|
Flevit Super Illam
The triumphal entry into Jerusalem is a narrative in the four canonical Gospels describing the arrival of Jesus in Jerusalem a few days before his crucifixion. This event is celebrated each year by Christians on Palm Sunday. According to the gospels, Jesus arrived in Jerusalem to celebrate Passover, entering the city riding a donkey. He was greeted by a crowd acclaiming him by waving palm branches and laying cloaks on the ground to honor him. This episode introduces the events of the Passion of Jesus, leading to his crucifixion and resurrection. The event is described in , , and . Gospel accounts Historical context All Jewish males are obliged to ascend to Jerusalem for the three pilgrimage festivals. The sabbath prior to Passover is called the Great Sabbath in Judaism, and it is when each household or community sets apart a Passover lamb. Passover celebrates God's deliverance of Israel from bondage in Egypt. By the early post-exilic period, according to Robin Rout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quest For The Historical Jesus
The quest for the historical Jesus consists of academic efforts to determine what words and actions, if any, may be attributed to Jesus, and to use the findings to provide portraits of the historical Jesus.. Conventionally, since the 18th century three scholarly quests for the historical Jesus are distinguished, each with distinct characteristics and based on different research criteria, which were often developed during each specific phase. These quests are distinguished from earlier approaches because they rely on the historical method to study biblical narratives. While textual analysis of biblical sources had taken place for centuries, these quests introduced new methods and specific techniques to establish the historical validity of their conclusions. The enthusiasm shown during the first quest diminished after Albert Schweitzer's critique of 1906 in which he pointed out various shortcomings in the approaches used at the time. The second quest began in 1953 and introduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dominic Crossan
John Dominic Crossan (born 17 February 1934) is an Irish-American New Testament scholar, historian of early Christianity and former Catholic priest. He was a prominent member of the Jesus Seminar, and is an emeritus professor at DePaul University. His research has focused on the historical Jesus, the theology of noncanonical gospels, and the application of postmodern hermeneutical approaches to the Bible. His work is controversial, portraying the Second Coming as a late corruption of Jesus' message and saying that Jesus' divinity is metaphorical.John Dominic Crossan . Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2016. Web. 13 Jan. 2016 In place of the eschatological message of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domesticated in Africa some years ago, and has been used mainly as a working animal since that time. There are more than 40 million donkeys in the world, mostly in underdeveloped countries, where they are used principally as Working animal, draught or pack animal, pack animals. While working donkeys are often associated with those living at or below subsistence, small numbers of donkeys or asses are kept for breeding, as pets, and for livestock protection in developed countries. An adult male donkey is a ''jack'' or ''jackass'', an adult female is a ''jenny'' or ''jennet'', and an immature donkey of either sex is a ''foal''. Jacks are often mated with horse, female horses (mares) to produce ''mule, mules''; the less common hybrid of a stalli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disciple (Christianity)
In Christianity, a disciple is a dedicated follower of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus. This term is found in the New Testament only in the Canonical Gospels, Gospels and Acts of the Apostles, Acts. Originating in the ancient Near East, the concept of a disciple is an adherent of a teacher. Discipleship is not the same as being a student in the modern sense; a disciple in the ancient biblical world actively imitation, imitated both the life and teaching of the master. It was a deliberate apprenticeship which made the fully formed disciple a living copy of the master. The New Testament records many followers of Jesus during Ministry of Jesus, his ministry. Some disciples were given a Christian mission, mission, such as the Matthew 10, Little Commission, the Seventy disciples, commission of the seventy in Luke's Gospel, the Great Commission after the resurrection of Jesus, or the Conversion of Paul the Apostle, conversion of Paul, making them ''Apostles in the New Testament, apostle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark, and Gospel of Luke, Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical wording. They stand in contrast to Gospel of John, John, whose content is largely distinct. The term ''synoptic'' (; ) comes via Latin from the Greek , ''synopsis'', i.e. "(a) seeing all together, synopsis". The modern sense of the word in English is of "giving an account of the events from the same point of view or under the same general aspect". , , , , , . It is in this sense that it is applied to the synoptic gospels. This strong Parallel passage, parallelism among the three gospels in content, arrangement, and specific language is widely attributed to literary interdependence, though the role of orality and memorization of sources has also been explored by scholars. The question of the precise nature of their literary relationship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paula Fredriksen
Paula Fredriksen (born January 6, 1951, Kingston, Rhode Island) is an American historian and scholar of early Christianity. She held the position of William Goodwin Aurelio Professor of Scripture at Boston University from 1990 to 2010. Now emerita, she has been distinguished visiting professor in the Department of Comparative Religion at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, since 2009. Fredriksen specializes in the history of Christianity in that developmental arc from its stirrings in an apocalyptic messianic sect within Second Temple Judaism to its transformation into an arm of Late Roman imperial government and its empowerment in the post-Roman West (1st through 7th centuries). She works to reconstruct the many ways that various ancient Mediterranean peoples – pagans, Jews and Christians – interacted with the many special social agents (e.g. high gods, apocalyptic forces, heavenly bodies, godlings, spirits, and divine humans) that populated both the ancient flat-dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Borg
Marcus Joel Borg (March 11, 1942 – January 21, 2015) was an American New Testament scholar and theologian. He was among the most widely known and influential voices in Liberal Christianity. Borg was a fellow of the Jesus Seminar and a major figure in historical Jesus scholarship.Marcus Borg Explore Faith. Accessed January 21, 2008. He retired as Hundere Distinguished Professor of Religion and Culture at in 2007. He died eight years later at the age of 72, of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis at his home in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephraim In The Wilderness
Ephraim (; , in pausa: ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was, according to the Book of Genesis, the second son of Joseph ben Jacob and Asenath, as well as the adopted son of his biological grandfather Jacob, making him the progenitor of the Tribe of Ephraim. Asenath was an ancient Egyptian woman whom Pharaoh gave to Joseph as wife, and daughter of Potipherah, priest of ʾOn (Heliopolis) (). Ephraim was born in Egypt before the arrival of the Israelites from Canaan. The Book of Numbers lists three sons of Ephraim: Shuthelah, Beker, and Tahan. However, 1 Chronicles 7 lists eight sons, including Ezer and Elead, who were killed in an attempt to steal cattle from the locals. After their deaths he had another son, Beriah. He was the ancestor of Joshua, son of Nun ben Elishama, the leader of the Israelite tribes in the conquest of Canaan. According to the biblical narrative, Jeroboam, who became the first king of the Northern Kingdom of Israel, was also from the house of Ephraim. Biblical c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
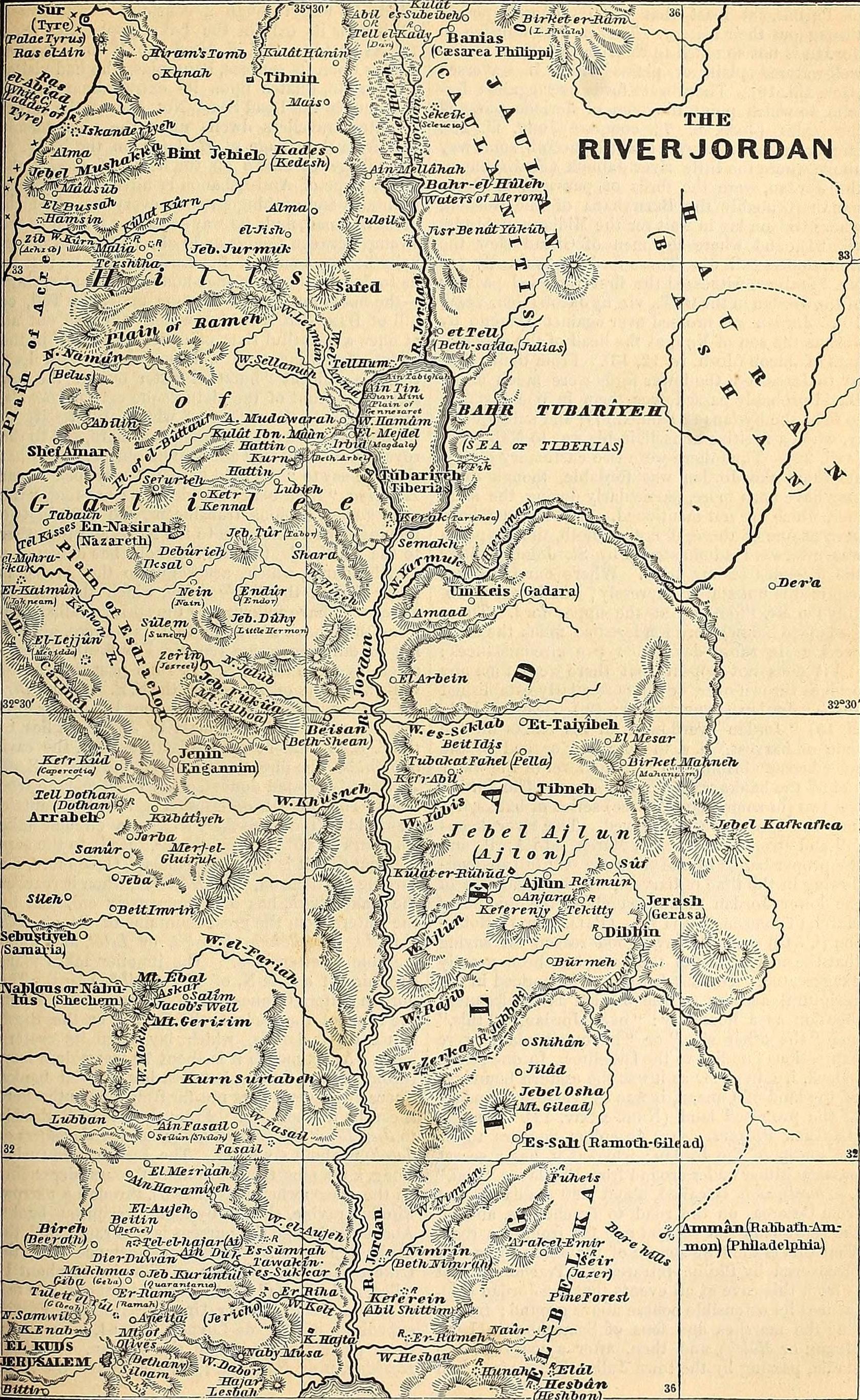
Jordan River
The Jordan River or River Jordan (, ''Nahr al-ʾUrdunn''; , ''Nəhar hayYardēn''), also known as ''Nahr Al-Sharieat'' (), is a endorheic river in the Levant that flows roughly north to south through the Sea of Galilee and drains to the Dead Sea. The river passes by or through Jordan, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories. Jordan and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights border the river to the east, while Israel and the Israeli-occupied West Bank lie to its west. Both Jordan and the West Bank derive their names in relation to the river. The river holds major significance in Judaism and Christianity. According to the Bible, the Israelites crossed it into the Promised Land and Jesus of Nazareth was baptized by John the Baptist in it. Etymology Several hypotheses for the origin of most of the river's names in modern languages (e.g., Jordan, Yarden, Urdunn), one is that it comes from Semitic 'Yard, on' 'flow down' <√ירד reflecting the river's declivity, possibly a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Of Olives
The Mount of Olives or Mount Olivet (; ; both lit. 'Mount of Olives'; in Arabic also , , 'the Mountain') is a mountain ridge in East Jerusalem, east of and adjacent to Old City of Jerusalem, Jerusalem's Old City. It is named for the olive, olive groves that once covered its slopes. The southern part of the mount was the Silwan necropolis, attributed to the elite of the ancient Kingdom of Judah. The western slopes of the mount, those facing Jerusalem, have been used as a Mount of Olives Jewish Cemetery, Jewish cemetery for over 3,000 years and holds approximately 150,000 graves, making it central in the tradition of Jewish cemetery, Jewish cemeteries. Atop the hill lies the State of Palestine, Palestinian neighbourhood of At-Tur (Mount of Olives), At-Tur, a former village that is now part of East Jerusalem. Several key events in the life of Jesus, as related in the Gospels, took place on the Mount of Olives, and in the Acts of the Apostles it is described as the place from which J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
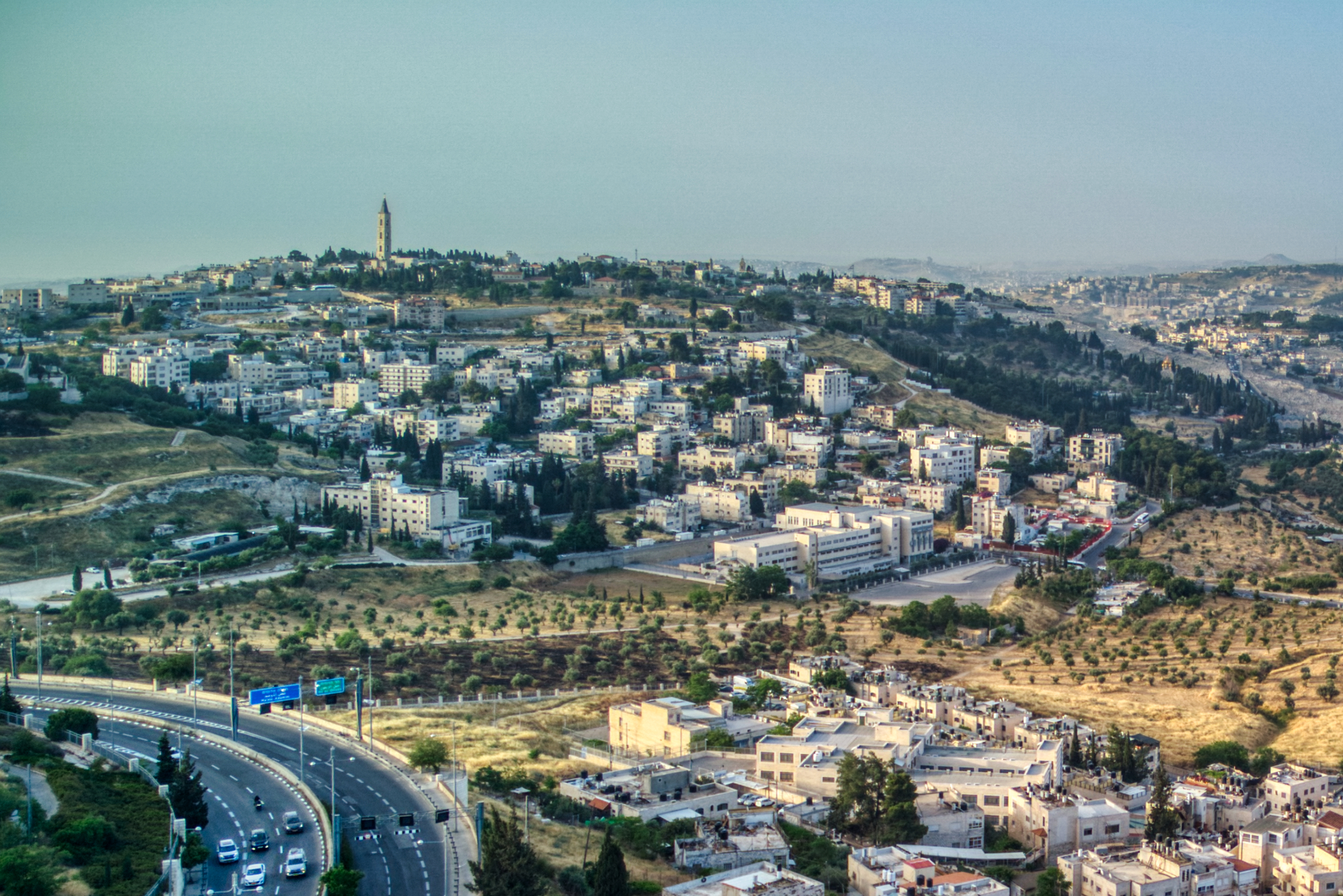
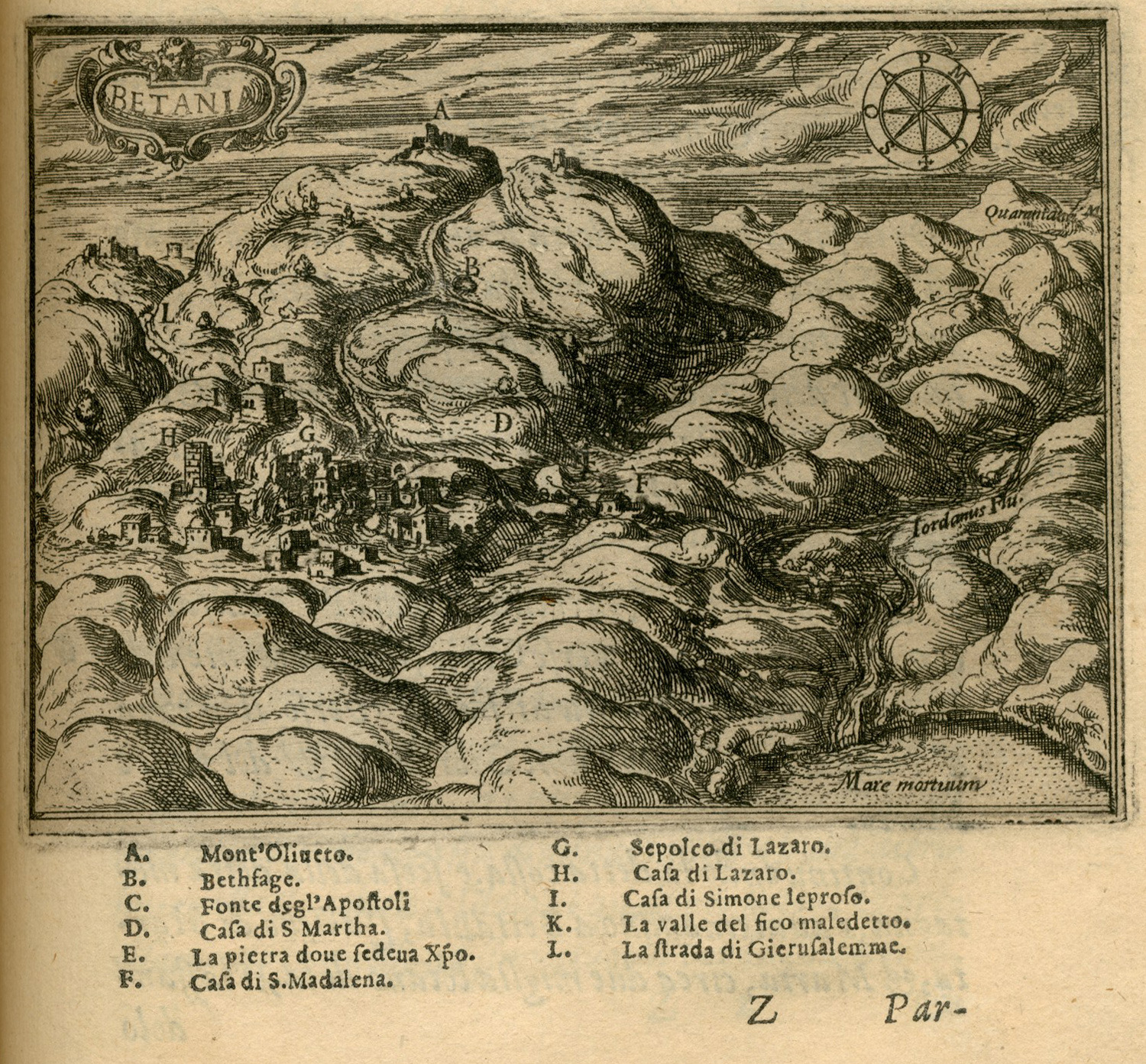
Bethany
Bethany (,Murphy-O'Connor, 2008, p152/ref> Syriac language, Syriac: ܒܝܬ ܥܢܝܐ ''Bēṯ ʿAnyā''), locally called in Palestinian Arabic, Arabic Al-Eizariya or al-Aizariya (, "Arabic nouns and adjectives#Nisba, [place] of Lazarus (name), Lazarus"), is a State of Palestine, Palestinian town in the Quds Governorate, Jerusalem Governorate of Palestine, bordering East Jerusalem, in the West Bank. The name al-Eizariya refers to the New Testament figure Lazarus of Bethany, who according to the Gospel of John, was Lazarus of Bethany, raised from the dead by Jesus in the town. The traditional site of the miracle, the Tomb of Lazarus, in the city is a place of pilgrimage. The town is located on the southeastern slope of the Mount of Olives, less than from Jerusalem. With a population of 22,928 inhabitants according to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics, it is the second largest city in the Quds Governorate of the State of Palestine, after only East Jerusalem, which Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |