|
Flags Of The English Interregnum
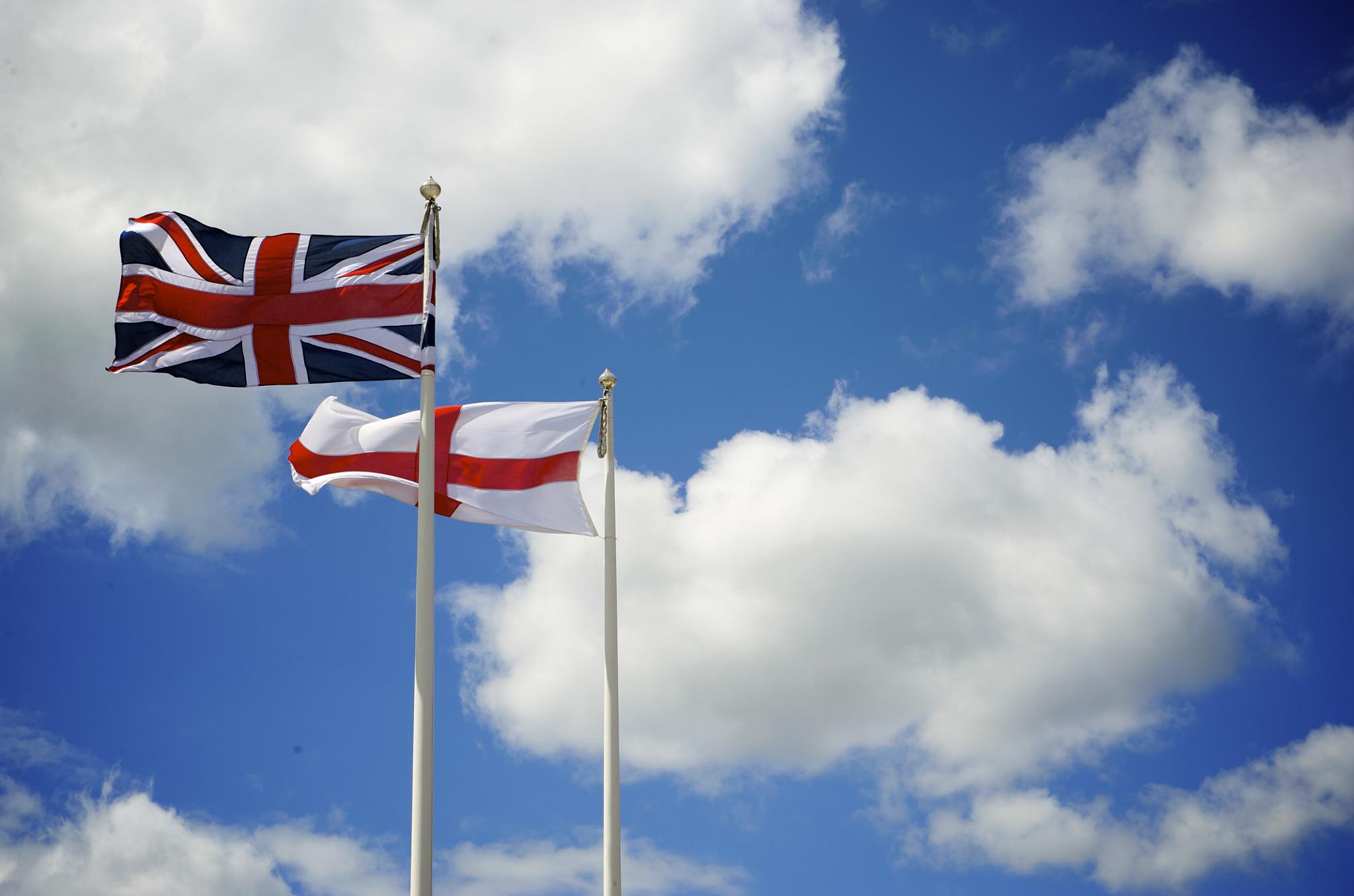
There were a variety of flags flown by ships of the Commonwealth during the Interregnum of 1649–1660. At sea, royalist ships continued to fly the Union Jack of 1606, while on 22 February 1649 the Council of State decided to send the parliamentary navy an order (signed by Oliver Cromwell on 23 February) that "the ships at sea in service of the State shall onely beare the red Crosse in a white flag" (viz., the flag of England). On 5 March 1649 the Council further ordered "that the Flagg that is to be borne by the Admiral, Vice-Admiral, and Rere-Admiral be that now presented, viz., the Armes of England and Ireland in two severall Escotcheons in a Red Flagg, within a compartment."cited afteDave Martucci, 29 September 1999/ref> A sole surviving example of a naval flag following this description is kept by the National Maritime Museum at Greenwich, others having fallen victim to the destruction of Commonwealth symbols at the Restoration of Charles II. Scotland was formally united w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Standard RMG L4481
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the 15th century. Originally a phrase (the common-wealth or the common wealth – echoed in the modern synonym "public wealth"), it comes from the old meaning of "wealth", which is "well-being", and was deemed analogous to the Latin ''res publica''. The term literally meant "common well-being". In the 17th century, the definition of "commonwealth" expanded from its original sense of "public welfare" or " commonweal" to mean "a state in which the supreme power is vested in the people; a republic or democratic state". The term evolved to become a title to a number of political entities. Three countries – Australia, the Bahamas, and Dominica – have the official title "Commonwealth", as do four U.S. states and two U.S. territories. Since the early 20th century, the term has been used to name som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Protectorate
The Protectorate, officially the Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, was the English form of government lasting from 16 December 1653 to 25 May 1659, under which the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, with their associated territories were joined together in the Commonwealth of England, governed by a Lord Protector. It began when Barebone's Parliament was dissolved, and the Instrument of Government appointed Oliver Cromwell as Lord Protector of the Commonwealth. Cromwell died in September 1658 and was succeeded by his son Richard Cromwell. Richard resigned in May 1659 due to his inability to control either the Army or Parliament of England, Parliament. He was replaced by the English Committee of Safety, which dissolved the Third Protectorate Parliament, and reseated the Rump Parliament dismissed by his father in April 1653. This marked the end of the Protectorate, with the Rump acting as the legisl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flags With Crosses
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular) with distinctive colours and design. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as " vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or "banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to a brigade in Arab countri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsolete National Flags
Obsolescence is the process of becoming antiquated, out of date, old-fashioned, no longer in general use, or no longer useful, or the condition of being in such a state. When used in a biological sense, it means imperfect or rudimentary when compared with the corresponding part of other organisms. The international standard IEC 62402:2019 Obsolescence Management defines obsolescence as the "transition from available to unavailable from the manufacturer in accordance with the original specification". Obsolescence frequently occurs because a replacement has become available that has, in sum, more advantages compared to the disadvantages incurred by maintaining or repairing the original. Obsolete also refers to something that is already disused or discarded, or antiquated. Typically, obsolescence is preceded by a gradual decline in popularity. Consequences Driven by rapid technological changes, new components are developed and launched on the market with increasing speed. The resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flags Of England
This is a list of English flags, including symbolic national and sub-national flags, standards and banners used exclusively in England. The College of Arms is the authority on the flying of flags in England and maintains the only official register of flags. It was established in 1484 and as part of the Royal Household operates under the authority of The Crown. A separate private body called the Flag Institute, financed by its own membership, also maintains a registry of United Kingdom flags that it styles 'the UK Flag Registry', though this has no official status under English law. Certain classes of flag enjoy a special status within English planning law and can be flown without needing planning permission as advertisements. These include any country's national flag, civil ensign or civil air ensign; the flag of the Commonwealth, the United Nations or any other international organisation of which the United Kingdom is a member; a flag of any island, county, district, borou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of England
The coat of arms of England is the coat of arms historically used as arms of dominion by the monarchs of the Kingdom of England, and now used to symbolise England generally.: "The three golden lions upon a ground of red have certainly continued to be the royal and national arms of England." The arms were adopted 1200 by the Plantagenet kings and continued to be used by successive English and British monarchs; they are currently quartered with the arms of Scotland and Ireland in the coat of arms of the United Kingdom. Historically they were also quartered with the arms of France, representing the English claim to the French throne, and Hanover. The arms continue to be used in heraldry to represent England, for example in the arms of Canada, although they rarely appear in isolation in royal or government contexts. They have also been adapted by English sporting bodies, forming the basis of the coat of arms of the Football Association, the logo of the England and Wales Cricket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of English Flags
This is a list of English flags, including symbolic national and sub-national flags, standards and banners used exclusively in England. The College of Arms is the authority on the flying of flags in England and maintains the only official register of flags. It was established in 1484 and as part of the Royal Household operates under the authority of The Crown. A separate private body called the Flag Institute, financed by its own membership, also maintains a registry of United Kingdom flags that it styles 'the UK Flag Registry', though this has no official status under English law. Certain classes of flag enjoy a special status within English planning law and can be flown without needing planning permission as advertisements. These include any country's national flag, civil ensign or civil air ensign; the flag of the Commonwealth, the United Nations or any other international organisation of which the United Kingdom is a member; a flag of any island, county, district, boro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
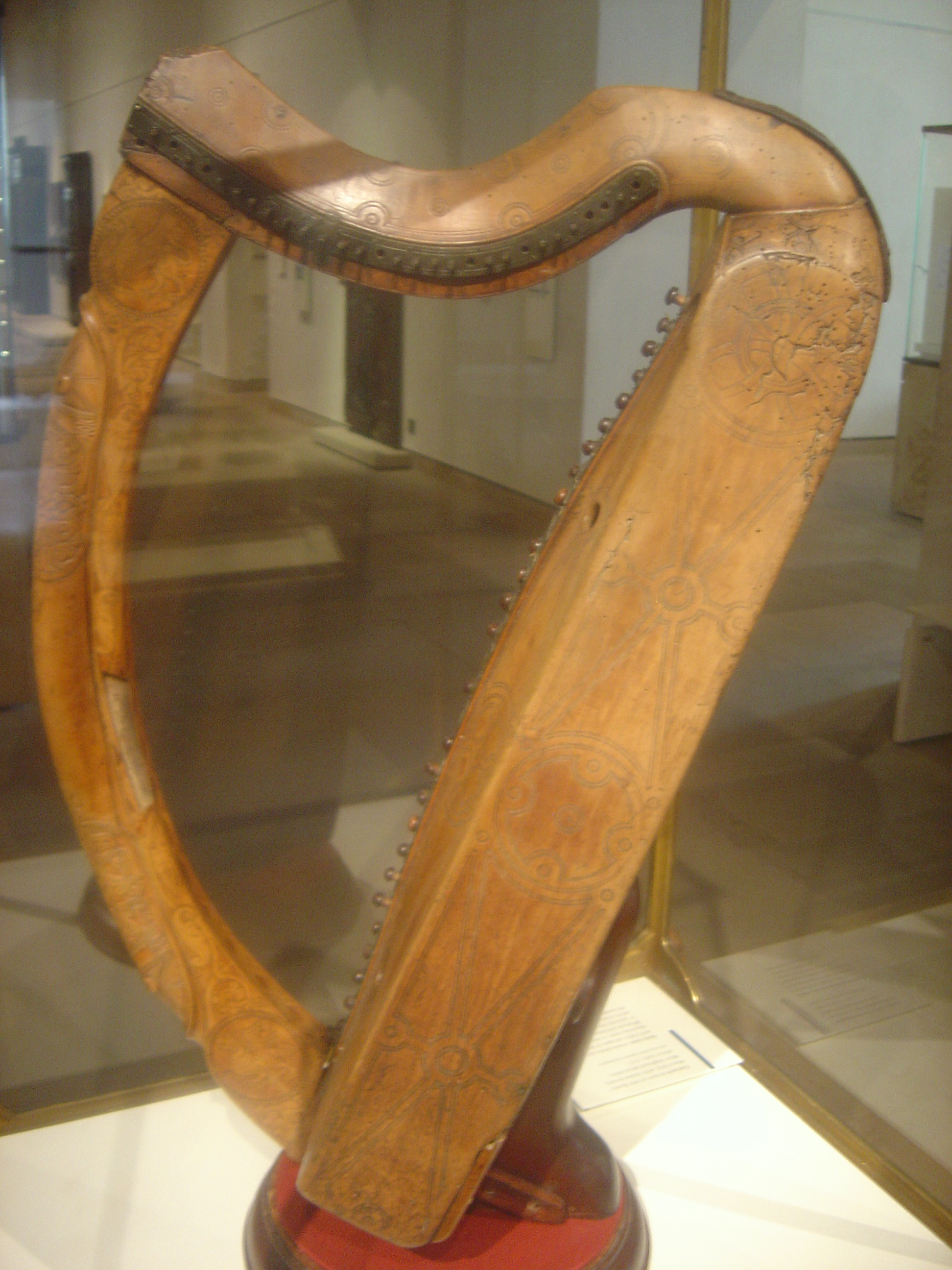
Irish Harp
The Celtic harp is a triangular frame harp traditional to the Celtic nations of northwest Europe. It is known as in Irish, in Scottish Gaelic, in Breton and in Welsh. In Ireland and Scotland, it was a wire-strung instrument requiring great skill and long practice to play, and was traditionally associated with the Gaelic nobility of Ireland. It appears on Irish coins, Guinness products, and the coat of arms of the Republic of Ireland, Montserrat, Canada and the United Kingdom. Early history The early history of the triangular frame harp in Europe is contested. The first instrument associated with the harping tradition in the Gaelic world was known as a . This word may originally have described a different stringed instrument, being etymologically related to the Welsh crwth. It has been suggested that the word / (from / , a board) was coined for the triangular frame harp which replaced the , and that this coining was of Scottish origin.John Bannerman, 'The Clàrs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Restoration
The Stuart Restoration was the reinstatement in May 1660 of the Stuart monarchy in Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland. It replaced the Commonwealth of England, established in January 1649 after the execution of Charles I, with his son Charles II of England, Charles II. The Commonwealth of England had been governed by Lord Protector Oliver Cromwell and then his son Richard Cromwell. The term is also used to describe the reign of Charles II (1660–1685), and sometimes that of his younger brother King James II, James II (1685–1688). The Protectorate After Richard Cromwell, Lord Protector from 1658 to 1659, ceded power to the Rump Parliament, Charles Fleetwood and John Lambert (general), John Lambert then dominated government for a year. On 20 October 1659, George Monck, the governor of Scotland under the Cromwells, marched south with his army from Scotland to oppose Fleetwood and Lambert. Lambert's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of England
The Commonwealth of England was the political structure during the period from 1649 to 1660 when Kingdom of England, England and Wales, later along with Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland and Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, were governed as a republic after the end of the Second English Civil War and the High Court of Justice for the trial of Charles I, trial and execution of Charles I. The republic's existence was declared through "An Act declaring England to be a Commonwealth", adopted by the Rump Parliament on 19 May 1649. Power in the early Commonwealth was vested primarily in the Parliament and a English Council of State, Council of State. During the period, fighting continued, particularly in Ireland and Scotland, between the parliamentary forces and those opposed to them, in the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland and the Anglo-Scottish war of 1650–1652. In 1653, after dissolution of the Rump Parliament, the Army Council (1647), Army Council adopted the Instrument of Gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Maritime Museum
The National Maritime Museum (NMM) is a maritime museum in Greenwich, London. It is part of Royal Museums Greenwich, a network of museums in the Maritime Greenwich World Heritage Site. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, it has no general admission charge; there are admission charges for most side-gallery temporary exhibitions, usually supplemented by many loaned works from other museums. Creation and official opening The museum was created by the National Maritime Museum Act 1934 under a Board of Trustees, appointed by HM Treasury. It is based on the generous donations of Sir James Caird (1864–1954). King George VI formally opened the museum on 27 April 1937 when his daughter Princess Elizabeth accompanied him for the journey along the Thames from London. The first director was Sir Geoffrey Callender. Collection Since the earliest times Greenwich has had associations with the sea and navigation. It was a landing place for the Romans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of England
The flag of England is the national flag of England, a constituent country of the United Kingdom. It is derived from Saint George's Cross (heraldic blazon: ''Argent, a cross gules''). The association of the red cross as an emblem of England can be traced back to the Late Middle Ages when it was gradually, increasingly, used alongside the Royal arms of England#Royal banner of England, Royal Banner. It became the only saint's flag permitted to be flown in public as part of the English Reformation and at a similar time became the pre-eminent maritime flag referred to as a white ensign. It was used as a component in the design of the Union Jack in 1606. It has been widely used since the 1990s, specifically at national sporting events, especially during the campaigns of England's national football teams. Origins In 1188 Henry II of England and Philip II of France agreed to go on Third Crusade, a crusade, and that Henry would use a white cross and Philip a red cross (and not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |