|
First 100 Days Of Donald Trump's First Presidency
The first 100 days of First presidency of Donald Trump, Donald Trump's first presidency began on January 20, 2017, the day Donald Trump was First inauguration of Donald Trump, inaugurated as the 45th president of the United States. The First hundred days (United States), first 100 days of a presidency took on symbolic significance during Franklin D. Roosevelt's first term in office, and the period is considered a benchmark to measure the early success of a president. The 100th day of Trump's first presidency was April 30, 2017. Institutionally, President Trump had the advantage of a Republican Party (United States), Republican Party majority in the U.S. United States House of Representatives, House of Representatives and the United States Senate, Senate, but was unable to fulfill his major pledges in his first 100 days, with some United States presidential approval rating, approval rating polls reporting around 40%. He reversed his position on a number of issues including lab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Presidency Of Donald Trump
Donald Trump's first tenure as the president of the United States began on January 20, 2017, when Trump First inauguration of Donald Trump, was inaugurated as the List of presidents of the United States, 45th president, and ended on January20, 2021. Trump, a Republican Party (United States), Republican from New York (state), New York, took office following his United States Electoral College, electoral college victory over Democratic Party (United States), Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton in the 2016 United States presidential election, 2016 presidential election. Upon his inauguration, he became the first president in American history List of presidents of the United States by previous experience, without prior public office or military background. Trump made an unprecedented number of False or misleading statements by Donald Trump, false or misleading statements during his Donald Trump 2016 presidential campaign, 2016 campaign and first presidency. Alongside Trump's pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chair Of The Federal Reserve
The chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System is the head of the Federal Reserve, and is the active executive officer of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. The chairman presides at meetings of the Board. The chairman serves a four-year term after being nominated by the president of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate; the officeholder serves concurrently as a member of the Board of Governors. The chairman may serve multiple terms, subject to re-nomination and confirmation each time; William McChesney Martin (1951–1970) was the longest serving chair, with Alan Greenspan (1987–2006) a close second. neither the president nor congress of the US can dismiss a chairman before the end of a term. Jerome Powell was sworn in as chairman on February 5, 2018. He had been first nominated to the position by President Donald Trump on November 2, 2017, and confirmed by the Senate. He was nomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Atlantic
''The Atlantic'' is an American magazine and multi-platform publisher based in Washington, D.C. It features articles on politics, foreign affairs, business and the economy, culture and the arts, technology, and science. It was founded in 1857 in Boston as ''The Atlantic Monthly'', a literary and cultural magazine that published leading writers' commentary on education, the abolition of slavery, and other major political issues of that time. Its founders included Francis H. Underwood and prominent writers Ralph Waldo Emerson, Oliver Wendell Holmes Sr., Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, Harriet Beecher Stowe, and John Greenleaf Whittier. James Russell Lowell was its first editor. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the magazine also published the annual ''The Atlantic Monthly Almanac''. The magazine was purchased in 1999 by businessman David G. Bradley, who fashioned it into a general editorial magazine primarily aimed at serious national readers and " thought leaders"; in 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate Republican Policy Committee
The Senate Republican Policy Committee is the policy research arm of the Republican Conference. Its predecessor, the Senate Republican Steering Committee was formed in March 1944 after Leader Charles L. McNary's death. It became formally funded and renamed the Policy Committee in 1947 along with its Democratic counterpart, the Senate Democratic Policy Committee, after the Legislative Reorganization Act of 1946. Funding for staff of both party policy committees comes directly from the legislative branch. According to '' Congressional Quarterly'', "the Policy Committee is in effect a legislative think tank A think tank, or public policy institute, is a research institute that performs research and advocacy concerning topics such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, technology, and culture. Most think tanks are non-governme .... The committee organizes the prominent Tuesday lunches with summaries of major bills, analysis of roll call votes and distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congressional Review Act
The Congressional Review Act (CRA) is a law that was enacted by the United States Congress as Subtitle E of the Contract with America Advancement Act of 1996 () and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on March 29, 1996. The law empowers Congress to review, by means of an expedited legislative process, new federal regulations issued by government agencies and, by passage of a joint resolution, to overrule a regulation. Once a rule is thus repealed, the CRA also prohibits the reissuing of the rule in substantially the same form or the issuing of a new rule that is substantially the same "unless the reissued or new rule is specifically authorized by a law enacted after the date of the joint resolution disapproving the original rule" (5 U.S. Code § 801(b)(2)). Congress has a window of time lasting 60 legislative days to disapprove of any given rule by simple-majority vote; otherwise, the rule will go into effect at the end of that period. Prior to 2017, the CRA had been succ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barack Obama
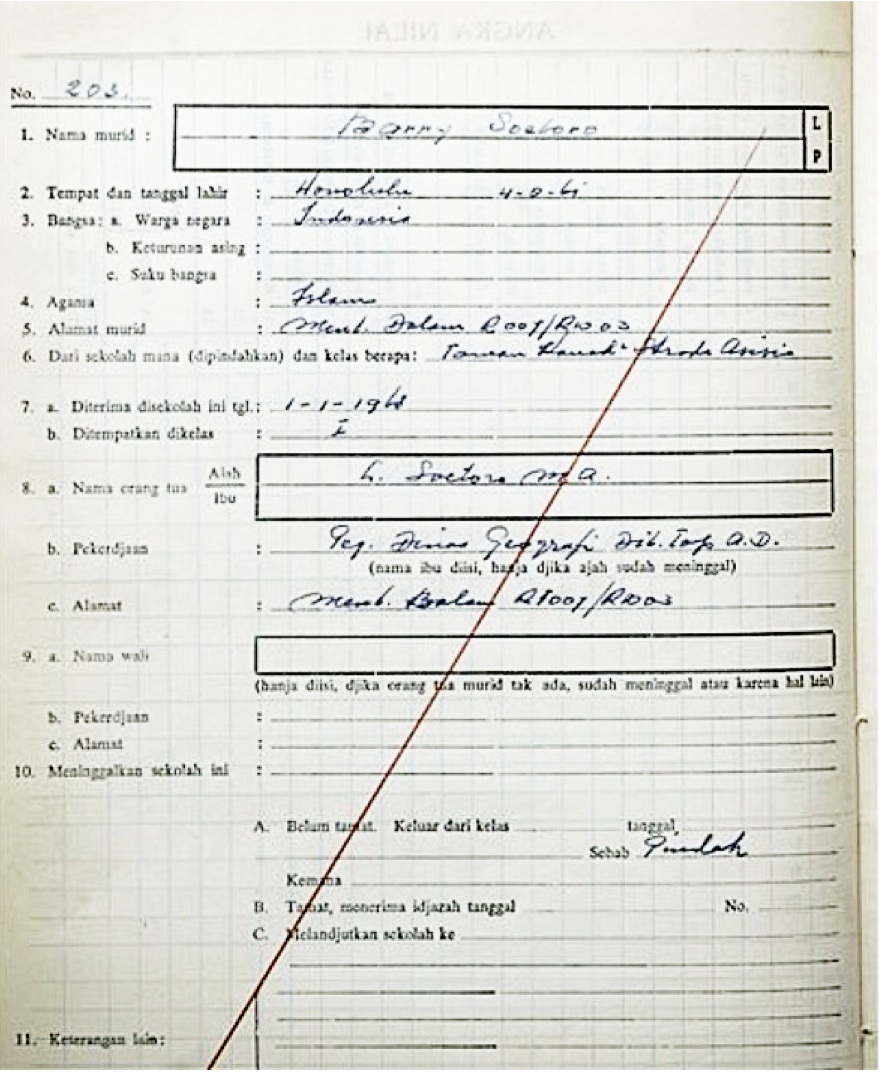
Barack Hussein Obama II (born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who was the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, he was the first African American president in American history. Obama previously served as a U.S. senator representing Illinois from 2005 to 2008 and as an Illinois state senator from 1997 to 2004. Born in Honolulu, Hawaii, Obama graduated from Columbia University in 1983 with a Bachelor of Arts degree in political science and later worked as a community organizer in Chicago. In 1988, Obama enrolled in Harvard Law School, where he was the first black president of the ''Harvard Law Review''. He became a civil rights attorney and an academic, teaching constitutional law at the University of Chicago Law School from 1992 to 2004. In 1996, Obama was elected to represent the 13th district in the Illinois Senate, a position he held until 2004, when he successfully ran for the U.S. Senate. In the 2008 pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill (United States Congress)
In the United States Congress, a bill is proposed legislation under consideration by either of the two chambers of Congress: the House of Representatives or the Senate. Anyone elected to either body can propose a bill. After both chambers approve a bill, it is sent to the President of the United States for consideration. Bill writing Ideas for legislation and drafts of legislation can come from many areas, including members of Congress, Congressional committees, constituents, lobbyists, state legislatures, the president, federal departments, and federal agencies. The House Office of the Legislative Counsel and Senate Office of the Legislative Counsel are available to create or modify legislation for members and committees. Introduction and sponsors In the House, a bill is introduced by a member placing a hard copy into a wooden box called a hopper. In the Senate, the bill is placed on the desk of the presiding officer. The bill must bear the signature of the member intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidential Proclamation
In the United States, a presidential proclamation is a statement issued by the president of the United States on an issue of public policy. It is a type of presidential directive. Details A presidential proclamation is an instrument that: *states a condition, *declares a law and requires obedience, *recognizes an event, or *triggers the implementation of a law, by recognizing that the circumstances described in the law have been realized. Proclamations issued by the president fall into two broad categories: #"ceremonial" proclamations, that designate special observances or celebrate national holidays, and #"substantive" proclamations, that usually relates to the conduct of foreign affairs and other sworn executive duties. These may be, but are not limited to, matters of international trade, the execution of set export controls, the establishment of tariffs, or the reservation of federal lands for the benefit of the public in some manner. Unless authorized by the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presidential Memoranda
A presidential memorandum (from Latin ''memorare'', 'to remember') is a type of directive issued by the president of the United States to manage and govern the actions, practices, and policies of the various departments and agencies found under the executive branch of the United States government. It has the force of law and is usually used to delegate tasks, direct specific government agencies to do something, or to start a regulatory process. There are three types of presidential memoranda: presidential determination or presidential finding, memorandum of disapproval, and hortatory memorandum. Sometimes used interchangeably, an executive order is a more prestigious form of executive action that must cite the specific constitutional or statutory authority the president has to use it. Unlike executive orders, memoranda are not required by law to be published in the ''Federal Register'', but publication is necessary in order to have "general applicability and legal effect". The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Order (United States)
In the United States, an executive order is a directive by the president of the United States that manages operations of the federal government. The legal or constitutional basis for executive orders has multiple sources. Article Two of the United States Constitution gives presidents broad executive and enforcement authority to use their discretion to determine how to enforce the law or to otherwise manage the resources and staff of the federal government's executive branch. The delegation of discretionary power to make such orders is required to be supported by either an expressed or implied congressional law, or the constitution itself.John Contrubis, '' Executive Orders and Proclamations'', CRS Report for Congress #95-722A, March 9, 1999, Pp. 1-2 The vast majority of executive orders are proposed by federal agencies before being issued by the president. Like both legislative statutes and the regulations promulgated by government agencies, executive orders are subjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Shutdown In The United States
In the United States, government shutdowns occur when funding legislation required to finance the federal government is not enacted before the next fiscal year begins. In a shutdown, the federal government curtails agency activities and services, ceases non-essential operations, furloughs non-essential workers, and retains only essential employees in departments that protect human life or property. Shutdowns can also disrupt state, territorial, and local levels of government. Funding gaps began to lead to shutdowns in 1980, when Attorney General Benjamin Civiletti issued a legal opinion requiring it. This opinion was not consistently adhered to through the 1980s, but since 1990 all funding gaps lasting longer than a few hours have led to a shutdown. As of February 2024, 10 funding shutdowns have led to federal employees being furloughed. The most significant include the 21-day shutdown of 1995–1996, during President Bill Clinton’s administration, over opposition to major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico–United States Border Wall
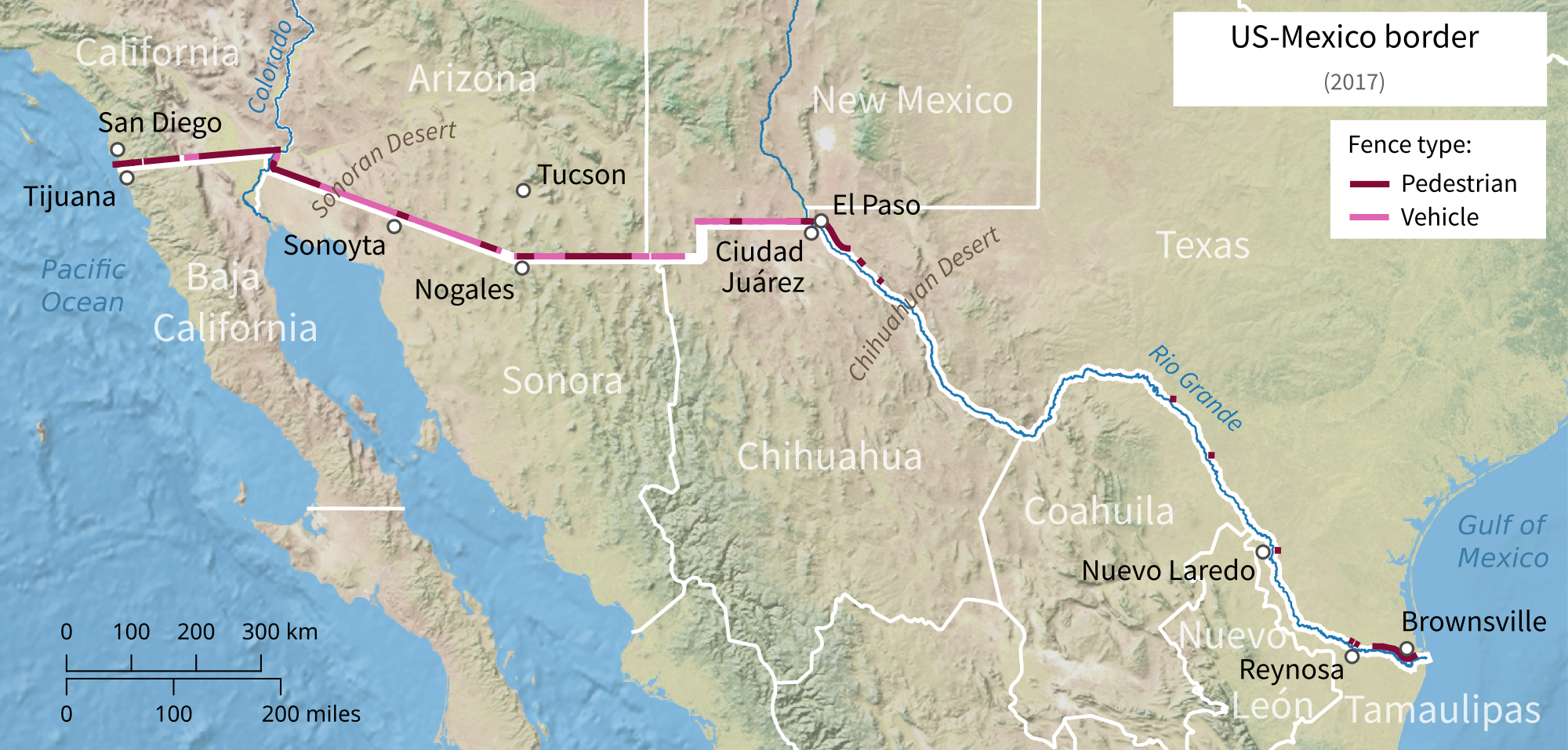
The Mexico–United States border wall is a series of disjoined physical barriers built along portions of the Mexico–United States border. The barriers were constructed in a piecemeal manner over the course of several President of the United States, presidential administrations in an attempt to reduce illegal immigration to the United States from Mexico.Chaichian, Mohammad. 2014. ''Empires and Walls: Globalization, Migration, and Colonial Domination'' (Brill, pp. 175–235) Between the physical barriers, security is provided by a "virtual fence" of sensors, cameras, and other Surveillance, surveillance equipment used to dispatch United States Border Patrol agents to suspected migrant crossings. In May 2011, the United States Department of Homeland Security, Department of Homeland Security (DHS) said it had of barriers in place. A total of of new primary barriers were built during Donald Trump's first presidency, dubbed the "Trump wall", though Trump had repeatedly promised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |