|
Film Grain
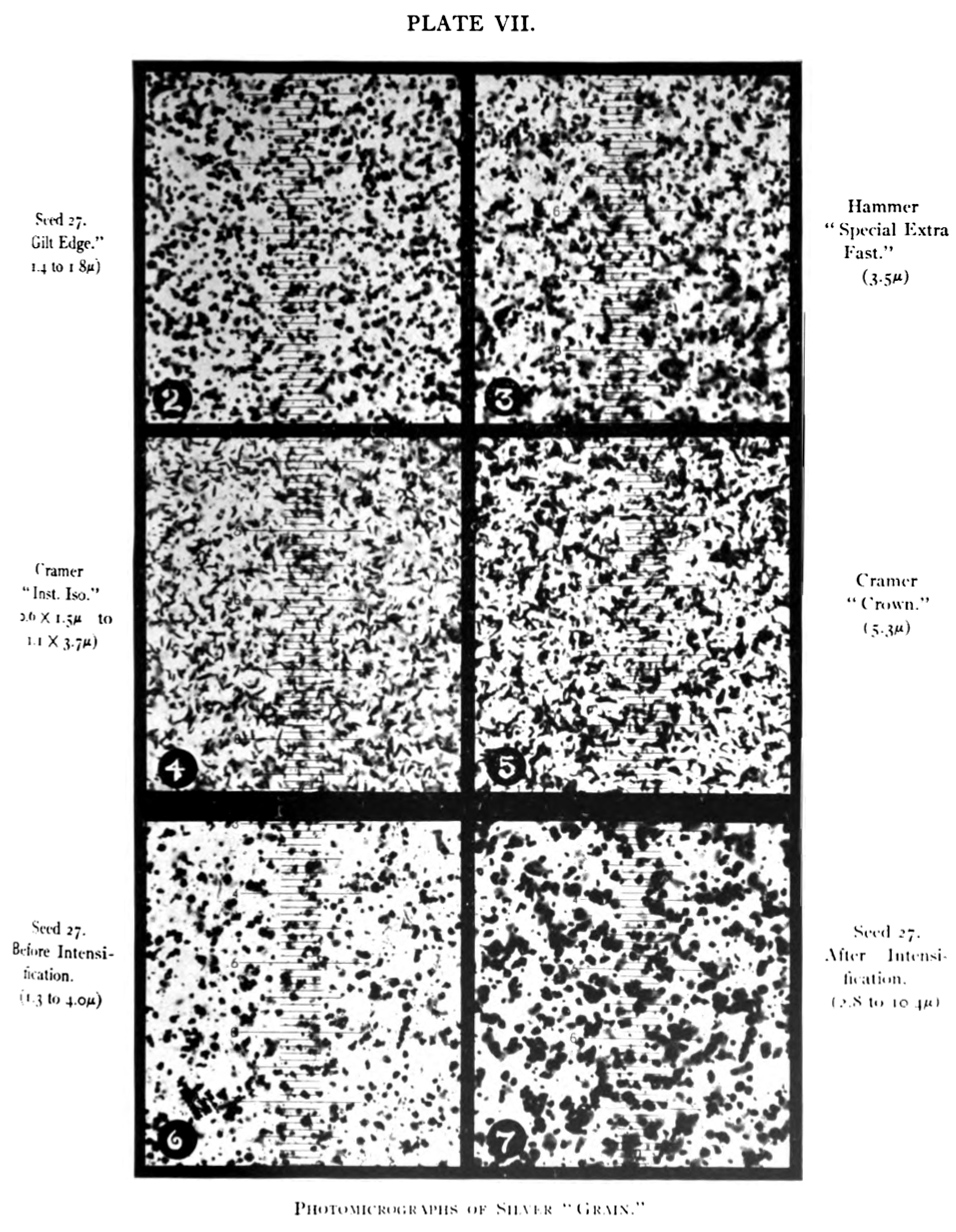
Film grain or film granularity is the random optical texture of processed photographic film. Film grain develops due to the presence of small particles of a metallic silver, or dye clouds, developed from silver halide that have received enough photons. While film grain is a function of such particles (or dye clouds) it is not a particle but an optical effect. The magnitude of the effect (also known as amount of grain) depends on both the film stock and the definition at which it is observed. It can be objectionably noticeable in an over-enlarged film photograph. Chemical background The size and morphology of the silver halide grains play crucial role in the image characteristics and exposure behavior. There is a tradeoff between the crystal size and light sensitivity (film speed); larger crystals have better chance to receive enough energy to flip them into developable state, as they have higher probability of receiving several photons needed for forming the Ag4 clusters that st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge-coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging. Overview In a CCD image sensor, pixels are represented by Doping (semiconductor), p-doped metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) capacitors. These MOS capacitors, the basic building blocks of a CCD, are biased above the threshold for inversion when image acquisition begins, allowing the conversion of incoming photons into electron charges at the semiconductor-oxide interface; the CCD is then used to read out these charges. Although CCDs are not the only technology to allow for light detection, CCD image sensors are widely used in professional, medical, and scientific applications where high-quality image data are required. In applications with less exacting quality demands, such as consumer and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system introduced in 1974. A closely related system, also known as ISO, is used to describe the relationship between exposure and output image lightness in digital cameras. Prior to ISO, the most common systems were ASA in the United States and DIN in Europe. The term ''speed'' comes from the early days of photography. Photographic emulsions that were more sensitive to light needed less time to generate an acceptable image and thus a complete exposure could be finished faster, with the subjects having to hold still for a shorter length of time. Emulsions that were less sensitive were deemed "slower" as the time to complete an exposure was much longer and often usable only for still life photography. Exposure times for photographic emulsions shortened from hours to fractions of a second by the late 19th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Noise
Image noise is random variation of brightness or color information in images. It can originate in film grain and in the unavoidable shot noise of an ideal photon detector. In digital photography is usually an aspect of electronic noise, produced by the image sensor of a digital camera. The circuitry of a Image scanner, scanner can also contribute to the effect. Image noise is often (but not necessarily) an undesirable by-product of image capture that obscures the desired information. Typically the term “image noise” is used to refer to noise in 2D images, not 3D images. The original meaning of "noise" was "unwanted signal"; Noise (radio), unwanted electrical fluctuations in signals received by AM radios caused audible acoustic noise ("static"). By analogy, unwanted electrical fluctuations are also called "noise". Image noise can range from almost imperceptible specks on a digital photograph taken in good light, to Optical astronomy, optical and Radioastronomy, radioast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nik Collection
The Nik Collection is a suite of photo editing plugins intended for use with a host application, such as Adobe Lightroom, Affinity Photo or DxO PhotoLab. History ''Nik Sharpener'' and ''Nik Color Efex'' were developed by Nik Multimedia Inc. in the 1990s as digital photo filters that could be used in Photoshop or as standalone applications. Some years later, in 2003, ''Dfine 1.0'', a denoising application and plugin was added to the list of products on offer. The newly rebranded Nik Software company then added ''Viveza'' and ''Silver Efex'' to the offer in 2008, and subsequently bundled all of their award-winning photo editing plugin applications, ''Dfine 2.0, Viveza, Color Efex Pro 3.0, Silver Efex Pro'' and ''Sharpener Pro 3.0'' together in a single Collection. The ''Complete Collection Ultimate Edition'' sold for $599.95 USD and the ''Complete Collection for Lightroom and Aperture'' for $299.95 USD. ''HDR EFex'' was added to the collection in 2010. After acquisition, Google ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe for Windows and macOS. It was created in 1987 by Thomas and John Knoll. It is the most used tool for professional digital art, especially in raster graphics editing, and its name has become genericised as a verb (e.g. "to photoshop an image", " photoshopping", and " photoshop contest") although Adobe disapproves of such use. Photoshop can edit and compose raster images in multiple layers and supports masks, alpha compositing and several color models. Photoshop uses its own PSD and PSB file formats to support these features. In addition to raster graphics, Photoshop has limited abilities to edit or render text and vector graphics (especially through clipping path for the latter), as well as 3D graphics and video. Its feature set can be expanded by plug-ins; programs developed and distributed independently of Photoshop that run inside it and offer new or enhanced features. Photoshop's naming sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DxO PhotoLab
DxO Labs (formerly DO Labs) is a privately owned photography software company. It was founded in 2003 by Jérôme Ménière, former CEO of Vision-IQ. The company's headquarters are in Paris, France. History Originally organized as a business unit of Vision IQ, a French software company founded in 1995 that specialized in computer vision, DO Labs was spun off to become an independent company after raising 7.3 million Euros of financing in venture capital. When DO Labs released DxO Optics Pro in 2004, which became DxO PhotoLab in 2017, it was the first product on the market to offer a way to correct photographic issues caused by camera-body electronics and lens optics without human intervention. These automated corrections, based on mathematical models of the physical characteristics of camera bodies and lenses as well as on the metadata (Exif) captured with each image, meant no human variables were involved. In 2005, following the OpenRAW campaign to simplify the interoperability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RawTherapee
RawTherapee is a free and open source application for processing photographs in raw image formats such as those created by many digital cameras. It comprises a subset of image editing operations specifically aimed at non-destructive post-production of raw photos and is primarily focused on improving a photographer's workflow by facilitating the handling of large numbers of images. It is notable for the advanced control it gives the user over the demosaicing and developing process. It is cross-platform, with versions for Microsoft Windows, macOS and Linux. RawTherapee was originally written by Gábor Horváth of Budapest, Hungary, and was re-licensed as free and open-source software under the GNU General Public License Version 3 in January 2010. It is written in C++, using a GTK+ front-end and a patched version of dcraw for reading raw files. The name "Therapee" was originally an acronym derived from "The Experimental Raw Photo Editor". Features RawTherapee involves the con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raw Image Format
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide- gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment. Rationale Raw image files are sometimes described as "digital negatives". Like transparency film and unlike negative film, raw image pixels contain positive exposure measurements. The raw datasets are more like undeveloped film: a raw image can be developed by software in a non-reversible manner to reach a complete image that resolves ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into signal (electrical engineering), signals, small bursts of electric current, current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronics, electronic imaging devices of both analogue electronics, analog and digital electronics, digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermography, thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technological change, technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2014 Ziarno Na Fotografii Analogowej
Fourteen or 14 may refer to: * 14 (number), the natural number following 13 and preceding 15 * one of the years 14 BC, AD 14, 1914, 2014 Music * 14th (band), a British electronic music duo * ''14'' (David Garrett album), 2013 *''14'', an unreleased album by Charli XCX * "14" (song), a 2007 song by Paula Cole from ''Courage'' * "Fourteen", a 2000 song by The Vandals from '' Look What I Almost Stepped In...'' Other uses * ''Fourteen'' (film), a 2019 American film directed by Dan Sallitt * ''Fourteen'' (play), a 1919 play by Alice Gerstenberg * ''Fourteen'' (manga), a 1990 manga series by Kazuo Umezu * ''14'' (novel), a 2013 science fiction novel by Peter Clines * ''The 14'', a 1973 British drama film directed by David Hemmings * Fourteen, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Lot Fourteen, redevelopment site in Adelaide, South Australia, previously occupied by the Royal Adelaide Hospital * "The Fourteen", a nickname for NASA Astronaut Group 3 * Fourteen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rallycross
Rallycross is a form of sprint style motorsport held on a mixed-surface circuit (racing), racing circuit using modified production touring automobile, cars or prototype racing cars. It began in the 1960s as a cross between rallying and autocross. It is popular in Nordic countries, Netherlands, Belgium, France and Great Britain. Internationally, the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) organise the FIA World Rallycross Championship, World and FIA European Rallycross Championship, European Rallycross Championships. History Origin The discipline started as television entertainment in Great Britain and first shown on 4 February 1967. ABC Weekend TV producer and ITV (TV network), ITV's ''World of Sport (UK TV series), World of Sport'' director, Robert Reed, had covered the Rally of Great Britain, RAC Rally of Great Britain for TV in November 1966 but had struggled to present it in a way that would appeal to mass audiences. His vision was "to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |