|
Flapping Tremor
Asterixis (more colloquially referred to as flapping tremor) is not actually a tremor, but rather a negative myoclonus. This movement disorder is characterized by an inability to maintain a position, which is demonstrated by jerking movements of the outstretched hands when bent upward at the wrist (which can be similar to a bird flapping its wings, hence the name "flapping tremor"). The tremor is caused by abnormal function of the diencephalic motor centers in the brain, which regulate the muscles involved in maintaining position. Asterixis is associated with various encephalopathies due especially to faulty metabolism. The term derives from the Greek ''a'', meaning "not" and ''stērixis'', meaning "support" or "stable position". Presentation Asterixis is normally asymptomatic and found during clinical examination for other reasons, but more rarely it can also be the leading symptom. Usually there are brief, arrhythmic interruptions of sustained voluntary muscle contraction, causi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine) , medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the Human brain, brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nervous system , peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system, using various techniques of neurotherapy. IEEE Brain (2019). "Neurotherapy: Treating Disorders by Retraining the Brain". ''The Future Neural Therapeutics White Paper''. Retrieved 23.01.2025 from: https://brain.ieee.org/topics/neurotherapy-treating-disorders-by-retraining-the-brain/#:~:text=Neurotherapy%20trains%20a%20patient's%20brain,wave%20activity%20through%20positive%20reinforcement International Neuromodulation Society, Retrieved 23 January 2025 from: https://www.neuromodulation.com/ Val Danilov I (2023). "The O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
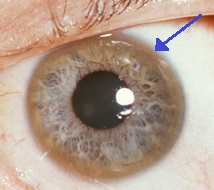
Wilson's Disease
Wilson's disease (also called hepatolenticular degeneration) is a genetic disorder characterized by the excess build-up of copper in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build-up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin, and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for people to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests, and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically tre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Delacy Adams
Raymond Delacy Adams (February 13, 1911 – October 18, 2008) was an American neurologist, neuropathologist, Bullard Professor of Neuropathology at Harvard Medical School and chief of neurology at Massachusetts General Hospital. Along with neurologist Maurice Victor, Adams was the author of ''Adams and Victor's Principles of Neurology'', the 12th edition of which appeared, 50 years after the original. Born near Portland, Oregon, Adams was the son of William Henry Adams and Eva Mabel Morriss. He graduated from the University of Oregon with a degree in Psychology. He received his M.D. from the Duke University School of Medicine in 1936. Adams became chief of neurology at Massachusetts General in 1951 retiring in 1977. Adams had an encyclopedic knowledge of adult neurology, pediatric neurology, and neuropathology and is widely regarded as a pre-eminent neurologist of the mid-20th century. He was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1955. He helped found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anticonvulsant, anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The intravenous form, fosphenytoin, is used for status epilepticus that does not improve with benzodiazepines. It may also be used for certain heart arrhythmias or neuropathic pain. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. The intravenous form generally begins working within 30 minutes and is effective for roughly 24 hours. Blood levels can be measured to determine the proper dose. Common side effects include nausea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, poor coordination, hypertrichosis, increased hair growth, and Gingival hyperplasia, enlargement of the gums. Potentially serious side effects include sleepiness, self harm, liver problems, bone marrow suppression, hypotension, low blood pressure, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and atrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
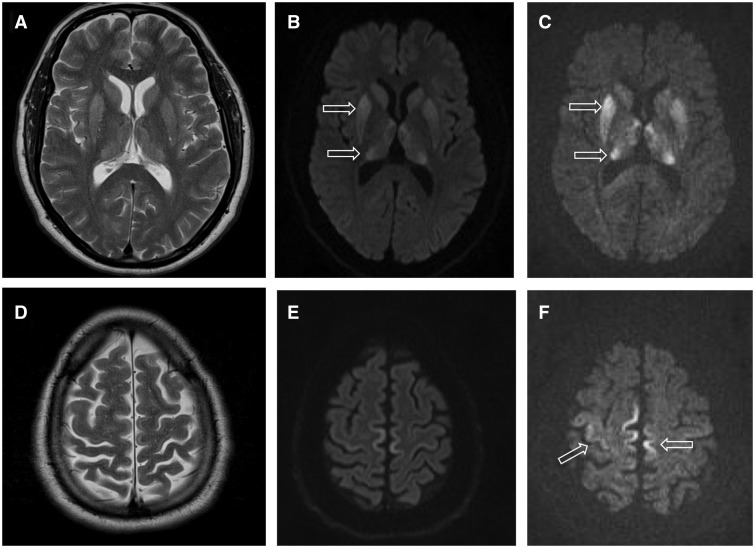
Brain Haemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as hemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain (i.e. the parenchyma), into its ventricles, or into both. An ICH is a type of bleeding within the skull and one kind of stroke (ischemic stroke being the other). Symptoms can vary dramatically depending on the severity (how much blood), acuity (over what timeframe), and location (anatomically) but can include headache, one-sided weakness, numbness, tingling, or paralysis, speech problems, vision or hearing problems, memory loss, attention problems, coordination problems, balance problems, dizziness or lightheadedness or vertigo, nausea/vomiting, seizures, decreased level of consciousness or total loss of consciousness, neck stiffness, and fever. Hemorrhagic stroke may occur on the background of alterations to the blood vessels in the brain, such as cerebral arteriolosclerosis, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, cerebral arteriovenous malformation, brain traum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) is an incurable, always fatal neurodegenerative disease belonging to the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) group. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, visual disturbances and auditory disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, deafness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of sufferers die within a year of diagnosis. The name "Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease" was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob. CJD is caused by abnormal folding of a protein known as a prion. Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded. About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; ) means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes. Types There are many types of encephalopathy. Some examples include: * Mitochondrial encephalopathy: Metabolic disorder caused by dysfunction of mitochondrial DNA. Can affect many body systems, particularly the brain and nervous system. * Acute necrotizing encephalopathy, rare disease that occurs following a viral infection. * Glycine encephalopathy: A genetic metabolic disorder involving excess production of glycine. * Hepatic encephalopathy: Arising from advanced cirrhosis of the liver. * Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Permanent or transitory encephalopathy arising from severely reduced oxygen delivery to the brain. * Static encephalopathy: Unchanging, or permanent, brain damage, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypomagnesaemia
Magnesium deficiency is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is a low level of magnesium in the body. Symptoms include tremor, poor coordination, muscle spasms, loss of appetite, personality changes, and nystagmus. Complications may include seizures or cardiac arrest such as from torsade de pointes. Those with low magnesium often have low potassium. Causes include low dietary intake, alcoholism, diarrhea, increased urinary loss, and poor absorption from the intestines. Some medications may also cause low magnesium, including proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and furosemide. The diagnosis is typically based on finding low blood magnesium levels, also called hypomagnesemia. Normal magnesium levels are between 0.6 and 1.1 mmol/L (1.46–2.68 mg/dL) with levels less than 0.6 mmol/L (1.46 mg/dL) defining hypomagnesemia. Specific electrocardiogram (ECG) changes may be seen. Treatment is with magnesium either by mouth or intravenously. For those with sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a low level of potassium (K+) in the blood serum. Mild low potassium does not typically cause symptoms. Symptoms may include feeling tired, leg cramps, weakness, and constipation. Low potassium also increases the risk of an abnormal heart rhythm, which is often too slow and can cause cardiac arrest. Causes of hypokalemia include vomiting, diarrhea, medications like furosemide and steroids, dialysis, diabetes insipidus, hyperaldosteronism, hypomagnesemia, and not enough intake in the diet. Normal potassium levels in humans are between 3.5 and 5.0 mmol/L (3.5 and 5.0 mEq/L) with levels below 3.5 mmol/L defined as hypokalemia. It is classified as severe when levels are less than 2.5 mmol/L. Low levels may also be suspected based on an electrocardiogram (ECG). The opposite state is called hyperkalemia that means high level of potassium in the blood serum. The speed at which potassium should be replaced depends on whether or not there are symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolyte Imbalance
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium. Electrolyte disturbances are involved in many disease processes and are an important part of patient management in medicine. The causes, severity, treatment, and outcomes of these disturbances can differ greatly depending on the implicated electrolyte. The most serious electrolyte disturbances involve abnormalities in the levels of sodium, potassium or calcium. Other electrolyte imbalances are less common and often occur in conjunction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia (also spelled hypoxaemia) is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease. Sometimes the concentration of oxygen in the air is decreased leading to hypoxemia. Definition ''Hypoxemia'' refers to the low level of oxygen in arterial blood. Tissue hypoxia refers to low levels of oxygen in the tissues of the body and the term ''hypoxia'' is a general term for low levels of oxygen. Hypoxemia is usually caused by pulmonary disease whereas tissue oxygenation requires additionally adequate circulation of blood and perfusion of tissue to meet metabolic demands. Hypoxemia is usually defined in terms of reduced partial pressure of oxygen (mm Hg) in arterial blood, but also in terms of reduced content of oxygen (ml oxygen per dl blood) or percentage saturation of hemoglobin (the oxygen-binding protein within red blood cells) with oxygen, which is either found singly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypercapnia
Hypercapnia (from the Greek ''hyper'', "above" or "too much" and ''kapnos'', "smoke"), also known as hypercarbia and CO2 retention, is a condition of abnormally elevated carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood. Carbon dioxide is a gaseous product of the body's metabolism and is normally expelled through the lungs. Carbon dioxide may accumulate in any condition that causes hypoventilation, a reduction of alveolar ventilation (the clearance of air from the small sacs of the lung where gas exchange takes place) as well as resulting from inhalation of CO2. Inability of the lungs to clear carbon dioxide, or inhalation of elevated levels of CO2, leads to respiratory acidosis. Eventually the body compensates for the raised acidity by retaining alkali in the kidneys, a process known as "metabolic compensation". Acute hypercapnia is called acute hypercapnic respiratory failure (AHRF) and is a medical emergency as it generally occurs in the context of acute illness. Chronic hypercapn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |