|
Fire Adaptations
Fire adaptations are traits of plants and animals that help them survive wildfire or to use resources created by wildfire. These traits can help plants and animals increase their survival rates during a fire and/or reproduce offspring after a fire. Both plants and animals have multiple strategies for surviving and reproducing after fire. Plants in wildfire-prone ecosystems often survive through adaptations to their local fire regime. Such adaptations include physical protection against heat, increased growth after a fire event, and flammable materials that encourage fire and may eliminate competition. For example, plants of the genus ''Eucalyptus'' contain flammable oils that encourage fire and hard sclerophyll leaves to resist heat and drought, ensuring their dominance over less fire-tolerant species. Dense bark, shedding lower branches, and high water content in external structures may also protect trees from rising temperatures. Fire-resistant seeds and reserve Shoot (botany), s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
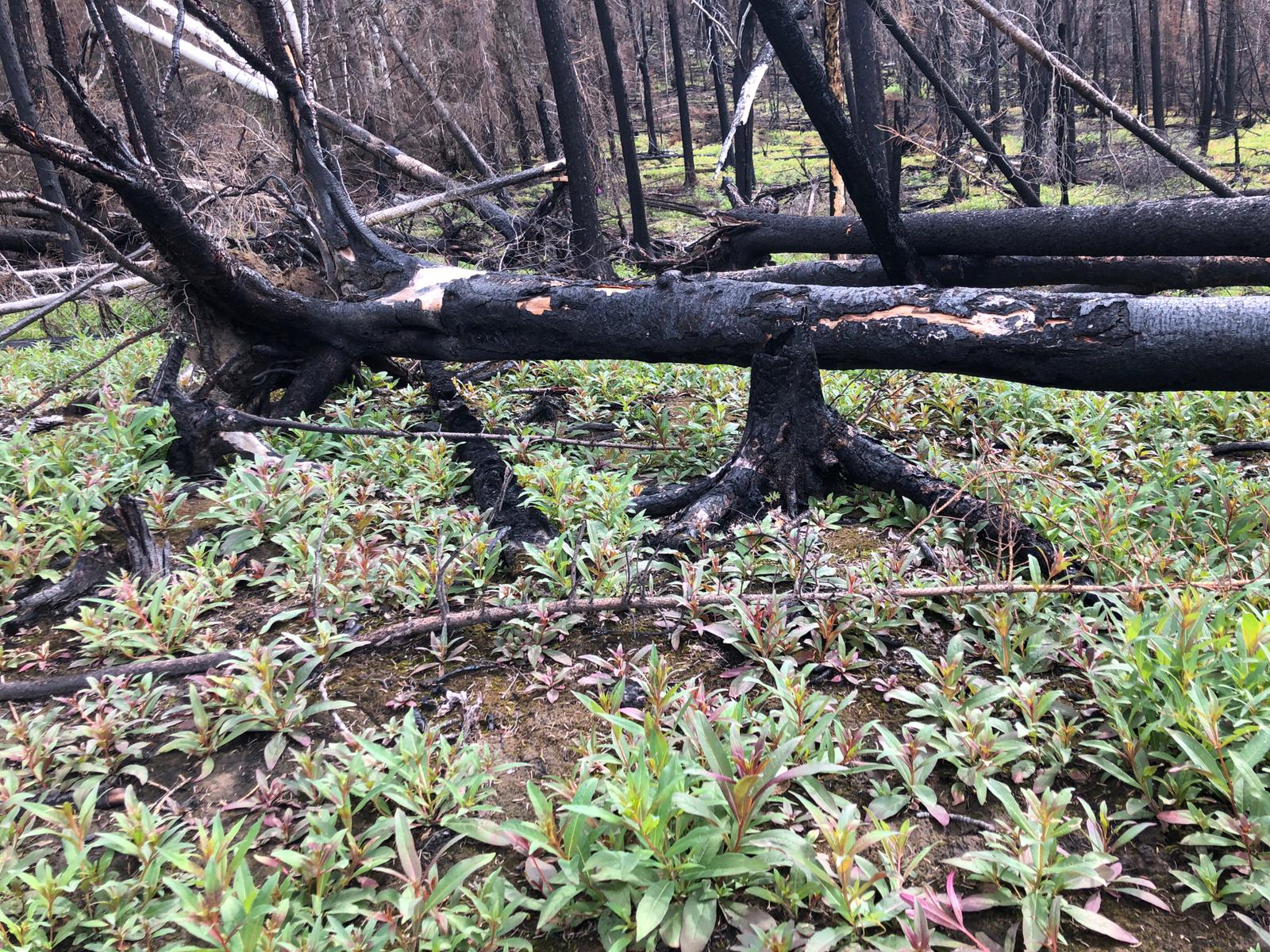
Boreal Pine Forest After Fire
Boreal, northern, of the north. Derived from the name of the god of the north wind from Ancient Greek civilisation, Boreas (god), Boreas. It may also refer to: Climatology and geography *Boreal (age), the first climatic phase of the Blytt-Sernander sequence of northern Europe, during the Holocene epoch *Boreal climate, a climate characterized by long winters and short, cool to mild summers *Boreal ecosystem, an ecosystem with a subarctic climate in the Northern Hemisphere *Boreal forest, a biome characterized by coniferous forests *Boreal Sea, a Mesozoic-era seaway Companies and organizations *Boreale, a Quebec microbrewery *Boreal Mountain Resort, a ski resort in the Lake Tahoe area of California *Boreal Norge, a Norwegian public transport operator *Collège Boréal, a francophone college in Ontario, Canada Other uses * Boreal (horse), a racehorse * Carlo Boreal, a fictional character in Philip Pullman's ''His Dark Materials'' trilogy *''Le Boreal'', a French cruise ship * Borea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Shoot
Basal shoots, root sprouts, adventitious shoots, and suckers are words for various kinds of shoots that grow from adventitious buds on the base of a tree or shrub, or from adventitious buds on its roots. Shoots that grow from buds on the base of a tree or shrub are called basal shoots; these are distinguished from shoots that grow from adventitious buds on the roots of a tree or shrub, which may be called root sprouts or suckers. A plant that produces root sprouts or Stolon, runners is described as surculose. Water sprouts produced by adventitious buds may occur on the above-ground stem, branches or both of trees and shrubs. Suckers are shoots arising underground from the roots some distance from the base of a tree or shrub. __TOC__ In botany and ecology In botany, a root sprout or sucker is a severable plant that grows not from a seed but from the meristem of a root at the base of or a certain distance from the original tree or shrub. Root sprouts may emerge a substantial distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fireweed
''Chamaenerion angustifolium'' is a perennial herbaceous flowering plant in the willowherb family, Onagraceae. It is known in North America as fireweed and in Britain and Ireland as rosebay willowherb. It is also known by the synonyms ''Chamerion angustifolium'' and ''Epilobium angustifolium''. It is native throughout the temperate Northern Hemisphere, including large parts of the boreal forests. Description The reddish stems of this herbaceous perennial are usually simple, erect, smooth, high with scattered alternate leaves. The leaves are spirally arranged, entire, narrowly lanceolate, and pinnately veined, the secondary leaf veins anastomosing, joining together to form a continuous marginal vein just inside the leaf margins. The inflorescence is a symmetrical terminal raceme that blooms progressively from bottom to top, producing a gracefully tapered shape. The flowers are in diameter, slightly asymmetrical, with four magenta to pink petals and four narrower pink sepals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrogenic Flowering
Pyrogenic flowering is the fire-adapted trait in plants that is defined by an increase or a peak in flowering after a fire event. Pyrogenic flowering allows for plants to persist in fire-prone environments. Pyrogenic flowering can be facultative, meaning the rate of flowering temporarily increases following burning, or obligate, meaning flowering only occurs post-fire. There is high variation in the length of time between when a fire occurs and when pyrogenic flowering is triggered, and it is frequently species specific. Some pyrogenic flowering does not occur until up to a year post-fire whereas in extreme cases some flowers can emerge just hours after fire disturbance. Precise physiological triggers for pyrogenic flowering have not been heavily studied as is likely to vary between groups. Some suggested stimuli of pyrogenic flowering are the increase in light due to loss of canopy or competition, nutrient changes in the soil, or chemicals associated with fires acting as a trigger. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scarification (botany)
Scarification in botany involves weakening, opening, or otherwise altering the coat of a seed to encourage germination. Scarification is often done mechanically, thermally, and chemically. The seeds of many plant species are often impervious to water and gases, thus preventing or delaying germination. Any process designed to make the testa (seed coat) more permeable to water and gases is known as scarification. Scarification, regardless of type, works by speeding up the natural processes which normally make seed coats permeable to water and air. For drupes (stone fruits), scarification also extends to weakening or removal of the hard endocarp shell around the seed. Types Regardless of the method, scarified seeds do not store well and need to be planted quickly, lest the seeds become unviable. Mechanical The most common type of scarification is mechanical scarification. In mechanical scarification, the testa is physically opened to allow moisture and air in. Seed coats may be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Seed Bank
The soil seed bank is the natural storage of seeds, often dormant, within the soil of most ecosystems. The study of soil seed banks started in 1859 when Charles Darwin observed the emergence of seedlings using soil samples from the bottom of a lake. The first scientific paper on the subject was published in 1882 and reported on the occurrence of seeds at different soil depths. Weed seed banks have been studied intensely in agricultural science because of their important economic impacts; other fields interested in soil seed banks include forest regeneration and restoration ecology. Henry David Thoreau wrote that the contemporary popular belief explaining the succession of a logged forest, specifically to trees of a dissimilar species to the trees cut down, was that seeds either spontaneously generated in the soil, or sprouted after lying dormant for centuries. However, he dismissed this idea, noting that heavy nuts unsuited for distribution by wind were distributed instead by an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banksia
''Banksia'' is a genus of around 170 species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. These Australian wildflowers and popular garden plants are easily recognised by their characteristic flower spikes, and woody fruiting "cones" and heads. ''Banksias'' range in size from prostrate woody shrubs to trees up to 30 metres (100 ft) tall. They are found in a wide variety of landscapes: sclerophyll forest, (occasionally) rainforest, shrubland, and some more arid landscapes, though not in Australia's deserts. Heavy producers of nectar, banksias are a vital part of the food chain in the Australian bush. They are an important food source for nectarivorous animals, including birds, bats, rats, possums, stingless bees and a host of invertebrates. Further, they are of economic importance to Australia's nursery and cut flower industries. However, these plants are threatened by a number of processes including land clearing, frequent burning and disease, and a number of species ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotiny
Serotiny in botany simply means 'following' or 'later'. In the case of serotinous flowers, it means flowers which grow following the growth of leaves, or even more simply, flowering later in the season than is customary with allied species. Having serotinous leaves is also possible, these follow the flowering. Serotiny is contrasted with coetany. Coetaneous flowers or leaves appear together with each other. In the case of serotinous fruit, the term is used in the more general sense of plants that release their seed over a long period of time, irrespective of whether release is spontaneous; in this sense the term is synonymous with bradyspory. In the case of certain Australian, North American, South African or Californian plants which grow in areas subjected to regular wildfires, serotinous fruit can also mean an ecological adaptation exhibited by some seed plants, in which seed release occurs in response to an environmental trigger, rather than spontaneously at seed maturati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Pine Needles And Red Pine Cones 2016-06-02 074
Jack may refer to: Places * Jack, Alabama, US, an unincorporated community * Jack, Missouri, US, an unincorporated community * Jack County, Texas, a county in Texas People and fictional characters * Jack (given name), a male given name, including a list of people and fictional characters with the name * Jack (surname), including a list of people with the surname * Jack (Tekken), multiple fictional characters in the fighting game series ''Tekken'' * Jack the Ripper, an unidentified British serial killer active in 1888 * Wolfman Jack (1938–1995), a stage name of American disk jockey Robert Weston Smith * New Jack, a stage name of Jerome Young (1963–2021), an American professional wrestler * Spring-heeled Jack, a creature in Victorian-era English folklore * Jack (hero), an archetypal Cornish and English hero and stock character Animals and plants Fish *Carangidae generally, including: **Almaco jack **Amberjack ** Bar jack ** Black jack (fish) ** Crevalle jack **Giant treva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pando (tree)
Pando () is the name of a quaking aspen (''Populus tremuloides'') clone located in Sevier County, Utah, United States, in the Fishlake National Forest. A male clonal organism, Pando has an estimated 47,000 stems (ramets) that appear to be individual trees but are not, because those stems are connected by a root system that spans . As a multi-stem tree, Pando is the world's largest tree by weight and landmass. Pando was identified as a single living organism because each of its stems possesses identical genetic markers. The massive interconnected root system coordinates energy production, defense and regeneration across the tree's landmass. Pando spans at its widest expanse along of the southwestern edge of the Fishlake Basin. It lies to the west of Fish Lake, the largest natural mountain freshwater lake in Utah. Pando's landmass spreads from above sea level to approximately above sea level along the western side of a steep basin wall. Pando is estimated to weigh collective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
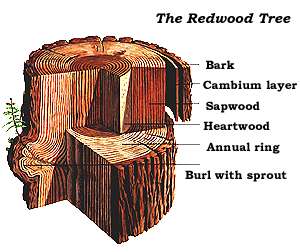
Sequoia Sempervirens
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995: 606–607 is the sole living species of the genus ''Sequoia (genus), Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the List of tallest trees, tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the List of oldest trees, longest-living trees on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred Native species, naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. Being the tallest tree species, with a small range and an extremely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |