|
Flagellum
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are known as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium '' Helicobacter pylori'', for example, uses its flagella to propel itself through the stomach to reach the mucous lining where it may colonise the epithelium and potentially cause gastritis, and ulcers – a risk factor for stomach cancer. In some swarming bacteria, the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota, the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means " whip" to describe its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in mutualistic, commensal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
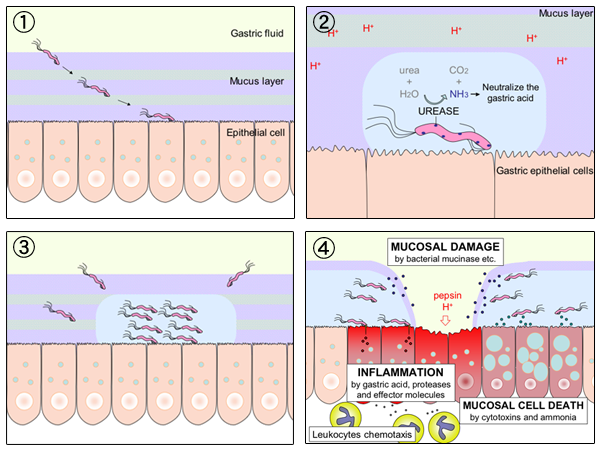
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its Helix, helical body (from which the genus name ''Helicobacter'' derives) is thought to have evolved to penetrate the gastric mucosa, mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. While many earlier reports of an association between bacteria and the ulcers had existed, such as the works of John Lykoudis, it was only in 1983 when the bacterium was formally described for the first time in the English-language Western literature as the causal agent of peptic ulcer, gastric ulcers by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, the pair was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery. Infection of the stomach with ''H. pylori'' doe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilus
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; : pili) is a hair-like cell-surface appendage found on many bacteria and archaea. The terms ''pilus'' and '' fimbria'' (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: ''fimbriae'') can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term ''pilus'' for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin – fibrous proteins, which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface. Some bacteria, viruses or bacteriophages attach to receptors on pili at the start of their reproductive cycle. Pili are antigenic. They are also fragile and constantly replaced, sometimes with pili of different composition, resulting in altered antigenicity. Specific host responses to old pili structures are not effective on the new structure. Recombination between genes of some (but not all) pili code for variable (V) and constant (C) regions of the pili (similar to immunoglobulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sperm Cell
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, which are known as spermatozoa, while some red algae and fungi produce non-motile sperm cells, known as spermatia. Flowering plants contain non-motile sperm inside pollen, while some more basal plants like ferns and some gymnosperms have motile sperm. Sperm cells form during the process known as spermatogenesis, which in amniotes (reptiles and mammals) takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. This process involves the production of several successive sperm cell precursors, starting with spermatogonia, which differentiate into spermatocytes. The spermatocytes then undergo meiosis, reducing their chromosome number by half, which produces spermatids. The spermatids then mature and, in animals, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotic
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a single-celled organism whose cell lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial mats. Prokaryotes are asexual, reproducing via binary fission. Horizontal gene transfer is common as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with two subtypes, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core, called the axoneme, determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the Biological life cycle, life cycles of many plants, algae, fungus, fungi and protozoa. They were thought to have appeared as early as the mid-late Ordovician period as an adaptation of early land plants. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. In some rare cases, a diploid spore is also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whip
A whip is a blunt weapon or implement used in a striking motion to create sound or pain. Whips can be used for flagellation against humans or animals to exert control through pain compliance or fear of pain, or be used as an audible cue through the distinct whipcrack effect. The portion used for striking is generally either a firm rod designed for direct contact, or a flexible line requiring a specialized swing. The former is easier and more precise, the latter offers longer reach and greater force. Some varieties, such as a hunting whip or lunge whip, have an extended stock section in addition to the line. Whips such as the "cat o' nine tails" and knout are specifically developed for corporal punishment or torture on human targets. Certain religious practices and BDSM activities involve the self-use of whips or the use of whips between consenting partners. Misuse on animals may be considered animal cruelty, and misuse on humans may be viewed as assault. Use Whips are genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagellate
A flagellate is a cell or organism with one or more whip-like appendages called flagella. The word ''flagellate'' also describes a particular construction (or level of organization) characteristic of many prokaryotes and eukaryotes and their means of motion. The term presently does not imply any specific relationship or classification of the organisms that possess flagella. However, several derivations of the term "flagellate" (such as " dinoflagellate" and " choanoflagellate") are more formally characterized. Form and behavior Flagella in eukaryotes are supported by microtubules in a characteristic arrangement, with nine fused pairs surrounding two central singlets. These arise from a basal body. In some flagellates, flagella direct food into a cytostome or mouth, where food is ingested. Flagella role in classifying eukaryotes. Among protoctists and microscopic animals, a flagellate is an organism with one or more flagella. Some cells in other animals may be flage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
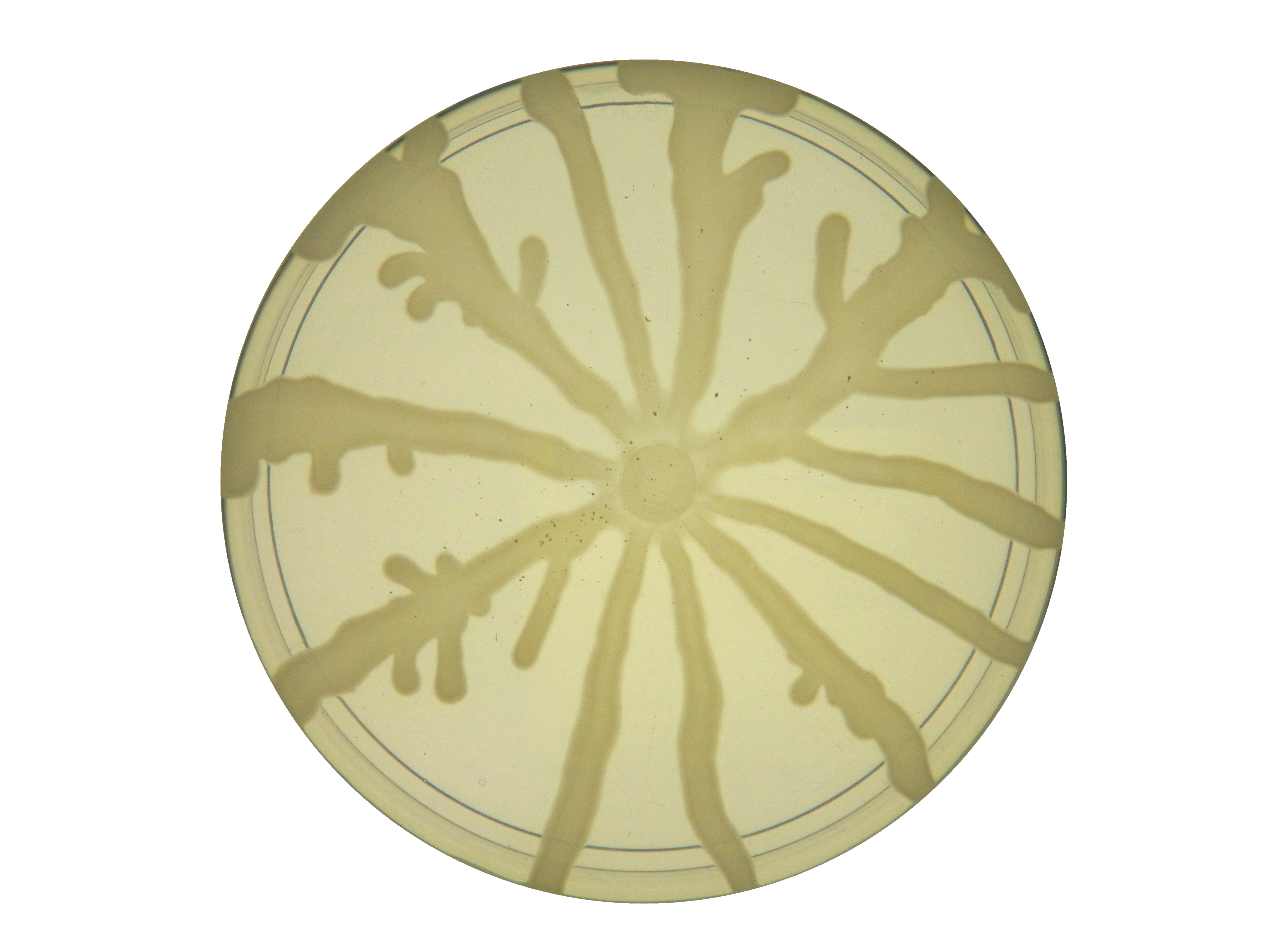
Swarming Motility
Swarming motility is a rapid (2–10 μm/s) and coordinated translocation of a bacterial population across solid or semi-solid surfaces, and is an example of bacterial multicellularity and swarm behaviour. Swarming motility was first reported by Jorgen Henrichsen and has been mostly studied in genus ''Serratia'', ''Salmonella'', ''Aeromonas'', ''Bacillus'', ''Yersinia'', ''Pseudomonas'', ''Proteus (bacterium), Proteus'', ''Vibrio'' and ''Escherichia''. This multicellular behavior has been mostly observed in controlled laboratory conditions and relies on two critical elements: 1) the nutrient composition and 2) viscosity of culture medium (i.e. % agar). One particular feature of this type of motility is the formation of dendritic fractal-like patterns formed by migrating swarms moving away from an initial location. Although the majority of species can produce tendrils when swarming, some species like ''Proteus mirabilis'' do form concentric circles motif instead of dendritic patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |