|
Florisbad Archaeological And Paleontological Site
The Florisbad archaeological and paleontological site is a provincial heritage site in Soutpan in the Free State province of South Africa. The most notable find at this site is the Florisbad Skull, the partial skull of an early human species that was discovered in 1932. In 1997 it was described in the Government Gazette as: The stratigraphic nature of the site is characterized by distinct sand and peat layers, with the latter allowing for increased preservation of organic materials. The artifact-rich mound contains deposits ranging from the late Middle Pleistocene through to the early Holocene. Excavations at this site go back to the early twentieth century, and a variety of artifact assemblages have been recovered from the site, including faunal remains and lithics. Archaeology Faunal remains The most widely known faunal assemblages from the Florisbad spring site comprise what is known as the Florisian Land Mammal Age. These fossils are considered a type assemblage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provincial Heritage Site (South Africa)
Provincial heritage sites in South Africa are places that are of historic or cultural importance within the context of the province concerned and which are for this reason declared in terms of Section 28 of the National Heritage Resources Act (NHRA) or legislation of the applicable province. The designation was a new one that came into effect with the introduction of the Act on 1 April 2000 when all former national monuments declared by the former National Monuments Council and its predecessors became provincial heritage sites as provided for in Section 58 of the Act. Both provincial and national heritage sites are protected under the terms of Section 27 of the NHRA or legislation of the relevant province and a permit is required to work on them. Provincial heritage sites are declared and administered by the relevant provincial heritage resources authority whilst national heritage sites are the responsibility of SAHRA. KwaZulu-Natal is the only province to have its own heritag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
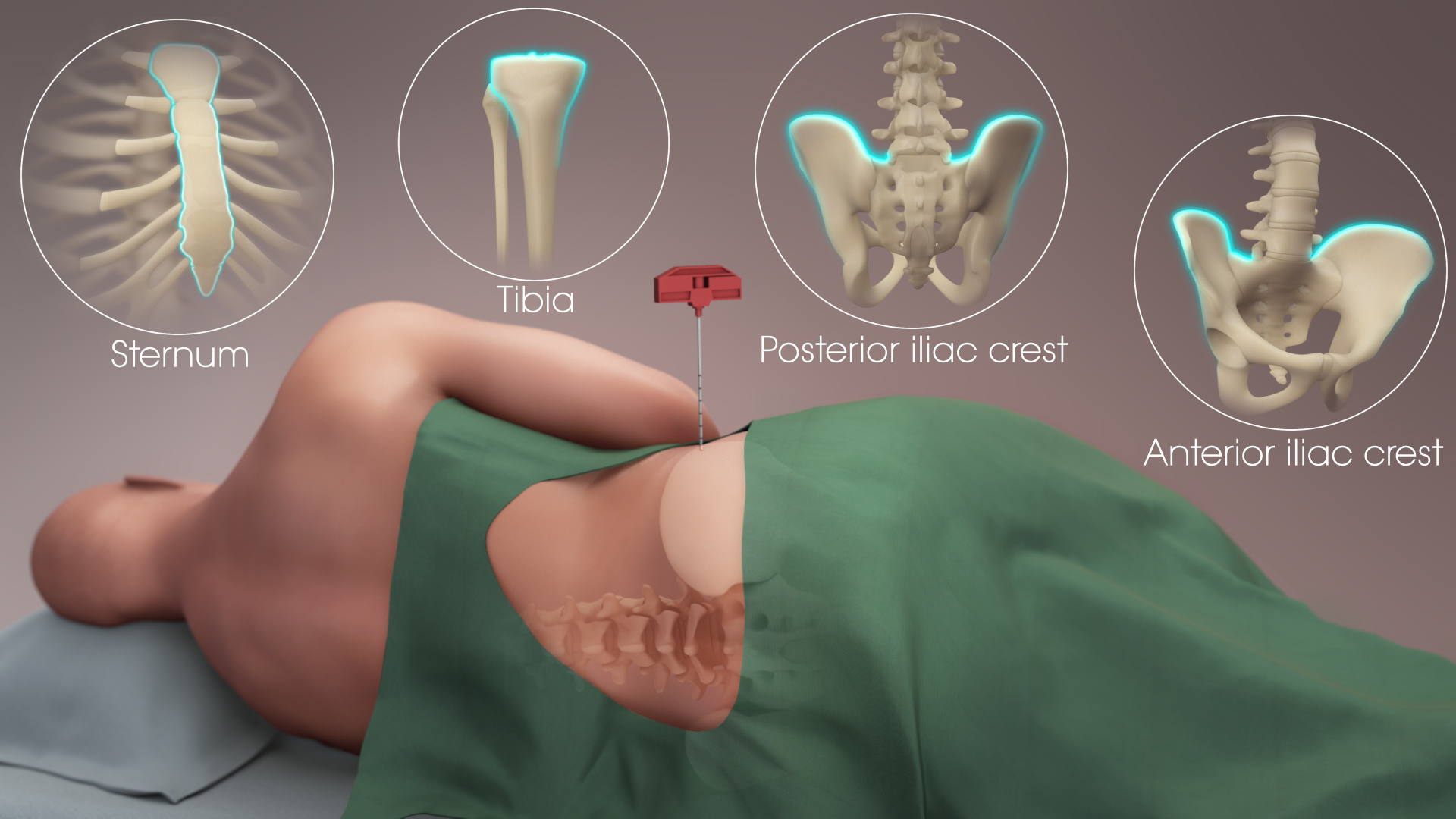
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In South Africa
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zimbabwe
file:Zimbabwe, relief map.jpg, upright=1.22, Zimbabwe, relief map Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the southwest, Zambia to the north, and Mozambique to the east. The capital and largest city is Harare, and the second largest is Bulawayo. A country of roughly 16.6 million people as per 2024 census, Zimbabwe's largest ethnic group are the Shona people, Shona, who make up 80% of the population, followed by the Northern Ndebele people, Northern Ndebele and other #Demographics, smaller minorities. Zimbabwe has 16 official languages, with English, Shona language, Shona, and Northern Ndebele language, Ndebele the most common. Zimbabwe is a member of the United Nations, the Southern African Development Community, the African Union, and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa. The region was long inhabited by the San people, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearth
A hearth () is the place in a home where a fire is or was traditionally kept for home heating and for cooking, usually constituted by a horizontal hearthstone and often enclosed to varying degrees by any combination of reredos (a low, partial wall behind a hearth), fireplace, oven, smoke hood, or chimney. Hearths are usually composed of masonry such as brick or rock (geology), stone. For millennia, the hearth was such an integral part of a home, usually its central and most important feature, that the concept has been metonym, generalized to refer to a homeplace or household, as in the terms "hearth and home" and "keep the home fires burning". In the modern era, since the advent of central heating, hearths are usually less central to most people's daily life because the heating of the home is instead done by a Furnace (house heating), furnace or a heating stove, and cooking is instead done with a kitchen stove/range (combination cooktop and oven) alongside other home appliances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hornfels
Hornfels is the group name for a set of Metamorphism#Contact .28thermal.29, contact metamorphic rocks that have been baked and hardened by the heat of Intrusive rock, intrusive igneous masses and have been rendered massive, hard, splintery, and in some cases exceedingly tough and durable. These properties are caused by fine grained non-aligned crystals with platy or prismatic Crystal habit, habits, characteristic of metamorphism at high temperature but without accompanying deformation. The term is derived from the German word ''Hornfels'', meaning "hornstone", because of its exceptional toughness and texture both reminiscent of animal horns. These rocks were referred to by miners in northern England as Sharpening stone, whetstones. Most hornfels are fine-grained, and while the original rocks (such as sandstone, shale, slate and limestone) may have been more or less fissile owing to the presence of bedding or Cleavage (geology), cleavage planes, this structure is effaced or rendered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is used across many disciplines to denote methods, observations, or interventions carried out in their natural or intended environment. By contrast, ' methods involve the removal or displacement of materials, specimens, or processes for study, preservation, or modification in a controlled setting, often at the cost of contextual integrity. The earliest known use of ''in situ'' in the English language dates back to the mid-17th century. In scientific literature, its usage increased from the late 19th century onward, initially in medicine and engineering. The natural sciences typically use methods to study phenomena in their original context. In geology, field analysis of soil composition and rock formations provides direct insights into Earth' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
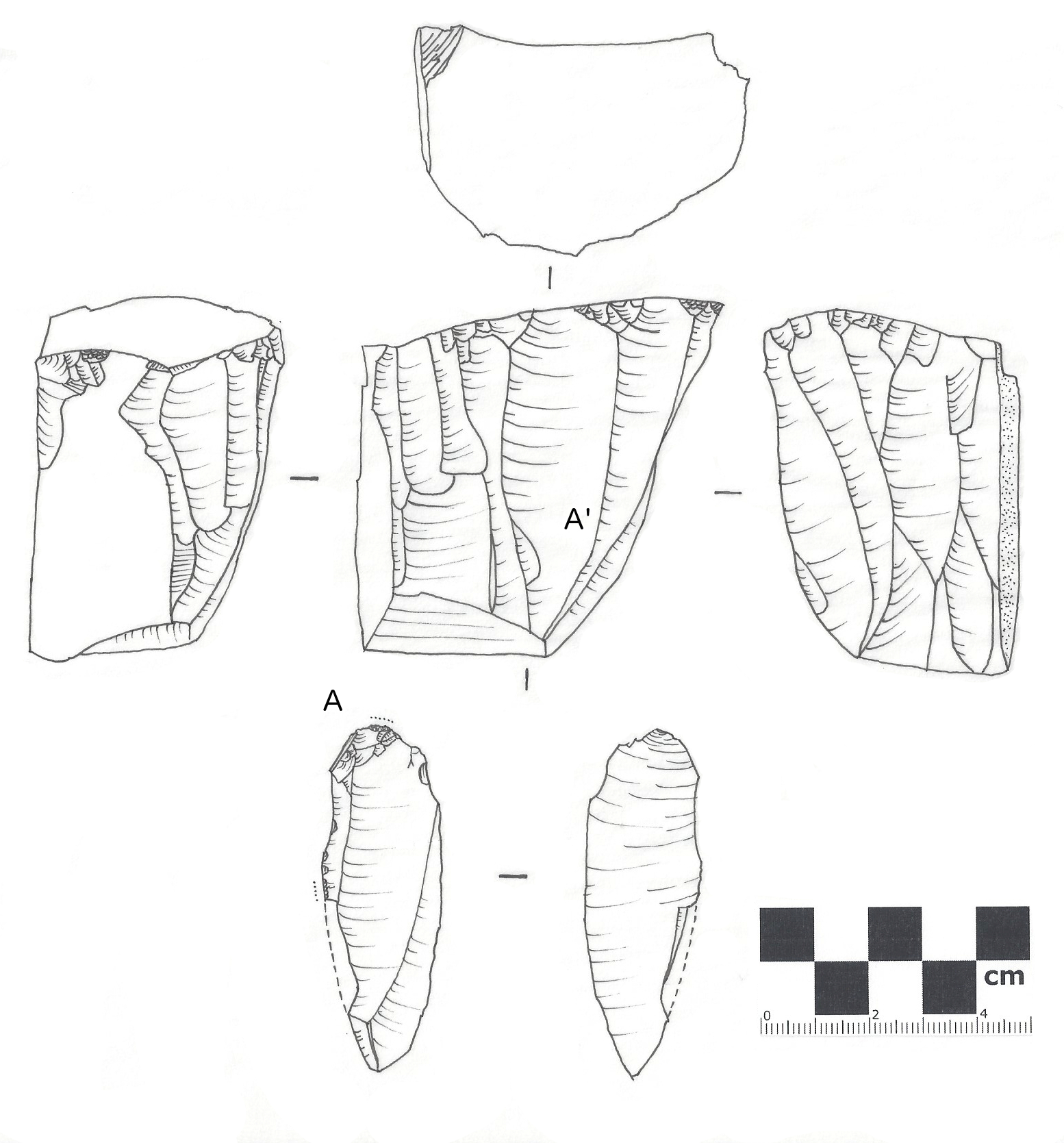
Lithic Core
In archaeology, a lithic core is a distinctive Artifact (archaeology), artifact that results from the practice of lithic reduction. In this sense, a core is the scarred nucleus resulting from the detachment of one or more lithic flake, flakes from a lump of source material or tool stone, usually by using a hard hammer precursor such as a hammerstone. The core is marked with the negative scars of these flakes. The surface area of the core which received the blows necessary for detaching the flakes is referred to as the striking platform. The core may be discarded or shaped further into a core tool, such as can be seen in some types of handaxe. Definitions A "core" can be defined in a number of different ways based on the theoretical and methodological approach of the archaeologist. Typological approaches to classify cores are generally based on a combination of the technological attributes and presumed function of an artefact while technological approaches are generally based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock (geology), rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a lithic core, core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler Tine (structural), tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often (termination type, but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scraper (archaeology)
In prehistoric archaeology, scrapers are unifacial tools thought to have been used for hideworking and woodworking. Many lithic analysts maintain that the only true scrapers are defined on the base of use-wear, and usually are those that were worked on the distal ends of blades—i.e., " end scrapers" (). Other scrapers include the so-called " side scrapers" or racloirs, which are made on the longest side of a flake, and notched scrapers, which have a cleft on either side that may have been used to attach them to something else. Scrapers are typically formed by chipping the end of a flake of stone in order to create one sharp side and to keep the rest of the sides dull to facilitate grasping it. Most scrapers are either circle or blade-like in shape. The working edges of scrapers tend to be convex, and many have trimmed and dulled lateral edges to facilitate hafting. One important variety of scraper is the thumbnail scraper, a scraper shaped much like its namesake. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Stone Age
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3.3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in the current archaeological record, until around 300,000 years ago, spanning the Oldowan ("mode 1") and Acheulean ("mode 2") lithics industries. In African archaeology, the time period roughly corresponds to the Early Stone Age, the earliest finds dating back to 3.3 million years ago, with Lomekwian stone tool technology, spanning Mode 1 stone tool technology, which begins roughly 2.6 million years ago and ends between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago, with Mode 2 technology. The Middle Paleolithic followed the Lower Paleolithic and recorded the appearance of the more advanced prepared-core tool-making technologies such as the Mousterian. Whether the earliest control of fire by hominins dates to the Lower or to the Middle Paleolithic rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Stone Age
The Later Stone Age (LSA) is a period in African prehistory that follows the Middle Stone Age. The Later Stone Age is associated with the advent of modern human behavior in Africa, although definitions of this concept and means of studying it are up for debate. The transition from the Middle Stone Age to the Late Stone Age is thought to have occurred first in eastern Africa between 50,000 and 39,000 years ago. It is also thought that Later Stone Age peoples and/or their technologies spread out of Africa over the next several thousand years. The terms "Early Stone Age", "Middle Stone Age" and "Later Stone Age" in the context of African archaeology are not to be confused with the terms Lower Paleolithic, Middle Paleolithic, and Upper Paleolithic. They were introduced in the 1920s, as it became clear that the existing chronological system of Upper, Middle, and Lower Paleolithic was not a suitable correlate to the prehistoric past in Africa. Some scholars, however, continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |