|
Flores Back-arc Thrust Fault
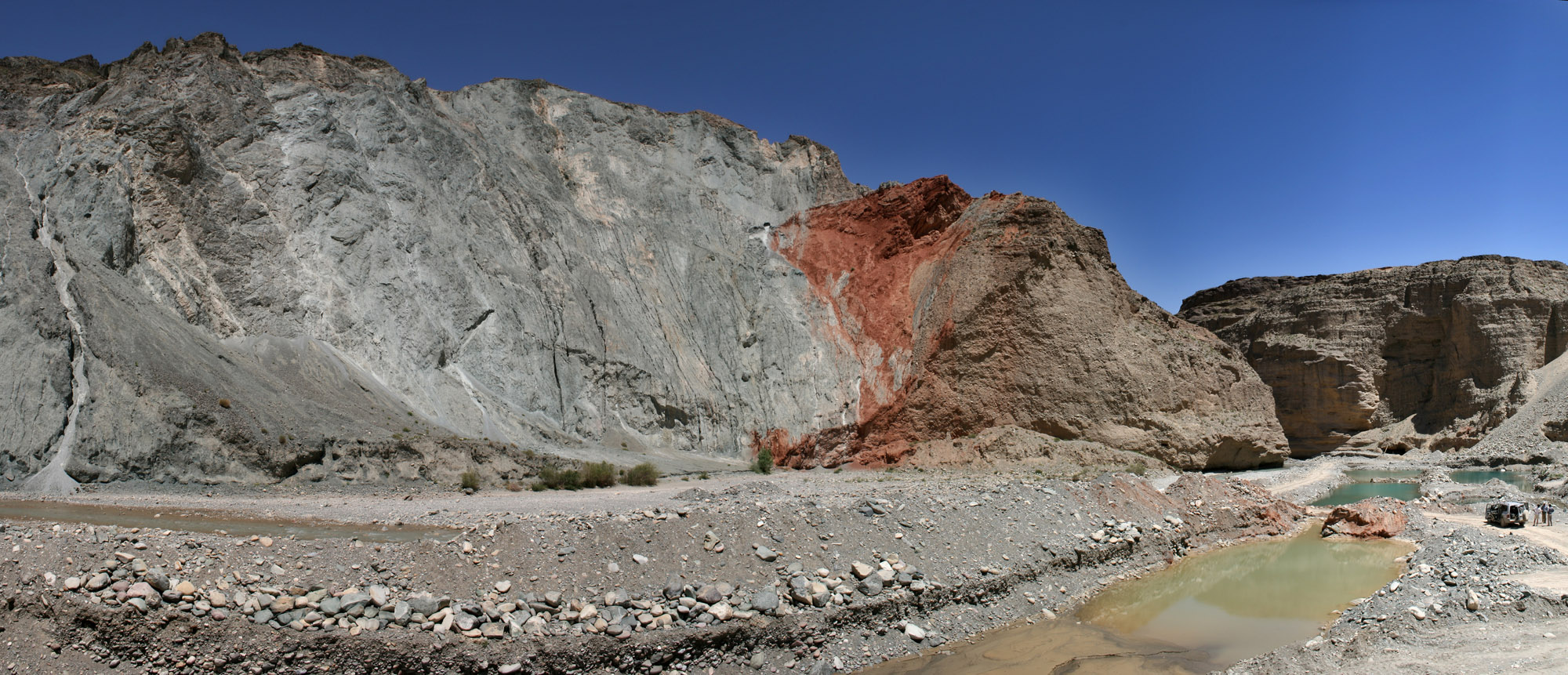
The Flores back-arc thrust fault is a major system of west–east trending thrust faults that extend eastwards from west of Lombok just south of where Sunda Shelf ends at Bali Sea, towards the islands of Sumbawa, Flores, and Alor, with a total length of at least 800 km., entering the Weber Basin and Aru Basin adjacent Sahul Shelf of the Australian plate. The thrust faults are south- dipping and lie within the back arc region of the Sunda–Banda Arc, which is related to the ongoing subduction of the Australian plate beneath the Sunda and Banda Sea plates. The thrust fault system developed as a result of the onset of continental collision as continental crust of the Australian plate reached the Sunda Trench. The eastern part of the fault system is also known as the Wetar thrust. Above the main thrust fault are a series of imbricate (overlapping) thrust faults. These imbricate thrust faults are shallower in depth than the main Flores thrust. Although the exact thrust faults ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrust Fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks. Thrust geometry and nomenclature Reverse faults A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less. If the angle of the fault plane is lower (often less than 15 degrees from the horizontal) and the displacement of the overlying block is large (often in the kilometer range) the fault is called an ''overthrust'' or ''overthrust fault''. Erosion can remove part of the overlying block, creating a ''fenster'' (or '' window'') – when the underlying block is exposed only in a relatively small area. When erosion removes most of the overlying block, leaving island-like remnants resting on the lower block, the remnants are called ''klippen'' (singular '' klippe''). Blind thrust faults If the fault plane terminates before it reaches the Earth's surface, it is referred to as a ''blind thrust'' fault. Because of the lack of surface evidence, blind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Arc
The Sunda Arc is a volcanic arc that produced the volcanoes that form the topographic spine of the islands of Sumatra, Nusa Tenggara, and Java, the Sunda Strait and the Lesser Sunda Islands. The Sunda Arc begins at Sumatra and ends at Flores, and is adjacent to the Banda Arc. The Sunda Arc is formed via the subduction of the Indo-Australian Plate beneath the Sunda and Burma plates at a velocity of 63–70 mm/year. Formation and geologic setting Mid-oceanic ridge basalts (MORB) form most of the oceanic basin south of Sunda, according to geodynamic studies. These plates began to converge in the Early Miocene. The Indo-Australian Plate is subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate with the dip angle of 49-56 degrees. The slab subducting under Java is continuous down to the lower mantle. However, the slab appears to beak apart under Sumatra Island''.'' Earthquake depth records indicate that there is no deep seismic activity in Sumatra, likely due to the age of the subduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Faults Of Southeast Asia
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. It also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletus (c. 585 BCE), Anaximenes of Miletus (c. 550 BCE), Aristotle (c. 340 BCE), and Zhan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 Lombok Earthquake
2018 Lombok earthquake may refer to the following 5 Thrust fault, thrust type earthquakes, with epicentres north of Rinjani volcano, that caused significant damage and deaths: *July 2018 Lombok earthquake ( and : 6.4, a foreshock) *5 August 2018 Lombok earthquake (Mw: 6.9, : 7.0, the mainshock) *9 August 2018 (: 5.9 aftershock, 6 deaths) *18 August 2018 23:10pm local time Lombok earthquakes (: 6.4 aftershock, 2 dead) *19 August 2018 Lombok earthquake ( 6.9 new earthquake, different fault.) See also * 2018 Indonesia earthquake (other), 2018 Indonesia earthquakes * List of earthquakes in Indonesia, including Lombok * List of earthquakes in 2018 {{Set index article 2018 disasters in Indonesia 2018 earthquakes Lombok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Trench
The Sunda Trench, earlier known as and sometimes still indicated as the Java Trench, is an oceanic trench located in the Indian Ocean near Sumatra, formed where the Australian- Capricorn plates subduct under a part of the Eurasian Plate. It is long with a maximum depth of 7,290 metres (23,920 feet). Its maximum depth is the deepest point in the Indian Ocean. The trench stretches from the Lesser Sunda Islands past Java, around the southern coast of Sumatra on to the Andaman Islands, and forms the boundary between Indo-Australian Plate and Eurasian plate (more specifically, Sunda Plate). The trench is considered to be part of the Pacific Ring of Fire as well as one of a ring of oceanic trenches around the northern edges of the Australian Plate. In 2005, scientists found evidence that the 2004 earthquake activity in the area of the Java Trench could lead to further catastrophic shifting within a relatively short period of time, perhaps less than a decade. This threat has result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
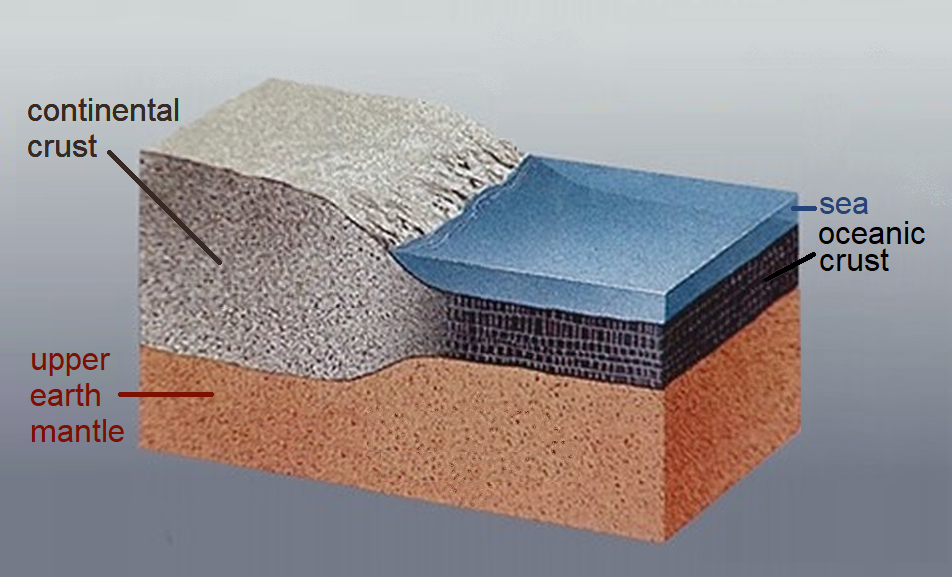
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called '' sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called '' sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
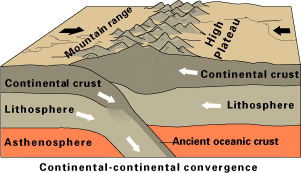
Continental Collision
In geology, continental collision is a phenomenon of plate tectonics that occurs at convergent boundaries. Continental collision is a variation on the fundamental process of subduction, whereby the subduction zone is destroyed, mountains produced, and two continents sutured together. Continental collision is only known to occur on Earth. Continental collision is not an instantaneous event, but may take several tens of millions of years before the faulting and folding caused by collisions stops. The collision between India and Asia has been going on for about 50 million years already and shows no signs of abating. Collision between East and West Gondwana to form the East African Orogen took about 100 million years from beginning (610 Ma) to end (510 Ma). The collision between Gondwana and Laurasia to form Pangea occurred in a relatively brief interval, about 50 million years long. Subduction zone: the collision site The process begins as two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banda Sea Plate
The Banda Sea Plate is a minor tectonic plate underlying the Banda Sea in southeast Asia. This plate also carries a portion of Sulawesi Island, the entire Seram Island, and the Banda Islands. Clockwise from the east it is bounded by the Bird's Head Plate of western New Guinea, Australian Plate, Timor Plate, Sunda Plate, and the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. The western border is a convergent boundary largely responsible for the mountains in western Sulawesi, subduction zones also exist on the eastern border near Seram and the southern border with the Timor Plate. A small rift is located in the middle of Sulawesi. It is a very seismically active area home to many volcanoes and the site of many large earthquakes, the largest of which was the 1938 Banda Sea earthquake which measured around 8.4 on the moment magnitude scale The moment magnitude scale (MMS; denoted explicitly with or Mw, and generally implied with use of a single M for magnitude) is a measure of an earthquake's magn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunda Plate
The Sunda Plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the Equator in the Eastern Hemisphere on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located. The Sunda Plate was formerly considered a part of the Eurasian Plate, but the GPS measurements have confirmed its independent movement at 10 mm/yr eastward relative to Eurasia. Extent The Sunda Plate includes the South China Sea, the Andaman Sea, southern parts of Vietnam and Thailand along with Malaysia and the islands of Borneo, Sumatra, Java, and part of Sulawesi in Indonesia, plus the south-western Philippines islands of Palawan and the Sulu Archipelago. The Sunda is bounded in the east by the Philippine Mobile Belt, Molucca Sea Collision Zone, Molucca Sea Plate, Banda Sea Plate and Timor Plate; to the south and west by the Australian Plate; and to the north by the Burma Plate, Eurasian Plate; and Yangtze Plate. The Indo-Australian Plate dips beneath the Sunda Plate along the Sunda Trench, which generates frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banda Arc
The Banda Arc (main arc, Inner, and Outer) is a set of island arcs in eastern Indonesia. It is the result of the collision of a continent and an intra-oceanic island arc. The presently active arc is located on what appears to be oceanic crust whereas the associated subduction trench is underlain by continental crust. The convergence of the Indo-Australian plates and Eurasia resulted in the formation of the Sunda and Banda island arcs. The transitional zone between the arcs is located south of Flores Island and is characterized by the change in the tectonic regime along the boundary. Terminology Some academic literature refers to the arcs by location – so that main arc can be referred to as the 'southern', the 'western' Situated at the centre of three converging and colliding major tectonic plates, Indo-Australia, Eurasia, Pacific, the Banda arc includes young oceanic crust enclosed by a volcanic inner arc, outer arc islands and a trough parallel to the Australian conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Arc
The back-arc region is the area behind a volcanic arc. In island volcanic arcs, it consists of back-arc basins of oceanic crust with abyssal depths, which may be separated by remnant arcs, similar to island arcs. In continental arcs, the back-arc region is part of continental platform, either dry land (subaerial) or forming shallow marine basins. Formation Back-arc deformation is a product of subduction at convergent plate tectonic boundaries. It initiates and evolves behind the volcanic arc on the overriding plate of a subduction zone. The stresses responsible for the deformation in this region of a subduction zone result from a combination of processes. The absolute motion of the upper plate as it moves towards or away from the trench strongly contributes to deformation in the back-arc region. Since the downgoing slab is partly anchored in the viscous layers of the mantle, and therefore its lateral movement is significantly slower than the surface plate, then any motion of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |