|
Firefighting In Antarctica
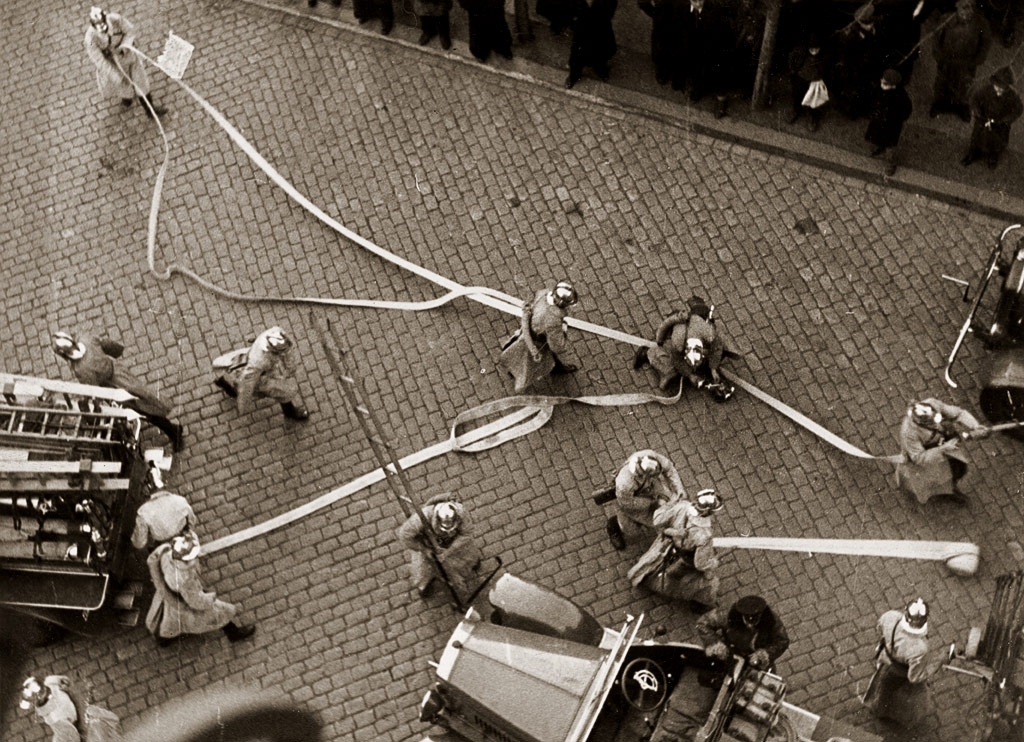
Firefighting in Antarctica encompasses various organizations and procedures designed to fight fires on the continent of Antarctica. Firefighting in Antarctica is complicated by the harsh conditions of the continent, the remoteness of the locations to be serviced, and the importance of protecting life-supporting shelter from immolation. Conditions and considerations Although there are no wildfires in Antarctica, fire represents a serious threat to human activity. Antarctica is the windiest place on earth, so there are often winds sufficient to quickly fan any flames. Due to the low temperatures, liquid water is often hard to obtain in large quantity. Because of the harsh conditions, shelter is a necessity of life and significant loss of shelter to fire could be disastrous to the survival of a base's residents, exacerbated by the remoteness of the bases from outside aid. Because of this, bases in Antarctica are often designed to mitigate the devastation of a fire by being made up of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefighting
Firefighting is the act of extinguishing or preventing the spread of unwanted fires from threatening human lives and destroying property and the environment. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter. Firefighters typically undergo a high degree of technical training. This involves structural firefighting and wildland firefighting. Specialized training includes aircraft firefighting, shipboard firefighting, aerial firefighting, maritime firefighting, and proximity firefighting. Firefighting is a dangerous profession due to the toxic environment created by combustible materials, with major risks are smoke, oxygen deficiency, elevated temperatures, poisonous atmospheres, and violent air flows. To combat some of these risks, firefighters carry self-contained breathing apparatus. Additional hazards include falls — a constant peril while navigating unfamiliar layouts or confined spaces amid shifting debris under limited visibility – and structural collaps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Cross Expedition
The ''Southern Cross'' Expedition, otherwise known as the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900, was the first British venture of the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration, and the forerunner of the more celebrated journeys of Robert Falcon Scott and Ernest Shackleton. The brainchild of the Anglo-Norwegian explorer Carsten Borchgrevink, it was the first expedition to over-winter on the Antarctic mainland, the first to visit the Great Ice Barrier—later known as the Ross Ice Shelf—since Sir James Clark Ross's groundbreaking expedition of 1839 to 1843, and the first to effect a landing on the Barrier's surface. It also pioneered the use of dogs and sledges in Antarctic travel. The expedition was privately financed by the British magazine publisher Sir George Newnes. Borchgrevink's party sailed in the , and spent the southern winter of 1899 at Cape Adare, the northwest extremity of the Ross Sea coastline. Here they carried out an extensive programme of scientific observations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
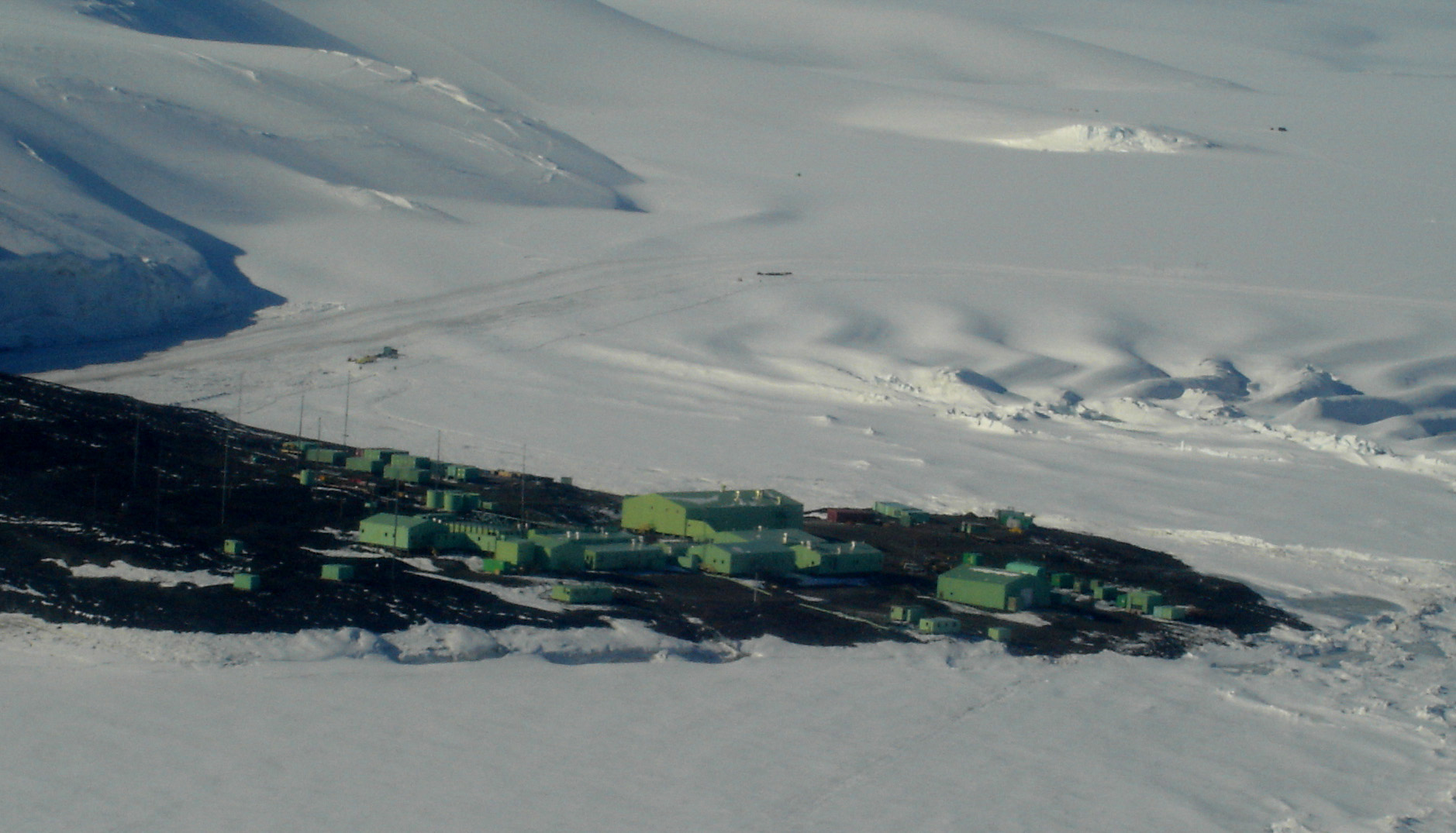
Progress Station
Progress (russian: Прогресс) is a Russian (formerly Soviet) research station in Antarctica. It is located at the Larsemann Hills antarctic oasis on the shore of Prydz Bay. The station was established by the 33rd Soviet Antarctic Expedition on April 1, 1988, and was moved to another place on February 26, 1989 In 2000, work was temporarily halted but it reopened in 2003. A landing field is located close to the station for air connection with other stations. From 1998 to 2001 works were performed to transfer transportation operations to Progress from the Mirny Station and make it the main support base for Vostok station. In 2004, work began on a year-round facility at the station. On October 4, 2008, a fire broke out at the construction site resulting in the death of a construction worker and two serious injuries. The fire resulted in the complete loss of the new structure, as well as damage to the station's communications and scientific equipment. In 2013, the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
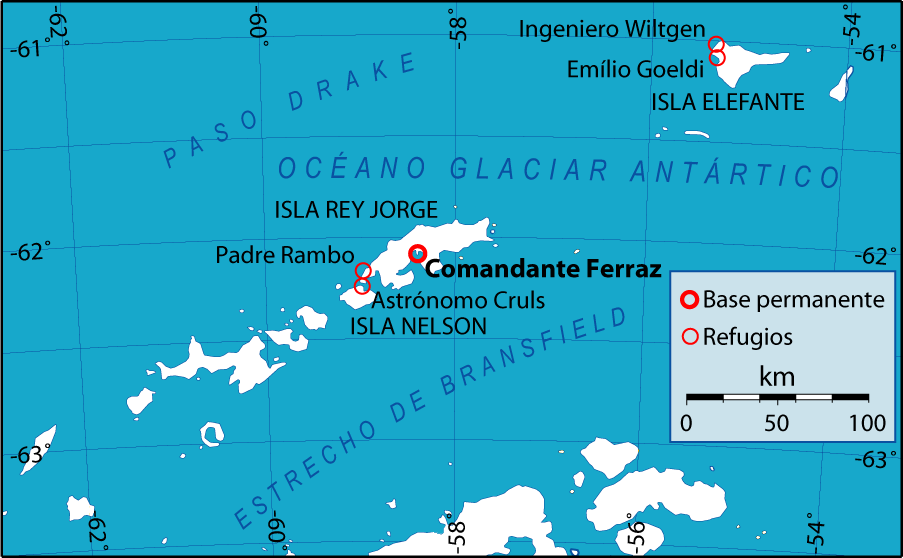
Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station
The Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station ( pt, Estação Antártica Comandante Ferraz) is a permanent Antarctic research station named after the Brazilian Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz (1940-1982), who visited Antarctica many times with the British exploration team and managed to convince his government to create a self-guided Brazilian Antarctic Program. Located in Admiralty Bay ( pt, Baía do Almirantado), King George Island ( pt, Ilha do Rei George), near the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, 130 km north of the peninsula, the station began operating on 6 February 1984, brought to Antarctica in modules by the oceanographic ship ''Barão de Teffé'' and several other Brazilian naval ships. It now houses about 64 people, including researchers, technicians and staff, military and civilians. History The station was named after Navy Commander Luís Antônio de Carvalho Ferraz, a hydrographer and oceanographer who visited Antarctica twice on British vessels. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comandante Ferraz Antarctic Station Fire
Commandant ( or ) is a title often given to the officer in charge of a military (or other uniformed service) training establishment or academy. This usage is common in English-speaking nations. In some countries it may be a military or police rank. It is also often used to refer to the commander of a military prison or prison camp (including concentration camps and prisoner of war camps). Bangladesh In Bangladesh Armed Forces commandant is not any rank. It is an appointment. The commandant serves as the head of any military training institutes or unit. Canada ''Commandant'' is the normal Canadian French-language term for the commanding officer of a mid-sized unit, such as a regiment or battalion, within the Canadian Forces. In smaller units, the commander is usually known in French as the ''officier commandant''. Conversely, in Canadian English, the word commandant is used exclusively for the commanding officers of military units that provide oversight and/or services to a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter-over Syndrome
The winter-over syndrome is a condition that occurs in individuals who "winter-over" throughout the Antarctic (or Arctic) winter, which can last seven to eight months. It has been observed in inhabitants of research stations in Antarctica, as well as in polar bases such as Thule, Alert and Eureka. It consists of a variety of behavioral and medical disturbances, including irritability, depression, insomnia, absentmindedness, aggressive behavior, and irritable bowel syndrome. Contributing factors The Antarctic winter is a period of no physical contact with other continents or Antarctic stations, including no airplanes, ships, or mail. The area has the driest desert climate on Earth, and a low air pressure and oxygen-poor atmosphere. It is completely cut off during winter, the mean temperature is , and the lowest recorded temperature is . For these reasons, the immobility, monotony, harsh physical environment, sexual deprivation, and the general isolation, are believed to contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almirante Brown Base
Brown Station ( es, Estación Científica Almirante Brown, or more often ''Base Brown'' or ''Estación Brown'') is an Argentine Antarctic base and scientific research station named after Admiral William Brown, the father of the Argentine Navy. It is located on Sanavirón Peninsula along Paradise Harbor, Danco Coast, in Graham Land, Antarctic Peninsula. Brown is one of 13 research bases in Antarctica operated by Argentina. From 1951 to 1984 it served as a permanent base; since then it is open during the summer season only. History Brown Station dates to 6 April 1951, when Argentina established the ''Almirante Brown'' Naval Detachment at Paradise Harbor. The Argentine Antarctic Institute took over the station in 1964–65, creating one of the most complete biology laboratories on the Antarctic Peninsula. It included a main house of ; two folding fuel tanks; and an additional building exclusive for scientific research, equipped with three labs, photography workshop, emergen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hope Bay
Hope Bay ( Spanish: ''Bahía Esperanza'') on Trinity Peninsula, is long and wide, indenting the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula and opening on Antarctic Sound. It is the site of the Argentinian Antarctic settlement Esperanza Base, established in 1952. Important Bird Area The bay has been identified as an Important Bird Area (IBA) by BirdLife International because it supports one of the largest Adélie penguin colonies in Antarctica with around 125,000 pairs. Other birds nesting at the site include gentoo penguins, brown skuas, Antarctic terns, Wilson's storm-petrels, kelp gulls and snowy sheathbills. History The Bay was discovered on January 15, 1902 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, who named it in commemoration of the winter spent there by J. Gunnar Andersson and S.A. Duse, Toralf Grunden of his expedition after his ship (the ''Antarctic'') was crushed by the ice and lost. They were eventually rescued by Argentine corvette ''Uruguay''. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zucchelli Station
Zucchelli Station is an Italian seasonal research station, located at Terra Nova Bay in Antarctica on a granitic headland along the coast of the Northern Foothills to north-east of Gerlache Inlet. It has been named after Mario Zucchelli, director of the activities, which conducted for sixteen years, for the ENEA-Unità Tecnica Antartide as part of the National Antarctic Research Program (PNRA). The main functions carried out by the Station are: * logistic support to scientific personnel operating in remote fields * logistical and operational support to the oceanographic ship * support to research activities with laboratories and instrumentation * support to personnel and material in transit for Concordia Station * support to air operations Description The Zucchelli Station is a seasonal (from mid-October until mid-March) research Antarctic Station on the Terra Nova Bay located at an altitude of and covers an area of approximately 7,500 square meters. In 2010, the Station was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Base
Scott Base is a New Zealand Antarctic research station at Pram Point on Ross Island near Mount Erebus in New Zealand's Ross Dependency territorial claim. It was named in honour of Captain Robert Falcon Scott, RN, leader of two British expeditions to the Ross Sea area of Antarctica. The base was set up as support to field research and the centre for research into earth sciences, and now conducts research in many fields, operated by Antarctica New Zealand. The base is from the larger U.S. McMurdo Station via Pegasus Road. History Scott Base was originally constructed in support of the UK inspired and privately managed Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (TAE). The New Zealand government provided support for the TAE and also for the International Geophysical Year (IGY) project of 1957, five of whose members were attached to the Expedition. In February 1956, 10 months before the TAE and IGY parties were due to head to the Antarctic, Frank Ponder, an architect at the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vostok Station
Vostok Station (russian: ста́нция Восто́к, translit=stántsiya Vostók, , meaning "Station East") is a Russian research station in inland Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica. Founded by the Soviet Union in 1957, the station lies at the southern Pole of Cold, with the lowest reliably measured natural temperature on Earth of .Global Measured Extremes of Temperature and Precipitation. . Retrieved on 21 June 2007. Research includes drilling and [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |