|
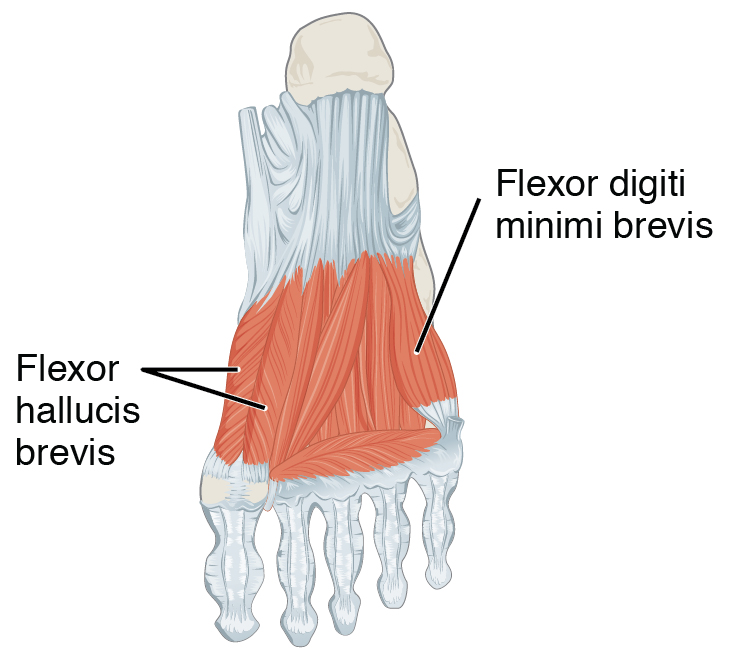
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a muscle of the foot that flexes the big toe. Structure Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint. Innervation The med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneocuboid Ligament
The calcaneocuboid ligament is a fibrous band that connects the superior surface of the calcaneus to the dorsal surface of the cuboid bone. It forms part of the bifurcated ligament The bifurcated ligament (internal calcaneocuboid, interosseous ligament or bifurcate ligament) is a strong band, attached behind to the deep hollow on the upper surface of the calcaneus and dividing in front in a Y-shaped manner into a calcaneocub .... References Foot Ligaments {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
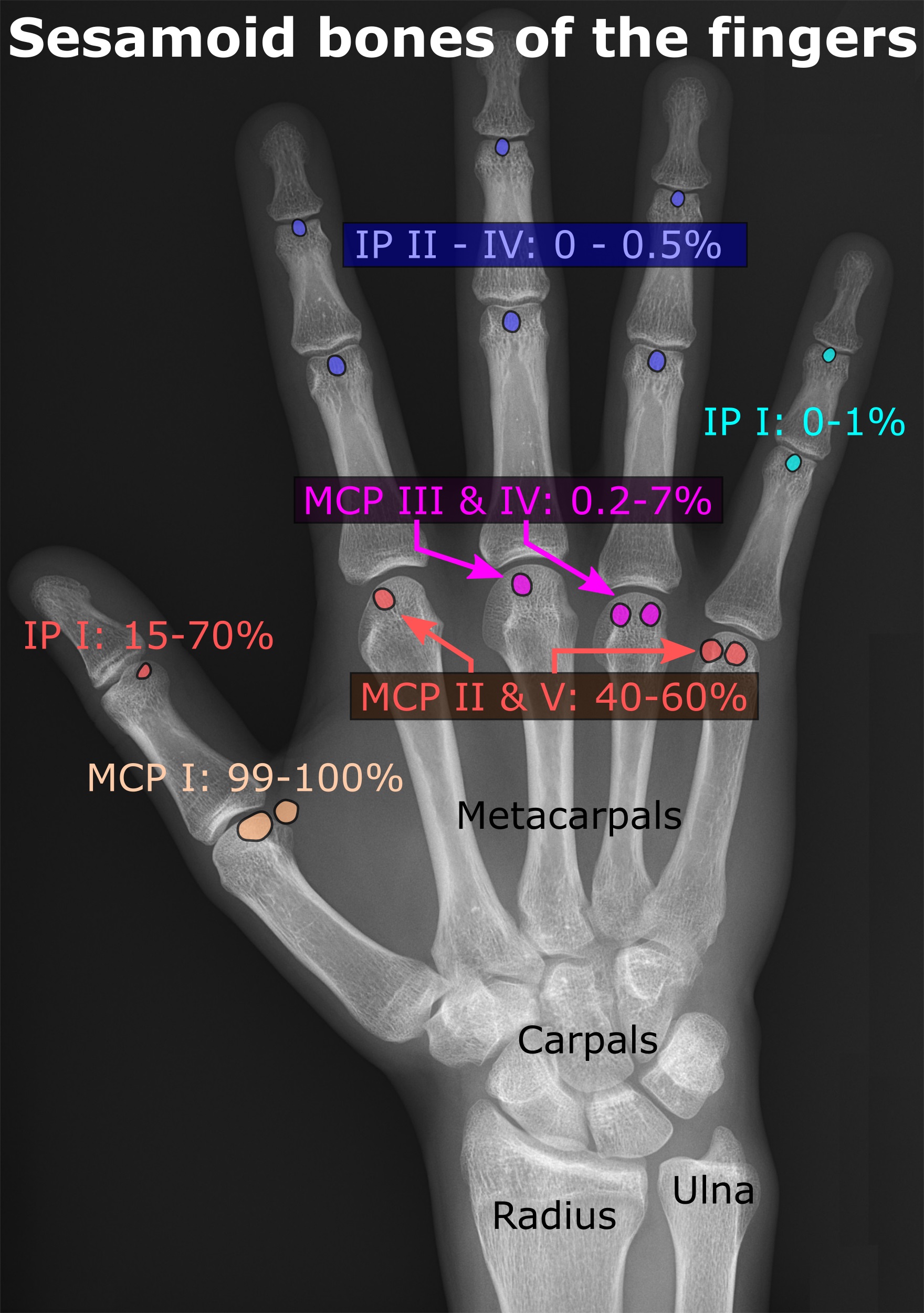
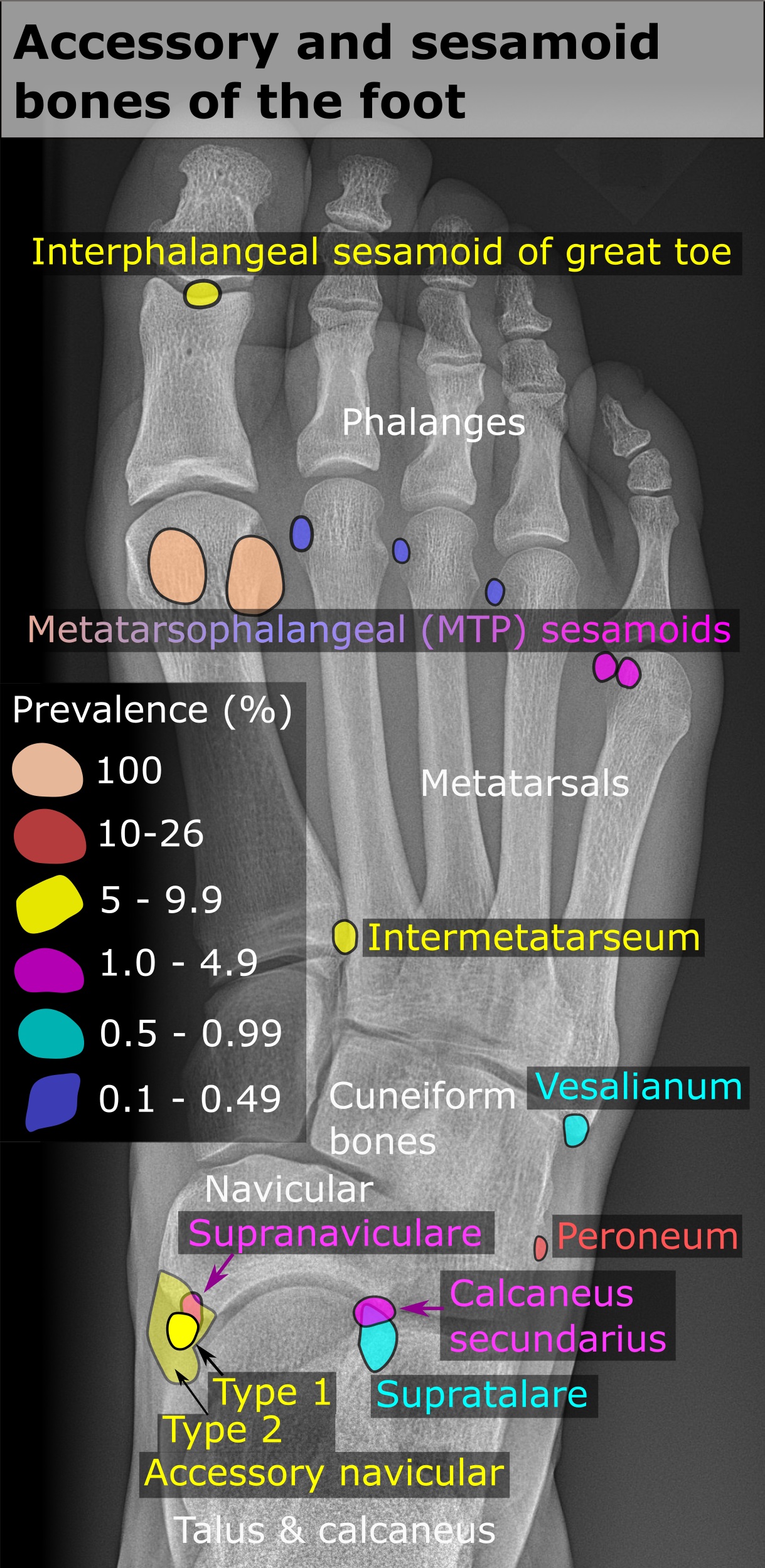
Sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the human body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone and fifth metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, prevent injuries, hone athletic skills, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many people choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, usually, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week is recommended for reducing the risk of health problems. At the same time, even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Only doing an hour and a quarter (11 minutes/day) of exercise could reduce the risk of early death, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsophalangeal
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints) are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are analogous to the knuckles of the hand, and are consequently known as toe knuckles in common speech. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges). The region of skin directly below the joints forms the ball of the foot. The ligaments are the plantar and two collateral. Movements The movements permitted in the metatarsophalangeal joints are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction. File:The feet of C. H. Unthan, the armless fiddler Wellcome L0034227.jpg, Left: toes adducted (pulled towards the center) and spread (abducted); right, both feet clenched (plantar flexed) File:Footgym rings1.jpg, The upper foot is clenching (plantarflexing) at the MTP joints and at the joints of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Plantar Nerve
The medial plantar nerve (internal plantar nerve) is the larger of the two terminal divisions of the tibial nerve (medial and lateral plantar nerve), which accompanies the medial plantar artery. From its origin under the laciniate ligament it passes under cover of the abductor hallucis muscle, and, appearing between this muscle and the flexor digitorum brevis, gives off a proper digital plantar nerve and finally divides opposite the bases of the metatarsal bones into three common digital plantar nerves. Branches The branches of the medial plantar nerve are: (1) cutaneous, (2) muscular, (3) articular, (4) a proper digital nerve to the medial side of the great toe, and (5) three common digital nerves. Cutaneous branches The cutaneous branches pierce the plantar aponeurosis between the abductor hallucis and the flexor digitorum brevis and are distributed to the skin of the sole of the foot. Muscular branches The muscular branches supply muscles on the medial side of the sole, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsophalangeal Joints
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints) are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are analogous to the knuckles of the hand, and are consequently known as toe knuckles in common speech. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an elliptical or rounded surface (of the metatarsal bones) comes close to a shallow cavity (of the proximal phalanges). The region of skin directly below the joints forms the ball of the foot. The ligaments are the plantar and two collateral. Movements The movements permitted in the metatarsophalangeal joints are flexion, extension, abduction, adduction and circumduction. File:The feet of C. H. Unthan, the armless fiddler Wellcome L0034227.jpg, Left: toes adducted (pulled towards the center) and spread (abducted); right, both feet clenched (plantar flexed) File:Footgym rings1.jpg, The upper foot is clenching (plantarflexing) at the MTP joints and at the joints of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesamoid Bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a anatomical variation, normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit Muscle#Function, muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the human body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the Anatomical terms of location#Arms, distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone and fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Hallucis Longus Muscle
The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) attaches to the plantar surface of phalanx of the great toe and is responsible for flexing that toe. The FHL is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg, the others being the flexor digitorum longus and the tibialis posterior. The tibialis posterior is the most powerful of these deep muscles. All three muscles are innervated by the tibial nerve which comprises half of the sciatic nerve. Structure The flexor hallucis longus is situated on the fibular side of the leg. It arises from the inferior two-thirds of the posterior surface of the body of the fibula, with the exception of 2.5 cm at its lowest part; from the lower part of the interosseous membrane; from an intermuscular septum between it and the peroneus muscles, laterally, and from the fascia covering the tibialis posterior, medially. The fibers pass obliquely downward and backward, where it passes through the tarsal tunnel on the medial side ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adductor Hallucis Muscle
The Adductor hallucis (adductor obliquus hallucis) arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve. Structure Oblique head The ''oblique head'' is a large, thick, fleshy mass, crossing the foot obliquely and occupying the hollow space under the first, second, third and fourth metatarsal bones. It arises from the bases of the second, third, and fourth metatarsal bones, and from the sheath of the tendon of the Peroneus longus, and is inserted, together with the lateral portion of the flexor hallucis brevis, into the lateral side of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe. Transverse head The ''transverse head'' (''Transversus pedis'') is a narrow, flat fasciculus which arises from the plantar metatarsophalangeal ligaments of the third, fourth, and fifth toes (sometimes only from the third and fourth), and from the transverse ligament of the metatarsals. It is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantar Interossei Muscles
In human anatomy, plantar interossei muscles are three muscles located between the metatarsal bones in the foot. Structure The three plantar interosseous muscles are unipennate, as opposed to the bipennate structure of dorsal interosseous muscles, and originate on a single metatarsal bone. The three muscles originate on the medial aspect of metatarsals III-V. The muscles cross the metatarsophalangeal joint of toes III-V so the insertions correspond with the origin and there is no crossing between toes. The muscles then continue distally along the foot and insert in the proximal phalanges III-V. The muscles cross the metatarsophalangeal joint of toes III-V so the insertions correspond with the origin and there is no crossing between toes. Innervation All three plantar interosseous muscles are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve. The lateral plantar nerve is a branch from the tibial nerve, which originally branches off the sciatic nerve from the sacral plexus. Function Sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductor Hallucis Muscle
The abductor hallucis muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the foot. It participates in the Anatomical terms of motion#Abduction and adduction, abduction and Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension, flexion of the Toe#Hallux, great toe. Structure The abductor hallucis muscle is located in the medial border of the foot and contributes to form the prominence that is observed on the region. It is inserted behind on the tuberosity of the calcaneus, the Flexor retinaculum of foot, flexor retinaculum, and the plantar aponeurosis. Its muscle body, relatively thick behind, flattens as it goes forward. It ends in a common tendon with the medial head of the flexor hallucis brevis that inserts on the medial surface of the base of the first Phalanx bone, proximal phalanx and its related sesamoid bone. Its medial surface is superficial and covered with the muscle's fascia and the skin. Nerve supply Abductor hallucis is supplied by the medial plantar nerve. The nerves that supply it ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |