a former colony) through indirect means. The term ''neocolonialism'' was first used after World War II to refer to the continuing dependence of former colonies on foreign countries, but its meaning soon broadened to apply, more generally, to places where the power of developed countries was used to produce a colonial-like exploitation. Neocolonialism takes the form of economic imperialism, globalization, cultural imperialism and conditional aid to influence or control a developing country instead of the previous colonial methods of direct military control or indirect political control ( hegemony). Neocolonialism differs from standard globalisation and development aid in that it typically results in a relationship of dependence, subservience, or financial obligation towards the neocolonialist nation. Coined by the French philosopher Jean-Paul Sar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aló Presidente
''Aló Presidente'' (English: ''Hello, Mr. President'') was a long-running, unscripted talk show hosted by Hugo Chávez, former President of Venezuela. It was broadcast on Venezuelan state television and radio channels, including Venezolana de Televisión, on Sundays from 11:00am until mid/late afternoon. The show was used to promote Chavista socialist principles to supporters in Venezuela and beyond. Many editions were filmed outdoors before large audiences, commonly featuring a local farm, factory, school, hospital, housing project or other public investment. Although Chávez typically appeared on television several times a week, ''Aló Presidente'' was his opportunity to reach most families on their day off. The show was criticized for its lack of seriousness, due to low production values, spontaneous announcements, random contributions from audience members, colorful informality and often outright tedium. Live footage of ''Aló Presidente'' would occasionally be broadcast sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Bronx
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County, New York, Westchester County to its north; to its south and west, the New York City borough of Manhattan is across the Harlem River; and to its south and east is the borough of Queens, across the East River. The Bronx, the only New York City borough not primarily located on an island, has a land area of and a population of 1,472,654 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It has the fourth-largest area, fourth-highest population, and third-highest population density of the boroughs.New York State Department of Health''Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State – 2010'' retrieved on August 8, 2015. The Bronx is divided by the Bronx River into a hillier section in the West Bronx, west, and a flatter East Bronx, easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Oil
Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Adoption of electric vehicles, biofuels, or more efficient transport (like trains and waterways) could help reduce oil demand. Peak oil relates closely to oil depletion; while petroleum reserves are finite, the key issue is the economic viability of extraction at current prices. Initially, it was believed that oil production would decline due to reserve depletion, but a new theory suggests that reduced oil demand could lower prices, affecting extraction costs. Demand may also decline due to persistent high prices. Over the last century, many predictions of peak oil timing have been made, often later proven incorrect due to increased extraction rates. M. King Hubbert introduced the concept in a 1956 paper, predicting U.S. production would peak between 1965 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to Earth's climate. The current rise in global temperatures is driven by human activities, especially fossil fuel burning since the Industrial Revolution. Fossil fuel use, deforestation, and some agricultural and industrial practices release greenhouse gases. These gases absorb some of the heat that the Earth radiates after it warms from sunlight, warming the lower atmosphere. Carbon dioxide, the primary gas driving global warming, has increased in concentration by about 50% since the pre-industrial era to levels not seen for millions of years. Climate change has an increasingly large impact on the environment. Deserts are expanding, while heat waves and wildfires are becoming more common. Amplified warming in the Arctic has c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millennium Development Goals
In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These were based on the OECD DAC International Development Goals agreed by Development Ministers in the "Shaping the 21st Century Strategy". The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) succeeded the MDGs in 2016. All 191 United Nations member states, and at least 22 international organizations, committed to help achieve the following Millennium Development Goals by 2015: # To eradicate extreme poverty and hunger # To achieve universal primary education # To promote gender equality and empower women # To reduce child mortality # To improve maternal health # To combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases # To ensure environmental sustainability # To develop a global partnership for development [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Of 77
The Group of 77 (G77) at the United Nations (UN) is a coalition of developing country, developing countries, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. The group consists of a diverse set of states with a common South–South cooperation, South-South ideology. There were 77 founding members of the organization headquartered in Geneva, but it has since expanded to 134 member countries. Iraq holds its chairmanship for 2025, succeeding Uganda. The group was founded on 15 June 1964, by 77 Non-Aligned Nations, non-aligned nations in the "Joint Declaration of the Seventy-Seven Countries" issued at the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). The first major meeting was in Algiers in 1967, where the ''Charter of Algiers'' was adopted and the basis for permanent institutional structures was begun under the leadership of Raúl Prebisch who had previously worked at United Nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALBA
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English-language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
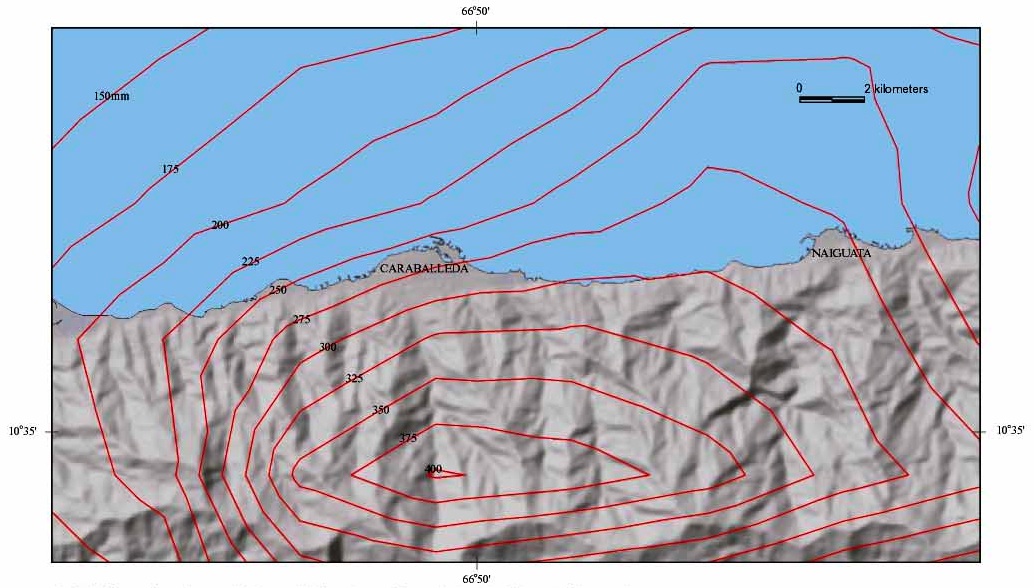
Vargas Tragedy
The Vargas tragedy was a natural disaster that occurred in Vargas State, Venezuela on 15 December 1999 (over the course of 10 days), when torrential rains caused flash floods and debris flows that killed tens of thousands of people, destroyed thousands of homes, and led to the complete collapse of the state's infrastructure. According to relief workers, the neighborhood of Los Corales was buried under of mud and a high percentage of homes were simply swept into the ocean. Entire towns including Cerro Grande and Carmen de Uria completely disappeared. As much as 10% of the population of Vargas died during the event. A deadlier natural disaster would not occur until the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. Background The coastal area of Vargas State has long been subject to mudslides and flooding. Deposits preserved on the alluvial fan deltas here show that geologically similar catastrophes have occurred with regularity since prehistoric times. Since the 17th century, at lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Medical Internationalism
After the 1959 Cuban Revolution, Cuba established a program to send its medical personnel overseas, particularly to Latin America, Africa, and Oceania, and to bring medical students and patients to Cuba for training and treatment respectively. In 2007, Cuba had 42,000 workers in international collaborations in 103 countries, of whom more than 30,000 were health personnel, including at least 19,000 physicians.Robert Huish and John M. Kirk (2007), "Cuban Medical Internationalism and the Development of the Latin American School of Medicine", ''Latin American Perspectives'', 34; 77 Cuba provides more medical personnel to the developing world than all the G8 countries combined. The Cuban missions have had substantial positive local impacts on the populations served. It is widely believed that medical workers are a vital export commodity for Cuba. According to '' Granma'', the Cuban state newspaper, the number of Cuban medical staff abroad fell from 50,000 in 2015 to 28,000 in 2020. A ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Military Internationalism
Cuban foreign policy during the Cold War emphasized providing direct military assistance to friendly governments and resistance movements worldwide. This policy was justified directly by the Marxist concept of proletarian internationalism and was first articulated by Cuban leader Fidel Castro at the Organization of Solidarity with the People of Asia, Africa and Latin America in 1966. However, as an informal policy it had been adopted as early as 1959, shortly after the Cuban Revolution. It formed the basis for a number of Cuban military initiatives in Africa and Latin America, often carried out in direct conjunction with the Soviet Union and Warsaw Pact member states which provided advisory or logistical support. These operations were often planned by the Cuban general staff through an overseas headquarters known as an internationalist mission. Military internationalism formed the crux of Cuba's foreign and military policy for almost three decades, and was subordinate only to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |